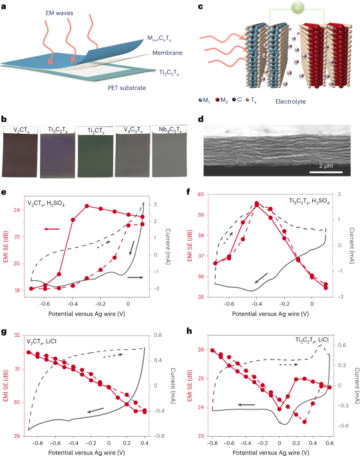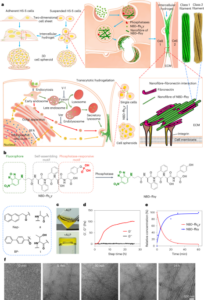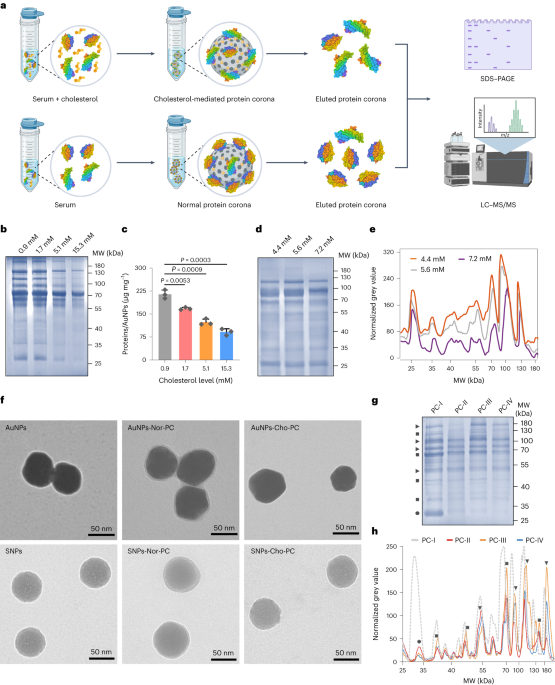
Quesada-Gonzalez, D. & Merkoci, A. Nanomaterial-based devices for point-of-care diagnostic applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 47, 4697–4709 (2018).
Irvine, D. J. & Dane, E. L. Enhancing cancer immunotherapy with nanomedicine. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 20, 321–334 (2020).
Stater, E. P., Sonay, A. Y., Hart, C. & Grimm, J. The ancillary effects of nanoparticles and their implications for nanomedicine. Nat. Nanotechnol. 16, 1180–1194 (2021).
Guerrini, G., Magrì, D., Gioria, S., Medaglini, D. & Calzolai, L. Characterization of nanoparticles-based vaccines for COVID-19. Nat. Nanotechnol. 17, 570–576 (2022).
Gadekar, V. et al. Nanomedicines accessible in the market for clinical interventions. J. Control. Release 330, 372–397 (2021).
Thi, T. T. H. et al. Lipid-based nanoparticles in the clinic and clinical trials: from cancer nanomedicine to COVID-19 vaccines. Vaccines 9, 359 (2021).
Monopoli, M. P., Åberg, C., Salvati, A. & Dawson, K. A. Biomolecular coronas provide the biological identity of nanosized materials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 7, 779–786 (2012).
Ren, J. et al. Chemical and biophysical signatures of the protein corona in nanomedicine. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 144, 9184–9205 (2022).
Latreille, P.-L. et al. Scratching the surface of the protein corona: challenging measurements and controversies. ACS Nano 16, 1689–1707 (2022).
Li, M. et al. Nanoparticle elasticity affects systemic circulation lifetime by modulating adsorption of apolipoprotein A-I in corona formation. Nat. Commun. 13, 4137 (2022).
Kamaly, N. Nanoparticle protein corona evolution: from biological impact to biomarker discovery. Nanoscale 14, 1606–1620 (2022).
Ju, Y. et al. Person-specific biomolecular coronas modulate nanoparticle interactions with immune cells in human blood. ACS Nano 14, 15723–15737 (2020).
Hajipour, M. J., Laurent, S., Aghaie, A., Rezaee, F. & Mahmoudi, M. Personalized protein coronas: a ‘key’ factor at the nano-bio interface. Biomater. Sci. 2, 1210–1221 (2014).
Shannahan, J. H. et al. From the cover: disease-induced disparities in formation of the nanoparticle-biocorona and the toxicological consequences. Toxicol. Sci. 152, 406–416 (2016).
Ren, J. et al. Precision nanomedicine development based on specific opsonization of human cancer patient-personalized protein coronas. Nano Lett. 19, 4692–4701 (2019).
Lazarovits, J. et al. Synthesis of patient-specific nanomaterials. Nano Lett. 19, 116–123 (2019).
Di Santo, R. et al. Personalized graphene oxide-protein corona in the human plasma of pancreatic cancer patients. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 8, 491 (2020).
Chetwynd, A. J. & Lynch, I. The rise of the nanomaterial metabolite corona, and emergence of the complete corona. Environ. Sci. Nano 7, 1041–1060 (2020).
Raesch, S. S. et al. Proteomic and lipidomic analysis of nanoparticle corona upon contact with lung surfactant reveals differences in protein, but not lipid composition. ACS Nano 9, 11872–11885 (2015).
Braccia, C. et al. The lipid composition of few layers graphene and graphene oxide biomolecular corona. Carbon 185, 591–598 (2021).
Liu, K., Salvati, A. & Sabirsh, A. Physiology, pathology and the biomolecular corona: the confounding factors in nanomedicine design. Nanoscale 14, 2136–2154 (2022).
Kobos, L. M. et al. An integrative proteomic/lipidomic analysis of the gold nanoparticle biocorona in healthy and obese conditions. Appl. Vitr. Toxicol. 5, 150–166 (2019).
Lima, T., Bernfur, K., Vilanova, M. & Cedervall, T. Understanding the lipid and protein corona formation on different sized polymeric nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 10, 1129 (2020).
Tavakol, M. et al. Disease-related metabolites affect protein-nanoparticle interactions. Nanoscale 10, 7108–7115 (2018).
Luo, J., Yang, H. & Song, B. L. Mechanisms and regulation of cholesterol homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 21, 225–245 (2020).
Civeira, F., Arca, M., Cenarro, A. & Hegele, R. A. A mechanism-based operational definition and classification of hypercholesterolemia. J. Clin. Lipidol. 16, 813–821 (2022).
Kim, S. H. et al. Understanding the biomolecular coronas of high-density lipoproteins on pegylated Au nanoparticles: implication for lipid corona formation in the blood. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 5, 2018–2028 (2022).
Kim, H., Kumar, S., Kang, D. W., Jo, H. & Park, J. H. Affinity-driven design of cargo-switching nanoparticles to leverage a cholesterol-rich microenvironment for atherosclerosis therapy. ACS Nano 14, 6519–6531 (2020).
Fu, Q., Yu, L., Wang, Y., Li, P. & Song, J. Biomarker-responsive nanosystems for chronic disease theranostics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 33, 2206300 (2023).
Kim, K. R., Kim, J., Back, J. H., Lee, J. E. & Ahn, D. R. Cholesterol-mediated seeding of protein corona on dna nanostructures for targeted delivery of oligonucleotide therapeutics to treat liver fibrosis. ACS Nano 16, 7331–7343 (2022).
Dreaden, E. C., Alkilany, A. M., Huang, X., Murphy, C. J. & El-Sayed, M. A. The golden age: gold nanoparticles for biomedicine. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 2740–2779 (2012).
Kim, S. E. et al. Ultrasmall nanoparticles induce ferroptosis in nutrient-deprived cancer cells and suppress tumour growth. Nat. Nanotechnol. 11, 977–985 (2016).
Ke, P. C., Lin, S., Parak, W. J., Davis, T. P. & Caruso, F. A decade of the protein corona. ACS Nano 11, 11773–11776 (2017).
Xiao, Q. et al. The effects of protein corona on in vivo fate of nanocarriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 186, 114356 (2022).
Blanco, E., Shen, H. & Ferrari, M. Principles of nanoparticle design for overcoming biological barriers to drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 33, 941–951 (2015).
Macia, E. et al. Dynasore, a cell-permeable inhibitor of dynamin. Dev. Cell 10, 839–850 (2006).
Francia, V. et al. Corona composition can affect the mechanisms cells use to internalize nanoparticles. ACS Nano 13, 11107–11121 (2019).
Lara, S. et al. Identification of receptor binding to the biomolecular corona of nanoparticles. ACS Nano 11, 1884–1893 (2017).
Ngo, W. et al. Identifying cell receptors for the nanoparticle protein corona using genome screens. Nat. Chem. Biol. 18, 1023–1031 (2022).
Benetti, F., Bregoli, L., Olivato, I. & Sabbioni, E. Effects of metal (loid)-based nanomaterials on essential element homeostasis: the central role of nanometallomics for nanotoxicology. Metallomics 6, 729–747 (2014).
Ashkarran, A. A. et al. Measurements of heterogeneity in proteomics analysis of the nanoparticle protein corona across core facilities. Nat. Commun. 13, 6610 (2022).
Sheibani, S. et al. Nanoscale characterization of the biomolecular corona by cryo-electron microscopy, cryo-electron tomography, and image simulation. Nat. Commun. 12, 573 (2021).
Shevchenko, A., Tomas, H., Havlis, J., Olsen, J. V. & Mann, M. In-gel digestion for mass spectrometric characterization of proteins and proteomes. Nat. Protoc. 1, 2856–2860 (2006).
Cao, Z. T. et al. Protein binding affinity of polymeric nanoparticles as a direct indicator of their pharmacokinetics. ACS Nano 14, 3563–3575 (2020).
Hess, B. P-LINCS: a parallel linear constraint solver for molecular simulation. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 4, 116–122 (2008).
- SEO Powered Content & PR Distribution. Get Amplified Today.
- PlatoData.Network Vertical Generative Ai. Empower Yourself. Access Here.
- PlatoAiStream. Web3 Intelligence. Knowledge Amplified. Access Here.
- PlatoESG. Automotive / EVs, Carbon, CleanTech, Energy, Environment, Solar, Waste Management. Access Here.
- BlockOffsets. Modernizing Environmental Offset Ownership. Access Here.
- Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41565-023-01455-7
- :not
- ][p
- 1
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15%
- 16
- 17
- 19
- 20
- 2006
- 2008
- 2012
- 2014
- 2015
- 2016
- 2017
- 2018
- 2019
- 2020
- 2021
- 2022
- 2023
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 36
- 39
- 40
- 65
- 7
- 8
- 9
- a
- accessible
- across
- affect
- age
- AL
- am
- an
- analysis
- and
- applications
- Arca
- article
- AS
- At
- b
- back
- barriers
- based
- binding
- biomarker
- blood
- but
- by
- CAN
- Cancer
- Cancer cells
- cancer patients
- carbon
- cell
- Cells
- central
- challenging
- changing
- chemical
- Circulation
- classification
- click
- clinic
- Clinical
- clinical trials
- complete
- composition
- conditions
- Consequences
- contact
- control
- Core
- Corona
- cover
- COVID-19
- Davis
- decade
- definition
- delivery
- Design
- Development
- Devices
- differences
- different
- direct
- discovery
- Disease
- dna
- drug
- Drug Delivery
- e
- E&T
- effects
- element
- emergence
- enhancing
- essential
- Ether (ETH)
- evolution
- facilities
- factor
- factors
- fate
- Ferrari
- few
- For
- formation
- from
- genome
- Gold
- Golden
- Graphene
- Growth
- healthy
- homeostasis
- http
- HTTPS
- huang
- human
- i
- Identification
- identifying
- Identity
- image
- immune
- immunotherapy
- Impact
- implications
- in
- Indicator
- interactions
- Interface
- interventions
- jo
- Kim
- layers
- Lee
- Leverage
- li
- lifetime
- lin
- LINK
- Liver
- Market
- Mass
- materials
- measurements
- mechanisms
- metal
- Microscopy
- MOL
- molecular
- nano
- Nanomaterials
- Nanomedicine
- nanotechnology
- Nature
- of
- on
- operational
- overcoming
- Parallel
- Park
- pathology
- patients
- Personalized
- Plasma
- plato
- Plato Data Intelligence
- PlatoData
- Precision
- principles
- Protein
- Proteins
- provide
- R
- Regulation
- response
- Reveals
- Rise
- Role
- s
- Scholar
- SCI
- screens
- Signatures
- simulation
- sized
- song
- specific
- Surface
- systemic
- T
- targeted
- The
- their
- theory
- therapeutics
- therapy
- to
- tomography
- treat
- trials
- understanding
- upon
- use
- using
- vaccines
- vivo
- W
- with
- X
- zephyrnet