Home > Press > Scientists edge toward scalable quantum simulations on a photonic chip: A system using photonics-based synthetic dimensions could be used to help explain complex natural phenomena
 |
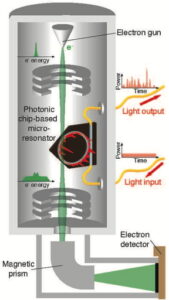
| A new system developed by researchers at the University of Rochester allows them to conduct quantum simulations in a synthetic space that mimics the physical world by controlling the frequency, or color, of quantum entangled photons as time elapses. CREDIT University of Rochester illustration / Michael Osadciw |
Abstract:
Scientists have made an important step toward developing computers advanced enough to simulate complex natural phenomena at the quantum level. While these types of simulations are too cumbersome or outright impossible for classical computers to handle, photonics-based quantum computing systems could provide a solution.
Scientists edge toward scalable quantum simulations on a photonic chip: A system using photonics-based synthetic dimensions could be used to help explain complex natural phenomena
Rochester, NY | Posted on June 30th, 2023
A team of researchers from the University of Rochester’s Hajim School of Engineering & Applied Sciences developed a new chip-scale optical quantum simulation system that could help make such a system feasible. The team, led by Qiang Lin, a professor of electrical and computer engineering and optics, published their findings in Nature Photonics.
Lin’s team ran the simulations in a synthetic space that mimics the physical world by controlling the frequency, or color, of quantum entangled photons as time elapses. This approach differs from the traditional photonics-based computing methods in which the paths of photons are controlled, and also drastically reduces the physical footprint and resource requirements.
“For the first time, we have been able to produce a quantum-correlated synthetic crystal,” says Lin. “Our approach significantly extends the dimensions of the synthetic space, enabling us to perform simulations of several quantum-scale phenomena such as random walks of quantum entangled photons.”
The researchers say that this system can serve as a basis for more intricate simulations in the future.
“Though the systems being simulated are well understood, this proof-of-principle experiment demonstrates the power of this new approach for scaling up to more complex simulations and computation tasks, something we are very excited to investigate in the future,” says Usman Javid ’23 PhD (optics), the lead author on the study.
Other coauthors from Lin’s group include Raymond Lopez-Rios, Jingwei Ling, Austin Graf, and Jeremy Staffa.
The project was supported with funding from the National Science Foundation, the Defense Threat Reduction Agency’s Joint Science and Technology Office for Chemical and Biological Defense, and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Luke Auburn
University of Rochester
Cell: 5854903198
Copyright © University of Rochester
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Electron collider on a chip June 30th, 2023
Electron collider on a chip June 30th, 2023
![]() Discovering features of band topology in amorphous thin films June 30th, 2023
Discovering features of band topology in amorphous thin films June 30th, 2023
![]() New single-photon Raman lidar can monitor for underwater oil leaks: System could be used aboard underwater vehicles for many applications June 30th, 2023
New single-photon Raman lidar can monitor for underwater oil leaks: System could be used aboard underwater vehicles for many applications June 30th, 2023
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics June 30th, 2023
The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics June 30th, 2023
![]() Breaking through the limits of stretchable semiconductors with molecular brakes that harness light June 9th, 2023
Breaking through the limits of stretchable semiconductors with molecular brakes that harness light June 9th, 2023
Possible Futures
![]() CityU awarded invention: Soft, ultrathin photonic material cools down wearable electronic devices June 30th, 2023
CityU awarded invention: Soft, ultrathin photonic material cools down wearable electronic devices June 30th, 2023
Chip Technology
![]() Electron collider on a chip June 30th, 2023
Electron collider on a chip June 30th, 2023
![]() Discovering features of band topology in amorphous thin films June 30th, 2023
Discovering features of band topology in amorphous thin films June 30th, 2023
![]() Breaking through the limits of stretchable semiconductors with molecular brakes that harness light June 9th, 2023
Breaking through the limits of stretchable semiconductors with molecular brakes that harness light June 9th, 2023
Quantum Computing
![]() Electron collider on a chip June 30th, 2023
Electron collider on a chip June 30th, 2023
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() USTC enhances fluorescence brightness of single silicon carbide spin color centers June 9th, 2023
USTC enhances fluorescence brightness of single silicon carbide spin color centers June 9th, 2023
![]() Laser direct writing of Ga2O3/liquid metal-based flexible humidity sensors May 12th, 2023
Laser direct writing of Ga2O3/liquid metal-based flexible humidity sensors May 12th, 2023
![]() Breakthrough in the optical properties of MXenes – two-dimensional heterostructures provide new ideas May 12th, 2023
Breakthrough in the optical properties of MXenes – two-dimensional heterostructures provide new ideas May 12th, 2023
Announcements
![]() New single-photon Raman lidar can monitor for underwater oil leaks: System could be used aboard underwater vehicles for many applications June 30th, 2023
New single-photon Raman lidar can monitor for underwater oil leaks: System could be used aboard underwater vehicles for many applications June 30th, 2023
![]() CityU awarded invention: Soft, ultrathin photonic material cools down wearable electronic devices June 30th, 2023
CityU awarded invention: Soft, ultrathin photonic material cools down wearable electronic devices June 30th, 2023
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() New single-photon Raman lidar can monitor for underwater oil leaks: System could be used aboard underwater vehicles for many applications June 30th, 2023
New single-photon Raman lidar can monitor for underwater oil leaks: System could be used aboard underwater vehicles for many applications June 30th, 2023
![]() CityU awarded invention: Soft, ultrathin photonic material cools down wearable electronic devices June 30th, 2023
CityU awarded invention: Soft, ultrathin photonic material cools down wearable electronic devices June 30th, 2023
Military
![]() The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics June 30th, 2023
The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics June 30th, 2023
![]() Optical switching at record speeds opens door for ultrafast, light-based electronics and computers: March 24th, 2023
Optical switching at record speeds opens door for ultrafast, light-based electronics and computers: March 24th, 2023
![]() Semiconductor lattice marries electrons and magnetic moments March 24th, 2023
Semiconductor lattice marries electrons and magnetic moments March 24th, 2023
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() New single-photon Raman lidar can monitor for underwater oil leaks: System could be used aboard underwater vehicles for many applications June 30th, 2023
New single-photon Raman lidar can monitor for underwater oil leaks: System could be used aboard underwater vehicles for many applications June 30th, 2023
![]() The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics June 30th, 2023
The picture of health: Virginia Tech researchers enhance bioimaging and sensing with quantum photonics June 30th, 2023
![]() USTC enhances fluorescence brightness of single silicon carbide spin color centers June 9th, 2023
USTC enhances fluorescence brightness of single silicon carbide spin color centers June 9th, 2023
- SEO Powered Content & PR Distribution. Get Amplified Today.
- PlatoData.Network Vertical Generative Ai. Empower Yourself. Access Here.
- PlatoAiStream. Web3 Intelligence. Knowledge Amplified. Access Here.
- PlatoESG. Automotive / EVs, Carbon, CleanTech, Energy, Environment, Solar, Waste Management. Access Here.
- BlockOffsets. Modernizing Environmental Offset Ownership. Access Here.
- Source: http://www.nanotech-now.com/news.cgi?story_id=57363
- :has
- :not
- $UP
- 10
- 28
- 2D
- 2D materials
- 30th
- 7
- 7th
- 9th
- a
- Able
- access
- accuracy
- across
- advanced
- agency
- AI
- allows
- also
- an
- and
- Announces
- applied
- approach
- ARE
- artificial
- artificial intelligence
- AS
- At
- austin
- author
- awarded
- BAND
- basis
- BE
- been
- being
- breakthrough
- Brown University
- built-in
- by
- CAN
- cellular
- Center
- CGI
- characteristic
- chemical
- chip
- click
- color
- COM
- comment
- Compensation
- complex
- computation
- computer
- Computer Engineering
- computers
- computing
- Conduct
- Confirm
- content
- controlled
- controlling
- could
- credit
- crucial
- Crystal
- data
- Defense
- Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency
- demonstrates
- developed
- developing
- device
- dimensions
- direct
- discover
- Dispersion
- Door
- down
- drastically
- Edge
- Electronic
- Electronics
- electrons
- enabling
- end
- Engineering
- enhance
- Enhances
- enough
- Errors
- essential
- Ether (ETH)
- Examines
- excited
- experiment
- Explain
- explore
- extends
- faster
- feasible
- Features
- field
- findings
- First
- first time
- flexible
- Footprint
- For
- found
- Foundation
- Frequency
- from
- functions
- funding
- future
- gif
- Gold
- Graphene
- Group
- handle
- harness
- Have
- Health
- help
- How
- http
- HTTPS
- identify
- if
- important
- impossible
- in
- Inc.
- include
- information
- insight
- Intelligence
- interacting
- interaction
- Internet
- into
- Invention
- investigate
- issue
- joint
- journal
- jpg
- june
- launch
- lead
- Leaks
- Led
- Level
- levels
- lidar
- limits
- lin
- links
- long-standing
- lowering
- machine
- made
- make
- many
- March
- material
- materials
- May..
- measured
- method
- methods
- Michael
- molecular
- Monitor
- more
- motion
- nanotechnology
- National
- National Science
- Natural
- Nature
- net
- New
- news
- novel
- now
- NSF
- NY
- of
- Office
- Oil
- on
- open
- opens
- optics
- or
- Paving
- perform
- Photons
- PHP
- physical
- picture
- plato
- Plato Data Intelligence
- PlatoData
- please
- Post
- posted
- potential
- power
- press
- Press Release
- probe
- produce
- Professor
- project
- projects
- properties
- Protein
- provide
- provides
- published
- Publishing
- Quantum
- quantum computing
- quantum information
- random
- rapidly
- receives
- record
- reduces
- reduction
- Regulate
- release
- Releases
- Requirements
- research
- researcher
- researchers
- resource
- responsible
- Results
- return
- Reveals
- Save
- say
- says
- scalable
- scaling
- School
- School of Engineering
- Science
- Science and Technology
- SCIENCES
- scientists
- Search
- Sectors
- Semiconductors
- serve
- several
- Share
- significant
- significantly
- Silicon
- silicon carbide
- simulation
- single
- Soft
- solely
- solid
- solution
- something
- Space
- special
- speeds
- Spin
- start
- Step
- structure
- Study
- submit
- such
- Supported
- synthetic
- system
- Systems
- tasks
- team
- tech
- Technology
- that
- The
- The Future
- their
- Them
- These
- this
- threat
- Through
- time
- to
- too
- toward
- traditional
- transformative
- Trevor
- types
- understanding
- understood
- underwater
- university
- us
- used
- uses
- using
- Vehicles
- very
- virginia
- was
- Wave
- Way..
- we
- wearable
- WELL
- which
- while
- with
- world
- writing
- Yahoo
- you
- zephyrnet