What is a transformational leader? Is it a hard-working one who relentlessly pushes their team to success? Or is it a ruthless one who demands excellence at all costs? In reality, transformational leadership is about something much more powerful: inspiring and motivating others to achieve their full potential. It’s about creating a positive and empowering work environment that fosters innovation, creativity, and continuous improvement.
It’s about building high-performing teams that are able to drive change and achieve exceptional outcomes. In this article, we’ll explore the history, characteristics, benefits, and potential disadvantages of transformational leadership.
We’ll also provide examples of transformational leaders and compare them to other leadership styles. By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of what it takes to become a transformational leader and why it’s such an important skill for today’s business world.
What is a transformational leader?
A transformational leader is a type of leader who inspires and motivates their followers to achieve exceptional outcomes by creating a positive, empowering, and growth-oriented work environment. Transformational leaders are often characterized by their ability to generate enthusiasm, encourage innovation, and cultivate individual talents and strengths among their team members.
The term “transformational leadership” was first coined by James MacGregor Burns in 1978 to describe a leadership style that goes beyond simply managing people to truly inspiring them to achieve their full potential. According to Burns, transformational leaders are those who “raise one another to higher levels of motivation and morality.”
Transformational leaders are different from other types of leaders, such as transactional leaders, who rely on reward and punishment to motivate their followers. Instead, transformational leaders use their own personal charisma, vision, and passion to inspire others to work toward a common goal.

History of transformational leadership
The concept of transformational leadership was initially introduced by James V. Downton, who first coined the term “transformational leadership” in the 1970s. Later, leadership expert and presidential biographer James MacGregor Burns developed the concept further, describing transformational leadership as occurring when “leaders and followers make each other advance to a higher level of morality and motivation.”
According to Burns, transformational leaders have the ability to inspire their followers to achieve exceptional outcomes by appealing to their higher values and ideals. Through the strength of their vision and personality, transformational leaders are able to change expectations, perceptions, and motivations, encouraging their followers to work towards common goals. Burns also described transformational leaders as those who can move followers up on Maslow’s hierarchy of needs and beyond their own interests.
Unlike the transactional approach, which is based on a “give and take” relationship, transformational leadership is based on the leader’s personality, traits, and ability to make a change through example, articulation of an energizing vision, and challenging goals. Transforming leaders are idealized in the sense that they are moral exemplars of working toward the benefit of the team, organization, and/or community.
The fantastic precursors of artificial intelligence
Burns theorized that transforming and transactional leadership were mutually exclusive styles. However, researcher Bernard M. Bass expanded upon Burns’ original ideas in 1985 to develop what is now referred to as Bass’ Transformational Leadership Theory. Bass explained the psychological mechanisms that underlay transformational and transactional leadership and introduced the term “transformational” in place of “transforming.”
Bass added to the initial concepts of Burns to help explain how transformational leadership could be measured, as well as how it impacts follower motivation and performance. According to Bass, transformational leaders garner trust, respect, and admiration from their followers and motivate them to work harder than originally expected. These outcomes occur because the transformational leader offers followers something more than just working for self-gain; they provide followers with an inspiring mission and vision and give them an identity.
The extent to which a leader is transformational is measured, first and foremost, in terms of his or her influence on the followers. The leader transforms and motivates followers through their idealized influence, intellectual stimulation, and individual consideration. In addition, transformational leaders encourage followers to come up with new and unique ways to challenge the status quo and to alter the environment to support being successful.
Finally, in contrast to Burns, Bass suggested that leadership can simultaneously display both transformational and transactional leadership. By 1985, transformational leadership had become more defined and developed, with leaders who use this style possessing traits such as idealized influence, productive commitment, and inspirational motivation. Transformational leadership made transactional leadership more effective.
Importance of transformational leadership in today’s business world
In today’s rapidly changing and complex business world, transformational leadership has become increasingly important for organizations to succeed. Here are a few reasons why:
- Inspires and motivates employees: Transformational leaders inspire and motivate their employees to achieve their full potential by creating a positive and empowering work environment. They provide a clear sense of direction and purpose and encourage creativity, innovation, and risk-taking among their employees. This can lead to increased job satisfaction, engagement, and retention among employees.
- Drives organizational change: Transformational leaders are adept at driving organizational change by creating a compelling vision and inspiring their employees to work towards it. They are not afraid to challenge the status quo and encourage their employees to come up with new and innovative ideas to improve the organization. By fostering a culture of continuous improvement and innovation, transformational leaders can help organizations adapt and thrive in a rapidly changing business environment.
- Builds high-performing teams: Transformational leaders focus on building high-performing teams by developing the skills and abilities of their employees. They provide individualized attention and support and encourage their employees to develop their strengths and talents. This can lead to increased collaboration, teamwork, and productivity among employees.
- Promotes ethical behavior: Transformational leaders are often seen as role models and moral exemplars, inspiring their employees to behave ethically and with integrity. They encourage their employees to work towards the greater good of the organization and society rather than just focusing on their own self-interest. This can lead to increased trust and credibility among stakeholders and a positive reputation for the organization.
- Achieves exceptional results: Transformational leaders are known for achieving exceptional results by inspiring and motivating their employees to work towards common goals. By fostering a culture of innovation, collaboration, and continuous improvement, transformational leaders can help organizations achieve sustainable growth and success.
Transformational leadership characteristics
Transformational leadership is characterized by several key traits that enable leaders to inspire and motivate their followers to achieve exceptional outcomes. Here are five common characteristics of transformational leaders:
Visionary
Transformational leaders are visionary, meaning they have a clear and compelling vision for the future that inspires their followers to work towards a common goal. They are able to articulate this vision in
Inspirational
Transformational leaders are inspirational, meaning they are able to inspire their followers to achieve extraordinary outcomes. They are skilled at creating a positive and empowering work environment that encourages creativity, innovation, and risk-taking. They are able to motivate their followers to work towards a shared vision and to achieve their full potential.
Empathetic
Transformational leaders are empathetic, meaning they are able to understand and relate to the needs, feelings, and perspectives of their followers. They are able to provide individualized attention and support to their followers, which helps to build trust and loyalty. They are also able to create a sense of community and belonging among their followers.

Charismatic
Transformational leaders are charismatic, meaning they possess a magnetic personality that inspires and motivates their followers. They are able to generate enthusiasm and excitement among their followers, which helps to build momentum and drive toward achieving goals. They are also able to build a strong personal connection with their followers, which helps to build trust and loyalty.
Innovative
Transformational leaders are innovative, meaning they are able to encourage their followers to think creatively and to come up with new and innovative solutions to problems. They are able to challenge the status quo and to encourage their followers to question assumptions and to take risks. They are also able to create a culture of continuous improvement and innovation, which helps to drive organizational success.
Benefits of transformational leadership
Transformational leadership can bring numerous benefits to organizations, including increased employee engagement, higher levels of motivation and productivity, improved organizational culture, stronger relationships with stakeholders, and enhanced decision-making capabilities. Here is a closer look at these benefits:
Increased employee engagement
Transformational leadership can increase employee engagement by creating a work environment that empowers employees, encourages creativity and innovation, and provides opportunities for growth and development. This can lead to higher levels of job satisfaction, loyalty, and commitment among employees.
Higher levels of motivation and productivity
Transformational leaders can inspire their followers to achieve exceptional outcomes by setting clear goals, providing feedback and recognition, and creating a sense of purpose and meaning in their work. This can lead to higher levels of motivation and productivity among employees.
Improved organizational culture
Transformational leaders can improve organizational culture by promoting collaboration, teamwork, and a shared sense of purpose among employees. They can foster a culture of continuous improvement and innovation, which can lead to better decision-making, higher levels of employee engagement, and improved organizational performance.

Stronger relationships with stakeholders
Transformational leaders can build stronger relationships with stakeholders by promoting ethical behavior, transparency, and accountability. They can inspire trust and credibility among stakeholders by leading by example and by promoting a shared vision and values.
Enhanced decision-making capabilities
Transformational leaders can enhance decision-making capabilities by encouraging their followers to think critically and creatively and by challenging the status quo. They can promote a culture of innovation and risk-taking, which can lead to better decision-making and improved organizational performance.
Transformational leadership can bring numerous benefits to organizations, including increased employee engagement, higher levels of motivation and productivity, improved organizational culture, stronger relationships with stakeholders, and enhanced decision-making capabilities. By inspiring and empowering their followers to achieve their full potential, transformational leaders can help organizations achieve sustainable growth and success.
Disadvantages of transformational leadership
While transformational leadership has numerous benefits, it also has some potential disadvantages that organizations should be aware of. Here are a few examples:
Over-reliance on the leader
One potential disadvantage of transformational leadership is that it can create an over-reliance on the leader. Because transformational leaders are often seen as charismatic and inspiring, there is a risk that followers may become too dependent on them for guidance and direction. This can limit the ability of followers to think for themselves and to develop their own leadership skills.
Risk of burnout
Transformational leadership can be demanding, as it requires leaders to be constantly inspiring and motivating their followers. This can lead to burnout among leaders who are unable to sustain the level of energy and enthusiasm required to be successful. In addition, followers may also experience burnout if they feel pressured to perform constantly at a high level.
Potential for misuse
Transformational leadership can be a powerful tool, but it also has the potential to be misused. Some leaders may use their charisma and influence to manipulate or exploit their followers rather than inspire them to achieve their full potential. This can lead to a toxic work environment and can undermine the trust and loyalty of followers.

Lack of attention to details
Transformational leaders are often focused on the big picture and may overlook the details that are necessary for achieving organizational goals. This can lead to a lack of attention to important details, which can compromise the quality of work and the ability to achieve desired outcomes.
Time and resource intensive
Transformational leadership requires a significant investment of time and resources, as it involves creating a positive and empowering work environment, building high-performing teams, and driving organizational change. This can be a challenge for organizations that are facing tight deadlines or resource constraints.
Transformational leadership has the potential to create some disadvantages, including over-reliance on the leader, risk of burnout, the potential for misuse, lack of attention to detail, and time and resource intensity. Organizations should be aware of these potential drawbacks and take steps to mitigate them to ensure that transformational leadership is used effectively and responsibly.
Examples of transformational leaders
Transformational leadership has been exemplified by many great leaders throughout history. Here are five examples of transformational leaders:
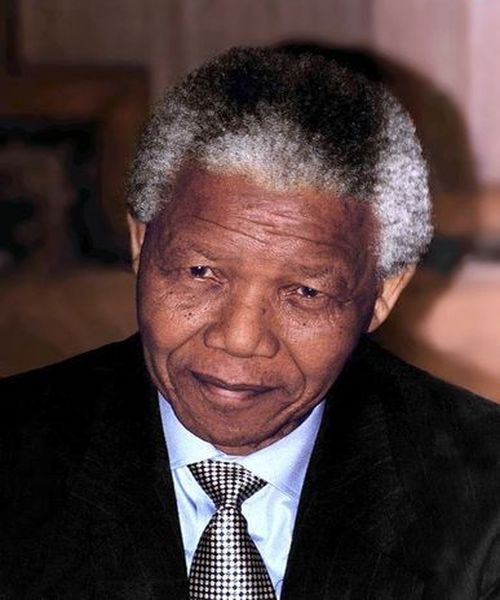

Nelson Mandela
Nelson Mandela, the former President of South Africa, is a prime example of a transformational leader. He led the fight against apartheid and worked to bring about reconciliation and unity among South Africans. Mandela was able to inspire and motivate his followers by embodying his vision of a democratic and free South Africa.

Steve Jobs
Steve Jobs, the co-founder of Apple, was a visionary leader who transformed the technology industry. He was able to inspire and motivate his employees by creating a positive and empowering work environment that encouraged creativity, innovation, and risk-taking. His leadership helped to revolutionize the computer, music, and phone industries.
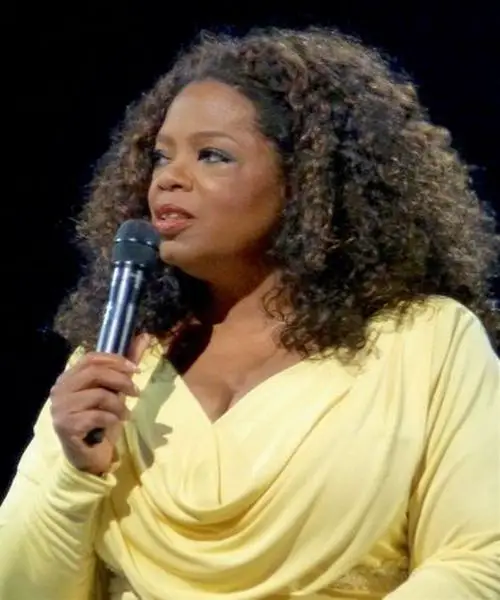

Oprah Winfrey
Oprah Winfrey, the media mogul, and philanthropist, is another example of a transformational leader. She has inspired and motivated millions of people through her television shows, books, and philanthropic efforts. Winfrey has created a positive and empowering work environment through her media empire, which has helped to uplift and empower countless individuals.
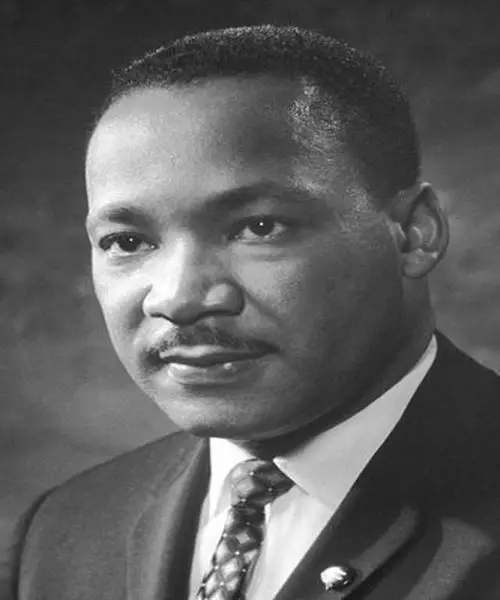

Martin Luther King Jr.
Martin Luther King Jr., the civil rights activist and Baptist minister, is known for his transformative leadership during the civil rights movement in the United States. He was able to inspire and motivate millions of people through his vision of a just and equitable society. King’s leadership helped to transform the United States and laid the foundation for progress in civil rights.
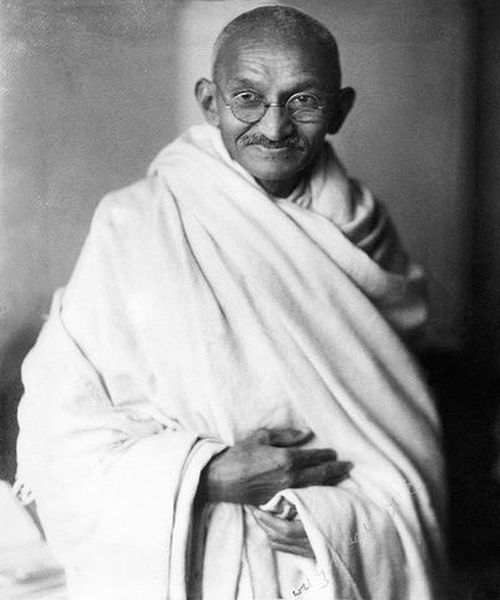

Mahatma Gandhi
Mahatma Gandhi, the leader of India’s independence movement, is another example of a transformational leader. He led the fight against British colonial rule through nonviolent resistance and civil disobedience. Gandhi was able to inspire and motivate his followers by embodying his vision of a free and independent India, and his leadership helped to transform India’s political landscape.
These five leaders are just a few examples of transformational leaders who have had a profound impact on society. By inspiring and empowering their followers to achieve their full potential and by driving organizational change, these leaders have left a lasting legacy and continue to inspire future generations of leaders.
Transformational leadership vs other leadership styles
Transformational leadership is just one of several different leadership styles that have been identified by researchers. Here is a comparison of transformational leadership with four other common leadership styles:
| Leadership Style | Description | Focus |
| Transformational Leadership | Inspires and motivates followers to achieve exceptional outcomes by setting a clear vision, providing individualized support, and promoting creativity and innovation. | Fosters a culture of continuous improvement and innovation, promotes a sense of purpose and meaning in work, and inspires loyalty and commitment among followers. |
| Transactional Leadership | Focuses on rewards and punishments to motivate followers to achieve organizational goals. Leaders use contingent rewards to incentivize high performance and corrective actions to address low performance. | Maintains the status quo, reinforces existing structures and processes, and emphasizes efficiency and productivity. |
| Servant Leadership | Focuses on serving the needs of followers and empowering them to achieve their full potential. Leaders prioritize the needs of their followers over their own self-interest and work to create a positive and empowering work environment. | Fosters collaboration, teamwork, and personal growth among followers. |
| Authentic Leadership | Emphasizes self-awareness, transparency, and ethical behavior. Leaders build trust and credibility by being true to themselves and their values, and by creating a culture of transparency and openness. | Promotes a positive and ethical work environment, inspires trust and loyalty among followers, and fosters personal and professional growth. |
| Situational Leadership | Adapts leadership style to meet the needs of the situation and the maturity level of followers. Leaders use different leadership styles depending on the situation, ranging from directive to supportive. | Increases the flexibility and adaptability of leaders, fosters collaboration and teamwork, and promotes individual and organizational growth. |
As shown in the table above, each leadership style has its own unique focus and approach to leadership. While some styles may be more effective in certain situations than others, all leadership styles can be effective when used appropriately. Transformational leadership stands out from other styles by its focus on inspiring and motivating followers to achieve exceptional outcomes and by creating a positive and empowering work environment that fosters innovation, creativity, and continuous improvement.
Conclusion
Back to our original question: What is a transformational leader? Transformational leadership is a powerful and effective leadership style that has been shown to bring numerous benefits to organizations, including increased employee engagement, higher levels of motivation and productivity, improved organizational culture, stronger relationships with stakeholders, and enhanced decision-making capabilities. By inspiring and empowering their followers to achieve their full potential, transformational leaders can help organizations achieve sustainable growth and success.
How can DevOps as a Service flourish efficiency in your business?
In this article, we discussed the history of transformational leadership, its key characteristics, benefits, potential disadvantages, examples, and how it compares to other leadership styles. We explored the importance of developing transformational leadership skills and how it can help individuals become effective leaders who are able to drive change and innovation in their organizations.
We encourage our readers to develop their own transformational leadership skills and to become leaders who are able to inspire and motivate their followers to achieve their full potential. By adopting a transformational leadership style, individuals can help create a positive and empowering work environment that fosters innovation, creativity, and continuous improvement.
Image courtesy of Wikipedia
- SEO Powered Content & PR Distribution. Get Amplified Today.
- Platoblockchain. Web3 Metaverse Intelligence. Knowledge Amplified. Access Here.
- Source: https://dataconomy.com/2023/03/what-is-a-transformational-leader-examples/
- :is
- $UP
- 1
- 10
- 1985
- 214
- 7
- 8
- 9
- a
- abilities
- ability
- Able
- About
- above
- According
- accountability
- Achieve
- achieving
- actions
- Activist
- adapt
- added
- addition
- address
- Adopting
- advance
- africa
- against
- All
- among
- and
- Another
- appealing
- Apple
- approach
- appropriately
- ARE
- article
- artificial
- AS
- At
- attention
- based
- BE
- because
- become
- being
- benefit
- benefits
- Better
- Beyond
- Big
- Big Picture
- Books
- bring
- British
- build
- build trust
- Building
- burns
- business
- by
- CAN
- capabilities
- certain
- challenge
- challenging
- change
- changing
- characteristics
- characterized
- Civil Rights
- clear
- closer
- Co-founder
- coined
- collaboration
- come
- commitment
- Common
- communicate
- community
- compare
- comparison
- compelling
- complex
- compromise
- computer
- concept
- concepts
- conclusion
- connection
- consideration
- constantly
- constraints
- continue
- continuous
- contrast
- Corporate
- Costs
- could
- create
- created
- Creating
- Creative
- Creatively
- creativity
- Credibility
- Cultivate
- Culture
- Decision Making
- defined
- demanding
- demands
- democratic
- dependent
- Depending
- describe
- described
- detail
- details
- develop
- developed
- developing
- Development
- DevOps
- different
- direction
- Disadvantage
- discussed
- Display
- drawbacks
- drive
- driving
- during
- each
- Effective
- effectively
- efficiency
- efforts
- emphasizes
- Empire
- Employee
- employees
- empower
- empowering
- empowers
- enable
- encourage
- encouraged
- encourages
- encouraging
- energy
- engagement
- enhanced
- ensure
- enthusiasm
- Environment
- ethical
- example
- examples
- Excellence
- exceptional
- Excitement
- Exclusive
- existing
- expanded
- expectations
- expected
- experience
- expert
- Explain
- explained
- Exploit
- explore
- Explored
- extraordinary
- facing
- fantastic
- feedback
- few
- fight
- First
- Flexibility
- flourish
- Focus
- focused
- focusing
- followers
- For
- foremost
- Former
- Foster
- fostering
- Foundation
- Free
- from
- full
- further
- future
- generate
- generations
- Give
- goal
- Goals
- Goes
- good
- great
- great leaders
- greater
- Growth
- guidance
- Have
- help
- helped
- helps
- here
- hierarchy
- High
- high-performing
- higher
- history
- holistic
- How
- However
- HTTPS
- ideas
- identified
- Identity
- Impact
- Impacts
- importance
- important
- improve
- improved
- improvement
- in
- incentivize
- Including
- Increase
- increased
- increasingly
- independence
- independent
- india
- individual
- individuals
- industries
- industry
- influence
- initial
- initially
- Innovation
- innovative
- Inspirational
- inspire
- inspired
- inspiring
- instead
- integrity
- intellectual
- interests
- introduced
- investment
- IT
- ITS
- Job
- Jobs
- join
- jpg
- just one
- Key
- King
- known
- Lack
- landscape
- lasting
- lead
- leader
- leaders
- Leadership
- leading
- Led
- Legacy
- Level
- levels
- LIMIT
- Look
- Low
- Loyalty
- made
- make
- managing
- many
- maturity
- max-width
- meaning
- Media
- Meet
- Members
- millions
- Mission
- Mitigate
- models
- Mogul
- Momentum
- morality
- more
- motivated
- Motivation
- motivations
- move
- movement
- Music
- mutually
- necessary
- needs
- New
- numerous
- numerous benefits
- of
- Offers
- on
- ONE
- Openness
- opportunities
- organization
- organizational
- organizations
- original
- originally
- Other
- Others
- own
- passion
- People
- perform
- performance
- personal
- Personality
- perspective
- perspectives
- philanthropic
- phone
- picture
- Place
- plato
- Plato Data Intelligence
- PlatoData
- political
- positive
- potential
- powerful
- president
- presidential
- Prime
- Prioritize
- problems
- processes
- productive
- productivity
- professional
- Progress
- promote
- promotes
- promoting
- provide
- provides
- providing
- purpose
- quality
- question
- ranging
- rapidly
- rather
- readers
- Reality
- reasons
- recognition
- reconciliation
- referred
- relationship
- Relationships
- reputation
- required
- requires
- researcher
- researchers
- Resistance
- resource
- Resources
- respect
- Results
- retention
- revolutionize
- Reward
- Rewards
- rights
- Risk
- risks
- Role
- Rule
- satisfaction
- Self-Awareness
- sense
- service
- serving
- setting
- settings
- several
- shared
- should
- shown
- Shows
- significant
- simply
- simultaneously
- situation
- situations
- skill
- skilled
- skills
- Society
- Solutions
- some
- something
- South
- South Africa
- stakeholders
- stands
- States
- Status
- Steps
- strength
- strengths
- strong
- stronger
- style
- styles
- succeed
- success
- successful
- such
- support
- supportive
- sustainable
- table
- Take
- takes
- talents
- team
- teams
- teamwork
- Technology
- television
- terms
- that
- The
- The Future
- their
- Them
- themselves
- These
- Thrive
- Through
- throughout
- time
- to
- today’s
- too
- tool
- toward
- towards
- transactional
- Transform
- transformational
- transformative
- transformed
- transforming
- Transparency
- true
- Trust
- types
- Undermine
- understand
- understanding
- unique
- United
- United States
- unity
- Uplift
- use
- Values
- vision
- visionary
- vs
- Way..
- ways
- WELL
- What
- What is
- which
- while
- WHO
- Wikipedia
- with
- Work
- worked
- working
- world
- Your
- zephyrnet