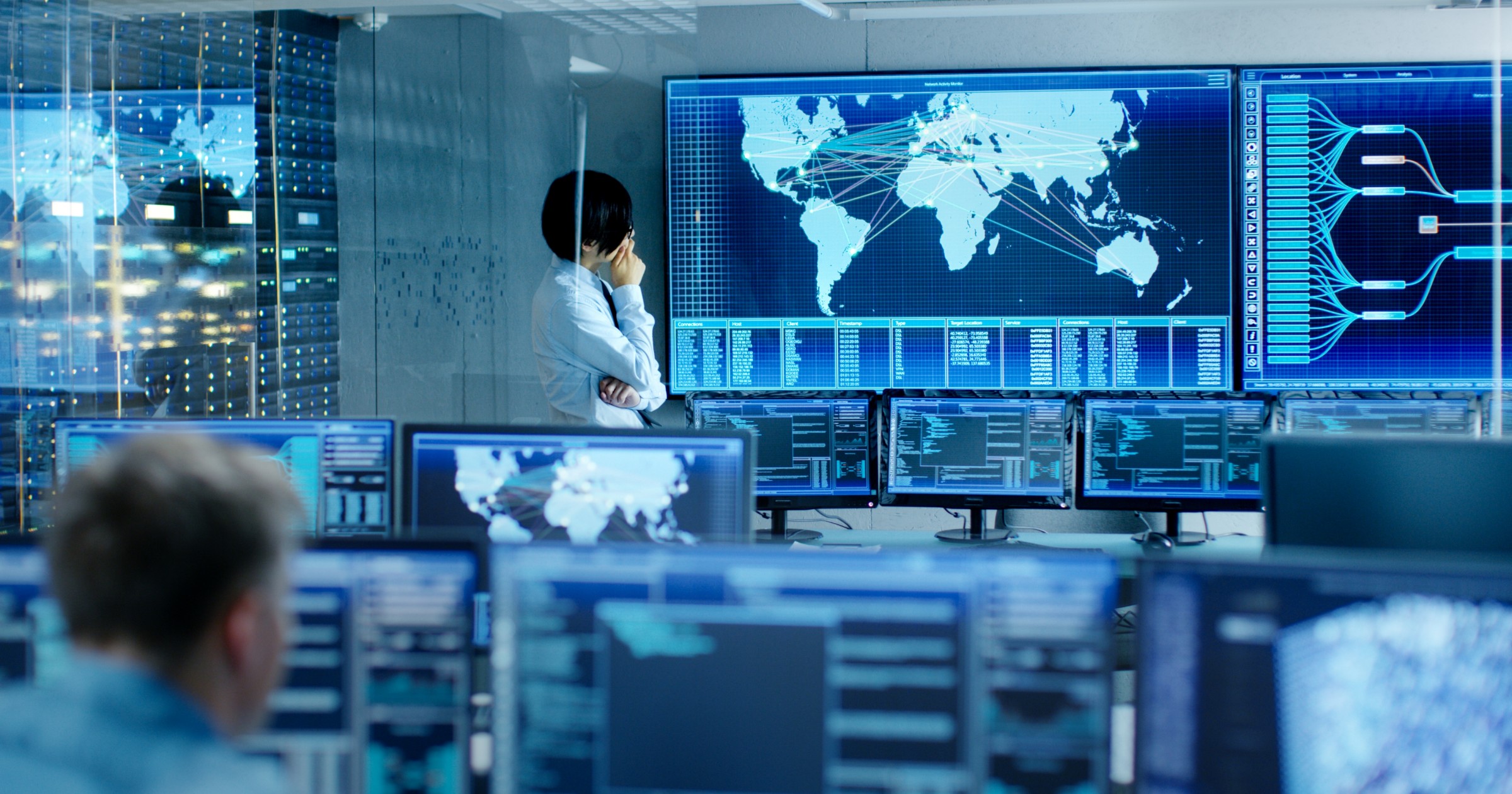

With the average cost of a data breach soaring to an all-time high at USD $4.45 million dollars in 2023, organizations face an ever-increasing array of cybersecurity threats. These threats can range from ransomware attacks to phishing campaigns and insider threats, potentially resulting in data breaches. As cybercriminals become more sophisticated and their tactics more varied, it’s essential for businesses to adopt advanced security measures to protect their sensitive data and digital assets. Two crucial tools in the modern cybersecurity arsenal are Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solutions and threat intelligence. By leveraging these resources, organizations can stay current on trending threats and proactively defend against potential attacks and adversaries.
Understanding SIEM and threat intelligence
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) solutions play a pivotal role in maintaining an organization’s cybersecurity posture. They collect and analyze vast amounts of security-related data from various sources within an organization’s IT infrastructure. Event log data from users, endpoints, applications, data sources, cloud workloads, and networks—as well as data from security hardware and software such as firewalls or antivirus software—is collected, correlated and analyzed in real-time. By centralizing and correlating this information, SIEM solutions can provide a comprehensive view of an organization’s security status.
Threat intelligence is data and insights with detailed knowledge about cybersecurity threats targeting an organization. It involves the collection, analysis, and dissemination of information about current and potential cybersecurity threats. This information can include indicators of compromise (IoCs), tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by cybercriminals, and vulnerabilities in software or systems. Threat intelligence teams consistently monitor various sources, including forums, dark web marketplaces, and malware samples, to provide organizations with near-real-time insight into emerging threats. According to research conducted by Gartner, utilizing threat intelligence can enhance security teams’ detection and response capabilities by increasing alert quality, reducing investigation time, and adding coverage for the latest attacks and adversaries.
The synergy between SIEM and threat intelligence
SIEM solutions are built to perform rule matching on log data from many sources. With the integration of threat intelligence, SIEM solutions can stay one step ahead of emerging threats and advisories. Let’s explore some benefits of incorporating threat intelligence within a SIEM platform:
- Real-time threat detection: Integrating Threat Intelligence feeds into a SIEM solution enhances its capabilities. By cross-referencing internal data with external threat intelligence, organizations can identify patterns and anomalies that might otherwise go unnoticed. This enables faster detection of vulnerabilities, new malware strains, or targeted attacks.
- Proactive defense: Threat hunting is key to effective cybersecurity. Instead of reacting to threats after they’ve caused damage, organizations can use SIEM and Threat Intelligence to identify threat actors that may already be lurking in an environment and thwart attacks before they continue. By staying informed about evolving tactics and vulnerabilities, organizations can adjust their threat hunting techniques to find and counter threats before they materialize.
- Improved incident response: When a security incident occurs, the combined power of SIEM and Threat intelligence is invaluable. SIEM solutions provide a timeline of events leading up to the breach, while Threat Intelligence supplies insights into the attacker’s TTPs and associated IOCs that can accelerate the investigation. This aids in incident response, containment, and recovery efforts.
How can the combination of QRadar SIEM and X-Force Threat Intelligence help organizations combat modern threats?
The IBM X-Force Threat Intelligence included with QRadar SIEM uses aggregated X-Force® Exchange data to help your organization stay ahead of emerging threats and exposure from the latest vulnerabilities. X-Force Threat Intelligence detects various events such as communication between endpoints and known malware distribution sites. Integrating X-Force Threat Intelligence with QRadar enables seamless ranking of new types of incidents by risk value. This data empowers you to establish distinct rules and watch lists for different threats. QRadar SIEM incorporates the latest malicious IP addresses, URLs and malware file hashes from IBM X-Force Threat Intelligence and other threat intelligence sources, enabling your SIEM platform to instantly detect critical and advanced global threats. Stay head of emerging threats without spending hours on research.
If you want to learn more about leveraging threat intelligence to address emerging threats, sign up for our upcoming webinar on September 7, 2023: “Unleash the Power of Threat Intelligence: How to prepare and Respond Faster”, where our QRadar SIEM and X-Force Threat Intelligence experts will dive into cutting-edge trends, advanced techniques, and proven strategies to elevate your threat awareness and strengthen your security posture.
In a digital landscape characterized by constantly evolving threats, organizations must remain vigilant and adaptive in their cybersecurity strategies. SIEM solutions and Threat Intelligence are vital tools that provide the necessary insights to stay ahead of the curve. By utilizing real-time threat detection, proactive defense capabilities, and enhanced incident response enabled by these technologies, businesses can fortify their defenses and protect their sensitive data from the ever-present dangers of the cyber world. Embracing SIEM and Threat Intelligence is no longer an option—it’s a necessity for any organization serious about cybersecurity.
If you are interested in learning more about how QRadar SIEM utilizes threat intelligence, schedule a 1:1 demo with an IBM Security expert here.
More from Cybersecurity

August 24, 2023
MDM vs. MAM: Top 5 differences
4 min read – It looks like an easy day for James, an IT Administrator. It is vacation time and most of his end users are out of the office, so he thinks it is time to have a look at some of the backlog tasks—maybe even procrastinate a bit. But then, the phone rings. It’s Robert, one of the end users in his company. Robert is very nervous—he’s calling from the hotel because he has lost his iOS smartphone on the beach. Their…
<!—->
August 23, 2023
Protect sensitive data in Azure and Microsoft Office while keeping control over your keys
6 min read – The average cost of a data breach is USD 4.35 million, and 83% of organizations have had more than one breach (of which 45% occur in the cloud). With these increases in the frequency and costs data breaches, an enterprise’s data protection and privacy in the cloud is more important than ever. The data protection needs of organizations are driven by concerns about protecting sensitive information and intellectual property and meeting compliance and regulatory requirements. Encryption is named the largest cost mitigation, and as such, mandated by…
<!—->

August 21, 2023
IBM Tech Now: August 21, 2023
< 1 min read – Welcome IBM Tech Now, our video web series featuring the latest and greatest news and announcements in the world of technology. Make sure you subscribe to our YouTube channel to be notified every time a new IBM Tech Now video is published. IBM Tech Now: Episode 81 On this episode, we’re covering the following topics: Cloudflare Bot Management on IBM CIS IBM Security X-Force’s detection and response framework for MFTs Stay plugged in You can check out the IBM Blog…
<!—->

August 18, 2023
Applying cyber resilience to DORA solutions
3 min read – The Digital Operational Resilience Act, or DORA, is a European Union (EU) regulation that created a binding, comprehensive information and communication technology (ICT) risk-management framework for the EU financial sector. DORA establishes technical standards that financial entities and their critical third-party technology service providers must implement in their ICT systems by January 17, 2025. DORA applies to all financial institutions in the EU. That includes traditional financial entities (like banks, investment firms and credit institutions) and non-traditional entities (like crypto-asset service providers and…
<!—->
- SEO Powered Content & PR Distribution. Get Amplified Today.
- PlatoData.Network Vertical Generative Ai. Empower Yourself. Access Here.
- PlatoAiStream. Web3 Intelligence. Knowledge Amplified. Access Here.
- PlatoESG. Automotive / EVs, Carbon, CleanTech, Energy, Environment, Solar, Waste Management. Access Here.
- PlatoHealth. Biotech and Clinical Trials Intelligence. Access Here.
- ChartPrime. Elevate your Trading Game with ChartPrime. Access Here.
- BlockOffsets. Modernizing Environmental Offset Ownership. Access Here.
- Source: https://www.ibm.com/blog/siem-and-threat-intelligence-stay-current-on-trending-threats/
- :has
- :is
- :where
- $UP
- 1
- 11
- 17
- 19
- 2023
- 2025
- 23
- 24
- 28
- 30
- 300
- 39
- 40
- 7
- 9
- a
- About
- accelerate
- According
- Act
- actors
- adaptive
- adding
- address
- addresses
- adjust
- adopt
- advanced
- Advertising
- After
- against
- ahead
- aids
- Alert
- All
- already
- amounts
- amp
- an
- analysis
- analytics
- analyze
- analyzed
- and
- Announcements
- antivirus
- any
- applications
- Applying
- ARE
- Array
- Arsenal
- article
- AS
- Assets
- associated
- At
- Attacks
- AUGUST
- author
- average
- awareness
- Azure
- back
- Banks
- BE
- Beach
- because
- become
- before
- benefits
- between
- binding
- Bit
- Blog
- blogs
- Bot
- breach
- breaches
- built
- businesses
- but
- by
- calling
- Campaigns
- CAN
- capabilities
- carbon
- card
- Cards
- CAT
- caused
- Channel
- characterized
- check
- CIS
- class
- Cloud
- CloudFlare
- collect
- collection
- color
- combat
- combination
- combined
- Communication
- company
- compliance
- comprehensive
- compromise
- Concerns
- conducted
- consistently
- constantly
- Container
- Containment
- continue
- control
- correlated
- correlating
- Cost
- Costs
- Counter
- coverage
- covering
- created
- credit
- critical
- cross-referencing
- crucial
- CSS
- Current
- curve
- custom
- cutting-edge
- cyber
- cybercriminals
- Cybersecurity
- damage
- dangers
- Dark
- Dark Web
- data
- data breach
- Data Breaches
- data protection
- Date
- day
- Default
- Defense
- definitions
- Demo
- description
- detailed
- Detection
- differences
- different
- digital
- Digital Assets
- discover
- distinct
- distribution
- dive
- dollars
- driven
- easy
- Effective
- efforts
- ELEVATE
- embracing
- emerging
- empowers
- enabled
- enables
- enabling
- end
- endpoints
- enhance
- enhanced
- Enhances
- Enter
- entities
- Environment
- episode
- essential
- establish
- establishes
- Ether (ETH)
- EU
- European
- european union
- European Union (EU)
- Even
- Event
- events
- EVER
- ever-increasing
- Every
- evolving
- Exit
- expert
- experts
- explore
- Exposure
- external
- Face
- faster
- Featuring
- File
- financial
- Financial institutions
- Financial sector
- Find
- firms
- follow
- following
- fonts
- For
- forums
- Framework
- Frequency
- from
- generator
- Global
- Go
- greatest
- Grid
- had
- Hardware
- Have
- he
- head
- height
- help
- High
- his
- hotel
- HOURS
- How
- How To
- HTTPS
- Hunting
- IBM
- ICO
- ICON
- ICT
- identify
- image
- implement
- important
- in
- incident
- incident response
- include
- included
- includes
- Including
- incorporates
- Increases
- increasing
- index
- Indicators
- information
- informed
- Infrastructure
- Insider
- insight
- insights
- instantly
- instead
- institutions
- Integrating
- integration
- intellectual
- intellectual property
- Intelligence
- interested
- internal
- into
- invaluable
- investigation
- investment
- investment firms
- iOS
- IP
- IP addresses
- IT
- ITS
- james
- January
- jpg
- keeping
- Key
- keys
- knowledge
- known
- landscape
- large
- latest
- leading
- LEARN
- learning
- leveraging
- like
- Lists
- locale
- log
- longer
- Look
- looking
- LOOKS
- lost
- maintaining
- make
- malware
- management
- many
- Marketing
- marketplaces
- matching
- materialize
- max-width
- May..
- measures
- meeting
- Microsoft
- Microsoft Office
- might
- million
- million dollars
- min
- minutes
- mitigation
- Mobile
- Modern
- Monitor
- more
- most
- must
- Named
- Navigation
- necessary
- necessity
- Need
- needs
- New
- news
- no
- nothing
- now
- occur
- of
- Office
- on
- ONE
- operational
- operational resilience
- optimized
- or
- organization
- organizations
- Other
- otherwise
- our
- out
- over
- page
- patterns
- perform
- phishing
- phone
- PHP
- pivotal
- platform
- plato
- Plato Data Intelligence
- PlatoData
- Play
- Plugged
- plugin
- policy
- position
- Post
- potential
- potentially
- power
- Prepare
- privacy
- Proactive
- procedures
- property
- protect
- protecting
- protection
- proven
- provide
- providers
- published
- quality
- range
- Ranking
- ransomware
- Ransomware Attacks
- RE
- Reading
- real-time
- recovery
- reducing
- Regulation
- regulatory
- remain
- Requirements
- research
- resilience
- Resources
- Respond
- response
- responsive
- resulting
- rising
- Risk
- ROBERT
- robots
- Role
- Rule
- rules
- s
- Screen
- scripts
- seamless
- sector
- security
- Security Measures
- sensitive
- seo
- September
- Series
- serious
- service
- service providers
- sign
- site
- Sites
- small
- smartphone
- So
- soaring
- Software
- solution
- Solutions
- some
- sophisticated
- Sources
- Spending
- Sponsored
- standards
- start
- Status
- stay
- Step
- Strains
- strategies
- Strengthen
- subscribe
- such
- sure
- synergy
- Systems
- tactics
- targeted
- targeting
- teams
- tech
- Technical
- techniques
- Technologies
- Technology
- than
- that
- The
- the world
- their
- theme
- then
- These
- they
- Thinks
- third-party
- this
- threat
- threat actors
- threat detection
- threat intelligence
- threats
- thumbnail
- time
- timeline
- Title
- to
- tools
- top
- top 5
- Topics
- traditional
- trending
- Trends
- two
- type
- types
- union
- upcoming
- urgent
- URL
- USD
- use
- used
- users
- uses
- utilizes
- Utilizing
- vacation
- value
- various
- Vast
- very
- Video
- View
- vital
- vs
- Vulnerabilities
- W
- want
- Watch
- we
- web
- webinar
- WELL
- when
- which
- while
- will
- with
- within
- without
- woman
- WordPress
- world
- written
- XML
- you
- Your
- youtube
- zephyrnet












