Abstract
Returns avoidance, gatekeeping, disposal, and other supply chain issues are related to reverse logistics. The product may need to travel in reverse through the entire supply chain network to retain the use of any service from the defective goods. There are closed-loop supply chain networks that include returns processing and the manufacturer has the intention to capture the additional value and integrate all supply chain activities. Usually, asset-based three 3PLs work as third parties who are specialized in waste management and related activities. Reuse of manufactured and sold goods After-sales service and returns management are sometimes related to the logistic companies.
Keywords: Logistics, manufacturers, reverse logistics.
Introduction
The concept of reverse logistics is related to reusing materials used in a supply chain. While logistics is involved with reaching the goods to the customer, reverse logistics is involved with sending some goods at least one step back i.e., to the distributor or to the manufacturers in a supply chain. Reverse logistics has an important role in the competitiveness, pricing and profit/loss of an industry.
Remanufacturing
Sometimes re-manufacturing is required in the supply chain. Reverse logistics is the prior step to doing this. Concerns over green supply chain management make re-manufacturing and refurbishing to some extent more relevant. Some small processing after the sales may involve reverse logistics. For leasing companies, reverse logistics is a more regular process. The product may need to travel in reverse through the entire supply chain network to retain the use of any service from the defective goods.

Reuse of manufactured and sold goods
Returns Management
After-sales service and returns management are sometimes related to logistics companies. Logistics companies return to the position where the goods are repaired or resold in a timely manner. There should be return management best practices. As a result, the returns process is addressed in a way that operational and customer retention issues are properly handled in a business. Returns avoidance, gatekeeping, disposal, and other supply chain issues are related to reverse logistics. In some businesses, returns management is an inevitable issue, which gives an important link between marketing and the logistics department.
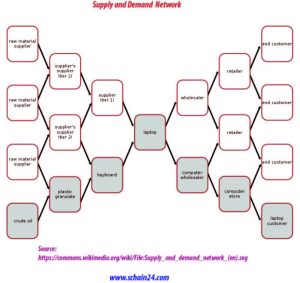
Closed-Loop Supply Chains
There are closed-loop supply chain networks that include returns processing and the manufacturer has the intention to capture the additional value and integrate all supply chain activities. These closed-loop supply chains are reusable packaging, i.e., reusable pallets, bottles, packages, etc. On the other hand, returned goods are returned to their origin and added to the inventory again.
Cost-effectiveness
Reverse Logistics related functions should be done in a cost-effective way. So that a supply chain is properly managed would not be out of business. They can amicably work with competitors. It is often necessary to partner with multiple organizations, leverage best practices, improve profit margins, precision management, etc. Manufacturers must consider spare parts cost, within warranty or without warranty issues also.
High-Value Products
Major activities are the return of used or deteriorated products, repair, disposal, etc. Third-party logistics providers give asset-related services and operate in repair depots. Other third parties work at the manufacturer and wholesale levels. Providers used to comply with broader service operations.
Green Products
In this case, the major activity is in the area of validation under recycling, environmental compliance, etc. Third parties usually work in niche and waste specialization areas. In about more than 40% of cases, third parties need to penetrate. And they need a good understanding of environmental regulations.
Waste Disposal
Wastes need to be disposed of or given some remedy to them after commercial or industrial operations. Usually, asset-based three 3PLs work as third parties who are specialized in waste management and related activities. These areas are heavily regulated and must comply with them.
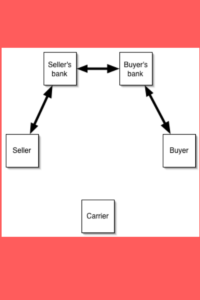
The courier service and the reverse logistics:
The pickup courier usually uses a relatively small vehicle/van to collect the parcels from the shipper to the local depot. Typically, a courier service is started from a pickup; once a courier company received a request from a customer, the origin courier depot arranges for a courier pickup. It is picked up by the local depot driver, labeled with a return identification number/paperwork, and then transported back to the shipper via the central hub and then the shipper’s local depot. Once the parcels reach the destination depot, they are sorted and ready for local distribution to their final destination. In the origin depot, the parcels are consolidated, then a larger vehicle is used to deliver the freight to the central hub.
Conclusion
In direct logistics, product quality is usually uniform, options clearer, routing of products more unambiguous. In reverse logistics, product quality is not uniform. The disposition is not clear, routing of the product is ambiguous. In direct logistics, the visibility of the process is usually transparent. But in revere logistics, the visibility of the process is less transparent.
Further reading:
1.https://www.newcastlesys.com/blog/the-importance-of-reverse-logistics-in-your-supply-chain
2. Wang, Michael. Wang, Bill. Chan, Ricky.(2020). “Reverse logistics uncertainty in a courier industry: a triadic model”. Modern Supply Chain Research and Applications.Emerald Publishing Limited.2631-3871.
3.https://fvrr.co/3uPSYBa
(Visited 1 times, 1 visits today)
- SEO Powered Content & PR Distribution. Get Amplified Today.
- PlatoData.Network Vertical Generative Ai. Empower Yourself. Access Here.
- PlatoAiStream. Web3 Intelligence. Knowledge Amplified. Access Here.
- PlatoESG. Automotive / EVs, Carbon, CleanTech, Energy, Environment, Solar, Waste Management. Access Here.
- BlockOffsets. Modernizing Environmental Offset Ownership. Access Here.
- Source: https://www.schain24.com/2023/07/12/understanding-the-reverse-logistics-concept-and-implications-in-supply-chain-management/?utm_source=rss&utm_medium=rss&utm_campaign=understanding-the-reverse-logistics-concept-and-implications-in-supply-chain-management
- :has
- :is
- :not
- :where
- $UP
- 1
- 2020
- 300
- a
- About
- activities
- activity
- added
- Additional
- After
- again
- All
- also
- an
- and
- any
- applications
- ARE
- AREA
- areas
- AS
- At
- auto
- back
- BE
- BEST
- best practices
- between
- Bill
- broader
- business
- businesses
- but
- by
- CAN
- capture
- case
- cases
- central
- chain
- chains
- chan
- clear
- clearer
- collect
- commercial
- Companies
- company
- competitiveness
- competitors
- compliance
- comply
- concept
- Concerns
- Consider
- Cost
- cost-effective
- Courier Service
- customer
- Customer Retention
- deliver
- Department
- destination
- direct
- distribution
- doing
- done
- driver
- e
- Emerald
- Entire
- environmental
- etc
- extent
- final
- For
- from
- functions
- gatekeeping
- Give
- given
- gives
- good
- goods
- Green
- hand
- heavily
- http
- HTTPS
- Hub
- i
- Identification
- implications
- important
- improve
- in
- include
- industrial
- industry
- inevitable
- integrate
- Intention
- inventory
- involve
- involved
- issue
- issues
- IT
- ITS
- jpg
- larger
- leasing
- least
- less
- levels
- Leverage
- Limited
- LINK
- local
- logistics
- major
- make
- managed
- management
- manner
- manufactured
- Manufacturer
- Manufacturers
- margins
- Marketing
- materials
- max-width
- May..
- Michael
- Modern
- more
- multiple
- must
- necessary
- Need
- network
- networks
- of
- often
- on
- once
- ONE
- operate
- operational
- Operations
- Options
- or
- organizations
- Origin
- Other
- out
- over
- packages
- packaging
- parties
- partner
- parts
- picked
- Pickup
- plato
- Plato Data Intelligence
- PlatoData
- position
- practices
- Precision
- Prior
- process
- processing
- Product
- Product Quality
- Products
- properly
- providers
- Publishing
- quality
- reach
- reaching
- Reading
- ready
- received
- recycling
- regular
- regulated
- regulations
- related
- relatively
- relevant
- repair
- request
- required
- research
- result
- retain
- retention
- return
- returns
- reusable
- reuse
- reverse
- Role
- routing
- sales
- sending
- service
- Services
- should
- small
- So
- sold
- some
- specialized
- started
- Step
- supply
- supply chain
- supply chain management
- Supply chains
- than
- that
- The
- The Area
- their
- Them
- then
- There.
- These
- they
- Third
- third parties
- this
- three
- Through
- times
- to
- today
- transparent
- transported
- travel
- true
- typically
- Uncertainty
- under
- understanding
- use
- used
- uses
- usually
- validation
- value
- vehicle
- via
- visibility
- visited
- Visits
- Waste
- Way..
- which
- while
- WHO
- wholesale
- with
- within
- without
- Work
- would
- zephyrnet