OpenAI Point-E brings artificial intelligence into 3D model generators, making one more step into the sweet, robotic, AI dominated future. In the same way that DALL-E has revolutionized the way we create two-dimensional graphics, Point-E will do the same for three-dimensional ones and is already significantly faster than its competitors like Google’s Dreamfusion or Nvidia’s Magic3D. But is it perfect?
In the conventional sense, Point-E does not produce 3D objects. Instead, it produces point clouds, or 3D models made up of discrete groupings of data points in space. Let’s take a deeper look to see if it’s true that OpenAI Point-E is better than its rivals, despite its low resolution.
What is OpenAI Point-E?
OpenAI Point-E is a 3D model generator that produces 3D images in minutes. Point-E, a machine learning system that can make a 3D object from text input, was released into the open-source community by OpenAI.
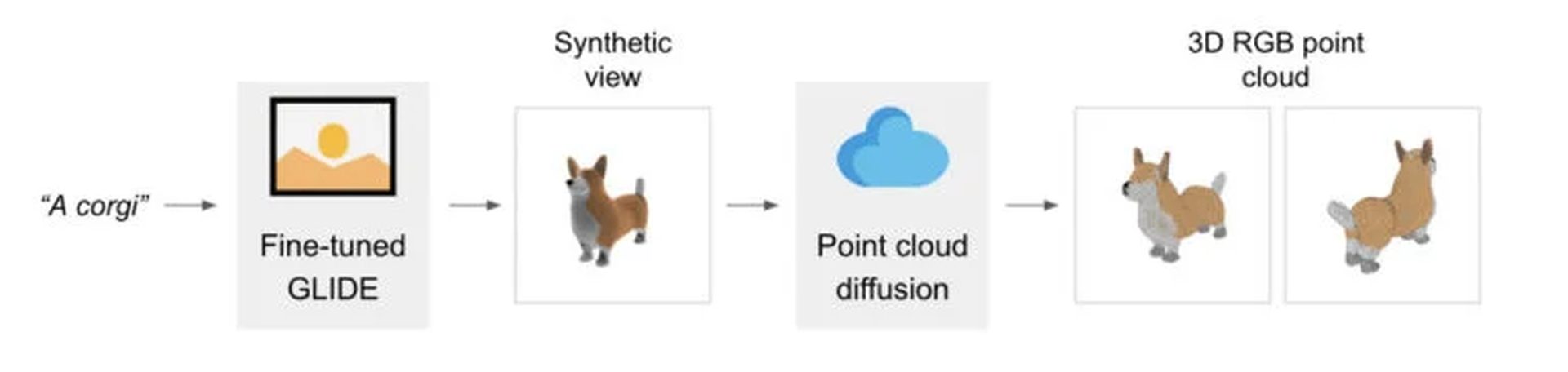
Using its text-to-image technology, OpenAI has released a new open-source software called Point-E. The software’s focus is on producing 3D models as its final result. It still prioritizes spreading artificial intelligence technology from its development, but unlike DALL-E, it will give three-dimensional models rather than still image production. In other words, OpenAI developed this technology similar to the DALL-E series, but consumers shouldn’t expect the same results.
OpenAI Point-E combines two separate models:
- An image-to-3D model and a GLIDE model. The former can make pictures from written descriptions, including programs like DALL-E or Stable Diffusion.
- OpenAI used photos and 3D objects to teach their second model how to create point clouds from photographs. Many millions of 3D objects and their information were used in the company’s training program.
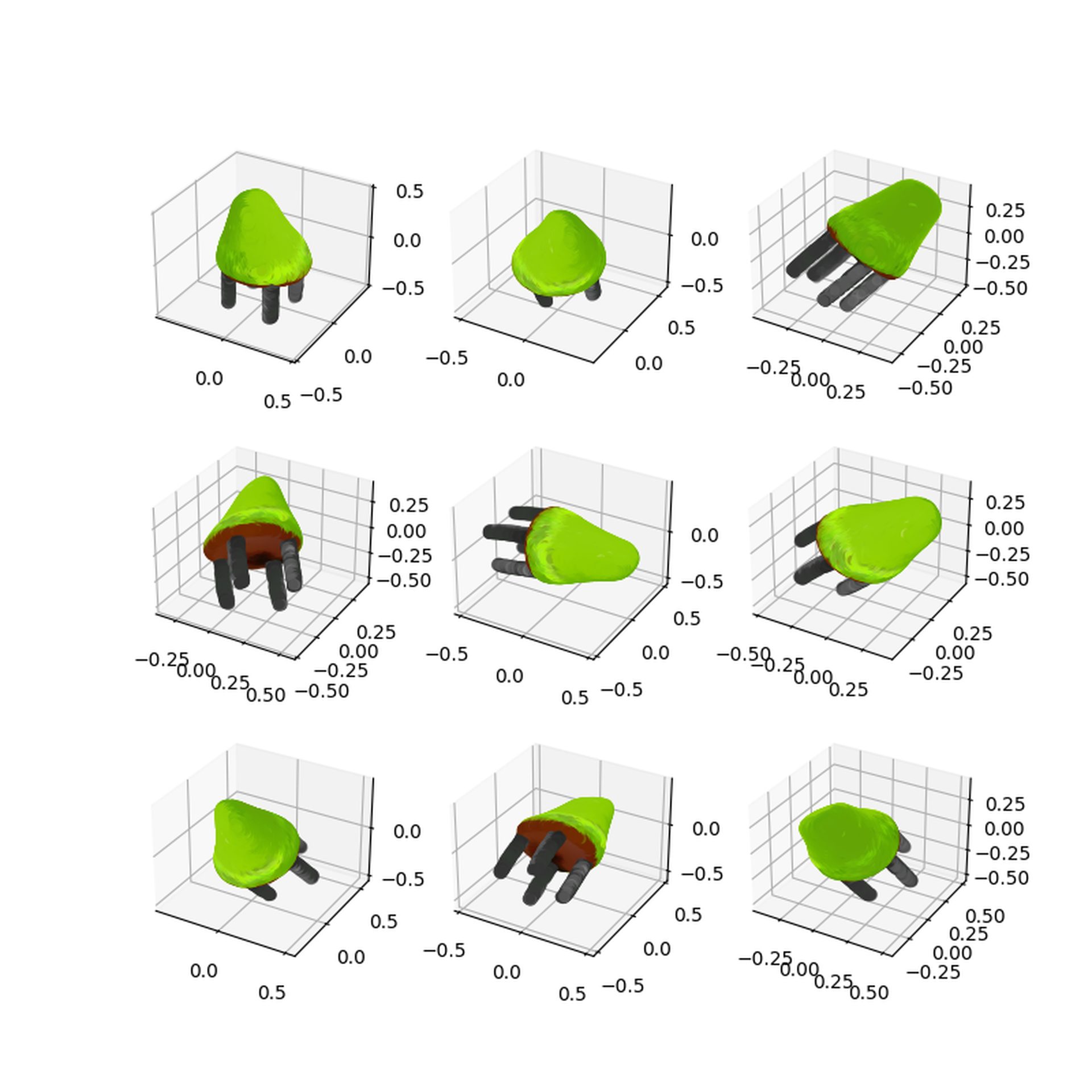
According to the findings of the OpenAI, there is room for error in this two-stage procedure. However, it is so quick that it can produce objects about 600 times faster than Dreamfusion.
“We have presented Point·E, a system for text-conditional synthesis of 3D point clouds that first generates synthetic views and then generates colored point clouds conditioned on these views. We find that Point·E is capable of efficiently producing diverse and complex 3D shapes conditioned on text prompts.”
OpenAI
Unlike other software, which can take hours to generate the same result, this one simply has to employ a single GPU to handle a user’s request for the aforementioned 3D model. Time and effort can be saved while still getting the desired results from 3D model render artists and designers.
The resulting images can be utilized in anything requiring a high degree of detail in three dimensions: video games, metaverse applications, or post-production for movies.
The DALL-E system has already transformed the way in which text is converted into images; Point-E intends to do the same for the third dimension. The generation of 3D landscapes using AI requires the creation of 3D objects and forms on demand at high speeds.
Check out the OpenAI ChatGPT chatbot; people have already fallen in love with it!
How does OpenAI Point-E work?
The OpenAI group built a collection containing several million 3D models and exported it from Blender. A point cloud was created from these renderings to represent the 3D object’s density of composition. After further processing, the dataset was prepared for input into the View Synthesis GLIDE model, including removing flat objects and clustering based on CLIP properties.
By modeling the point cloud as a tensor of a shape, the team developed a novel approach to point cloud diffusion. These tensors are then gradually denoised to take on the form of the required 3D object, going from a more random shape to the desired one. This diffusion model’s output is then sent into a point cloud upsampler, enhancing the final product’s quality. Blender is then used to transform the point clouds into meshes, making them usable in most 3D modeling programs.
In response to a text query such as “A cat eating a burrito,” Point-E will first create a synthetic perspective 3D representation of a cat eating a tortilla. After generating an image, it will go through a sequence of diffusion models to produce a 3D, RGB point cloud of the original image, starting with a coarse model of 1,024 points and ending with a fine model of 4,096 points.
OpenAI has posted the project’s open-source code on Github.
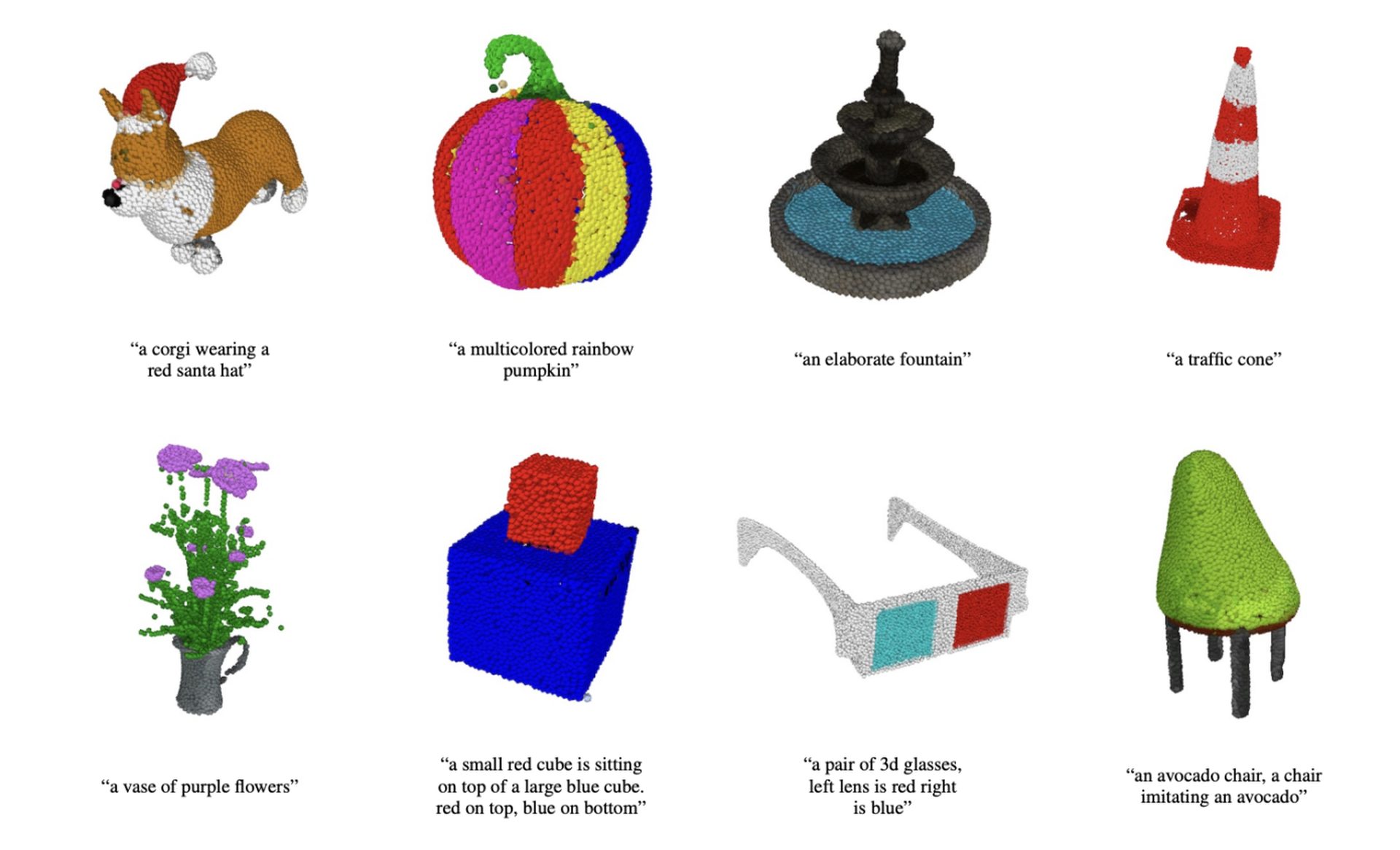
OpenAI Point-E examples
OpenAI Point-E is still in the early phase, but the outcomes are promising.
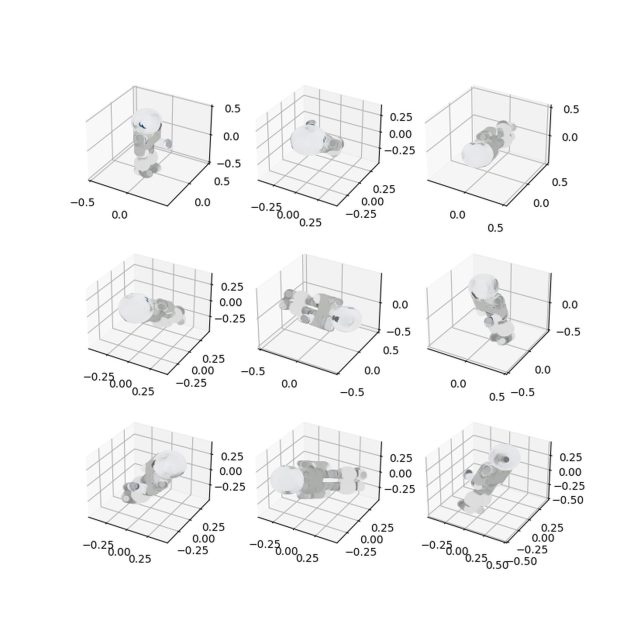
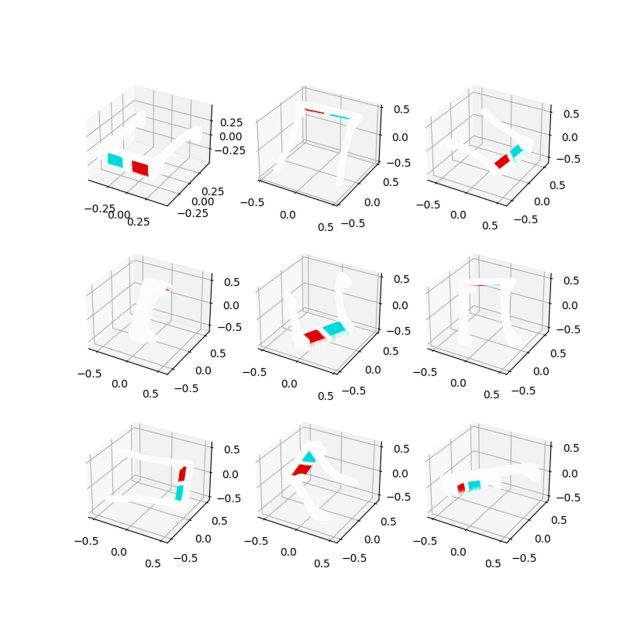
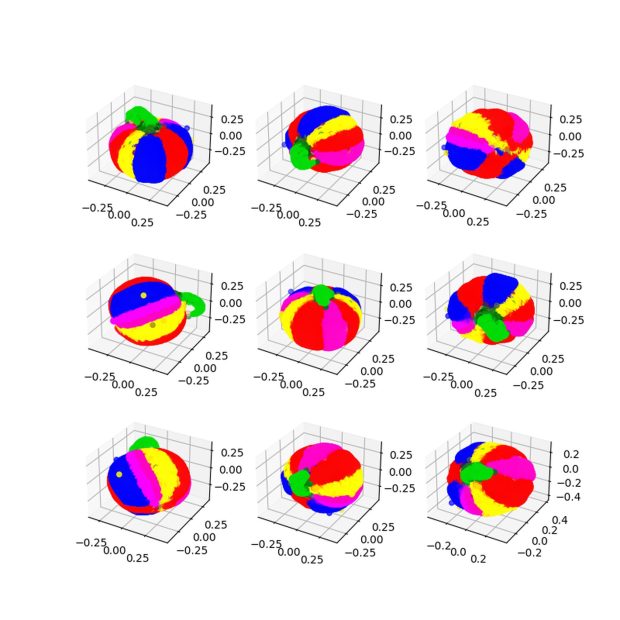
Of course, OpenAI Point-E is not flawless. Check out the example below.
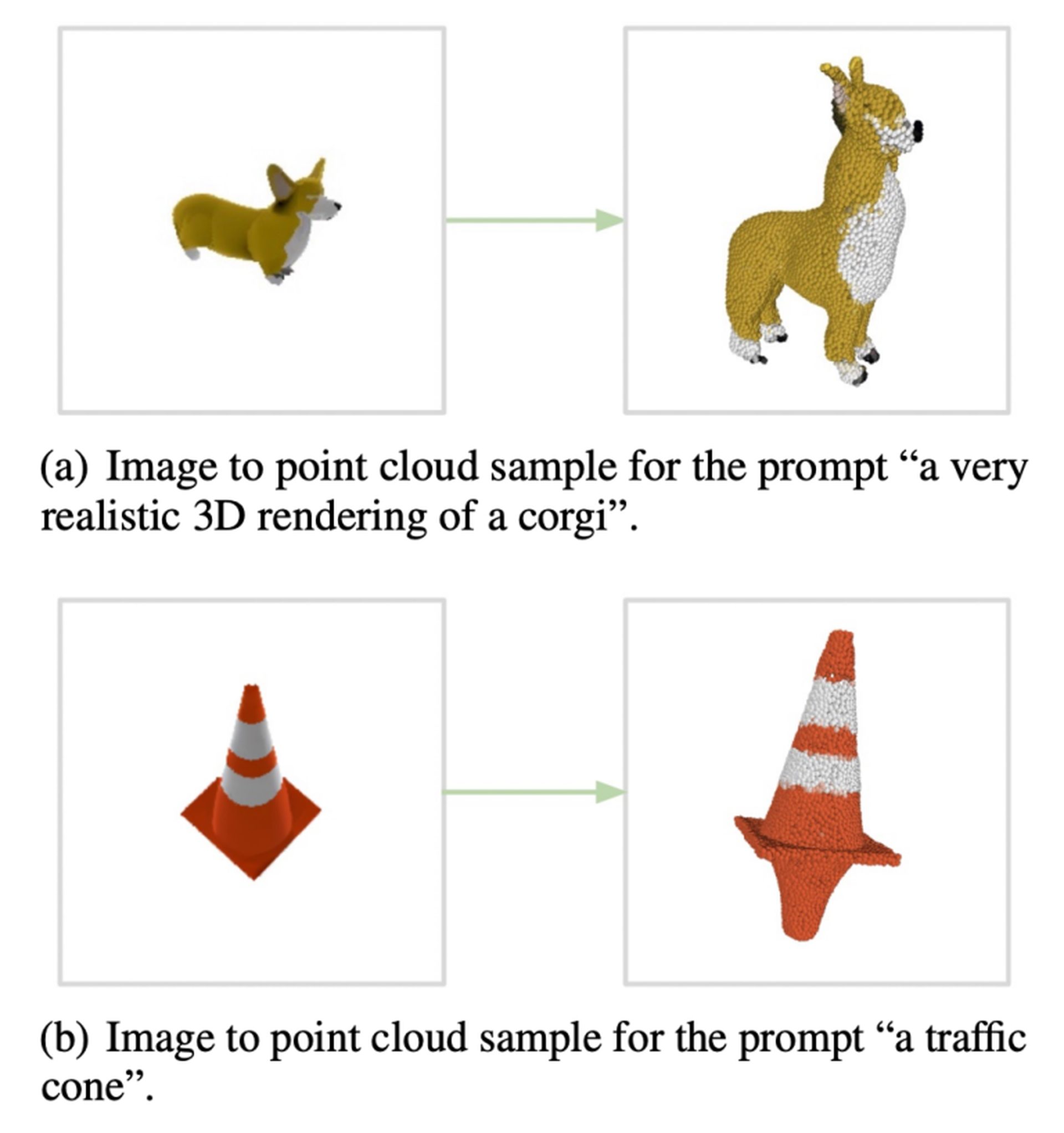
You can try it by clicking here. This demonstration generates 3D point clouds from textual descriptions using a small, lower-quality text-to-3D model.
Are you wondering how your room will be in cyberpunk style? Try Interior AI
Artificial intelligence controversy among designers
What kind of intellectual property disputes may we expect to see in the future? Artists can sell their work on sites like CGStudio and CreativeMarket, which cater to the growing demand for 3D models. Model artists may object if Point-E becomes popular and its models enter the markets, arguing that current generative AI steals substantially from its training data, in this example, existing 3D models.
Like DALL-E 2, Point-E doesn’t acknowledge or reference any artists or other creatives who may have affected its development.
There is also an ongoing debate on ArtStation, and designers say “No to AI-generated images.”
Nonetheless, OpenAI is putting that concern off for the time being. The Point-E article and GitHub page both fail to cite copyright.
Will AI replace designers?
The newest craze in design is artificial intelligence. Today, many IT organizations and individuals are turning to artificial intelligence to automate their procedures totally. They act this way because they understand that future society will be ruled by technologies that can drastically cut the number of labor humans must perform.

The design industry is not an exception, as we have already started to witness sector trends advance due to AI. We have already explained artificial intelligence design’s advantages and disadvantages. Don’t decide before checking it out.
Welcome to the AI-driven era
We have already explained some of the best AI tools like Uberduck AI, MOVIO AI, Meta’s Galactica AI, Notion AI, Make-A-Video, AI Dungeon, Chai, and NovelAI. Do you know there are also AI art robots? Check the Ai-Da.
Are you into AI image generation? You can try these tools:
Don’t be scared of AI jargon; we have created a detailed AI glossary for the most commonly used artificial intelligence terms and explain the basics of artificial intelligence as well as the risks and benefits of artificial intelligence.
- SEO Powered Content & PR Distribution. Get Amplified Today.
- Platoblockchain. Web3 Metaverse Intelligence. Knowledge Amplified. Access Here.
- Source: https://dataconomy.com/2022/12/openai-point-e-3d-modeling-in-minutes/
- 1
- 3d
- 7
- 9
- a
- About
- acknowledge
- Act
- advance
- advantages
- After
- AI
- ai art
- allows
- already
- among
- and
- Anime
- applications
- approach
- Art
- article
- artificial
- artificial intelligence
- Artists
- automate
- based
- because
- becomes
- before
- being
- believe
- below
- benefits
- BEST
- Better
- Blender
- Brings
- built
- called
- capable
- CAT
- Chair
- ChatGPT
- check
- checking
- class
- Cloud
- clustering
- code
- collection
- combines
- commonly
- community
- Company’s
- comparing
- competitors
- complex
- Concern
- Consumers
- content
- controversy
- conventional
- converted
- copyright
- course
- create
- created
- creation
- creatives
- Current
- Cut
- cyberpunk
- dall-e
- data
- data points
- debate
- deeper
- Degree
- Demand
- Design
- designers
- Despite
- detail
- developed
- Development
- Dimension
- dimensions
- disputes
- diverse
- Doesn’t
- Dont
- drastically
- Early
- efficiently
- effort
- enhancing
- Enter
- error
- example
- exception
- existing
- expect
- Explain
- explained
- FAIL
- Fallen
- faster
- final
- Find
- fine
- First
- flat
- Focus
- form
- Former
- forms
- from
- further
- future
- Games
- generate
- generates
- generating
- generation
- generative
- Generative AI
- generator
- generators
- getting
- GitHub
- Give
- Go
- Goes
- going
- Google’s
- GPU
- gradually
- graphics
- Group
- Growing
- handle
- High
- HOURS
- How
- How To
- However
- HTTPS
- Humanoid
- Humans
- image
- images
- in
- In other
- Including
- industry
- information
- input
- instead
- intellectual
- intellectual property
- Intelligence
- intends
- IT
- jargon
- Kind
- Know
- labor
- learning
- Look
- love
- Low
- machine
- machine learning
- made
- make
- Making
- many
- Markets
- max-width
- Meitu
- Metaverse
- million
- millions
- minutes
- model
- models
- more
- most
- Movies
- New
- Newest
- novel
- number
- object
- objects
- ONE
- ongoing
- open source
- open-source code
- OpenAI
- organizations
- original
- Other
- People
- perfect
- perform
- perspective
- phase
- Pictures
- plato
- Plato Data Intelligence
- PlatoData
- Point
- points
- Popular
- posted
- prepared
- presented
- procedures
- processing
- produce
- Production
- Program
- Programs
- projects
- promising
- properties
- property
- Putting
- quality
- Quick
- random
- Red
- released
- removing
- replace
- represent
- representation
- request
- required
- requires
- Resolution
- response
- result
- resulting
- Results
- revolutionary
- revolutionized
- RGB
- rivals
- robot
- robots
- Room
- round
- same
- scared
- Second
- sector
- sell
- sense
- Sequence
- Series
- several
- Shape
- shapes
- significantly
- similar
- simply
- single
- Sites
- small
- So
- Society
- Software
- some
- Space
- speeds
- Spreading
- stable
- started
- Starting
- steals
- Step
- Still
- style
- such
- sweet
- synthetic
- system
- Take
- Talent
- team
- Technologies
- Technology
- The
- their
- Third
- three
- three-dimensional
- Through
- time
- times
- to
- today
- tools
- TOTALLY
- Training
- Transform
- transformed
- Trends
- true
- Turning
- understand
- utilized
- version
- Video
- video games
- View
- views
- What
- which
- while
- WHO
- will
- witness
- wondering
- words
- Work
- would
- written
- Your
- zephyrnet