September 18, 2023
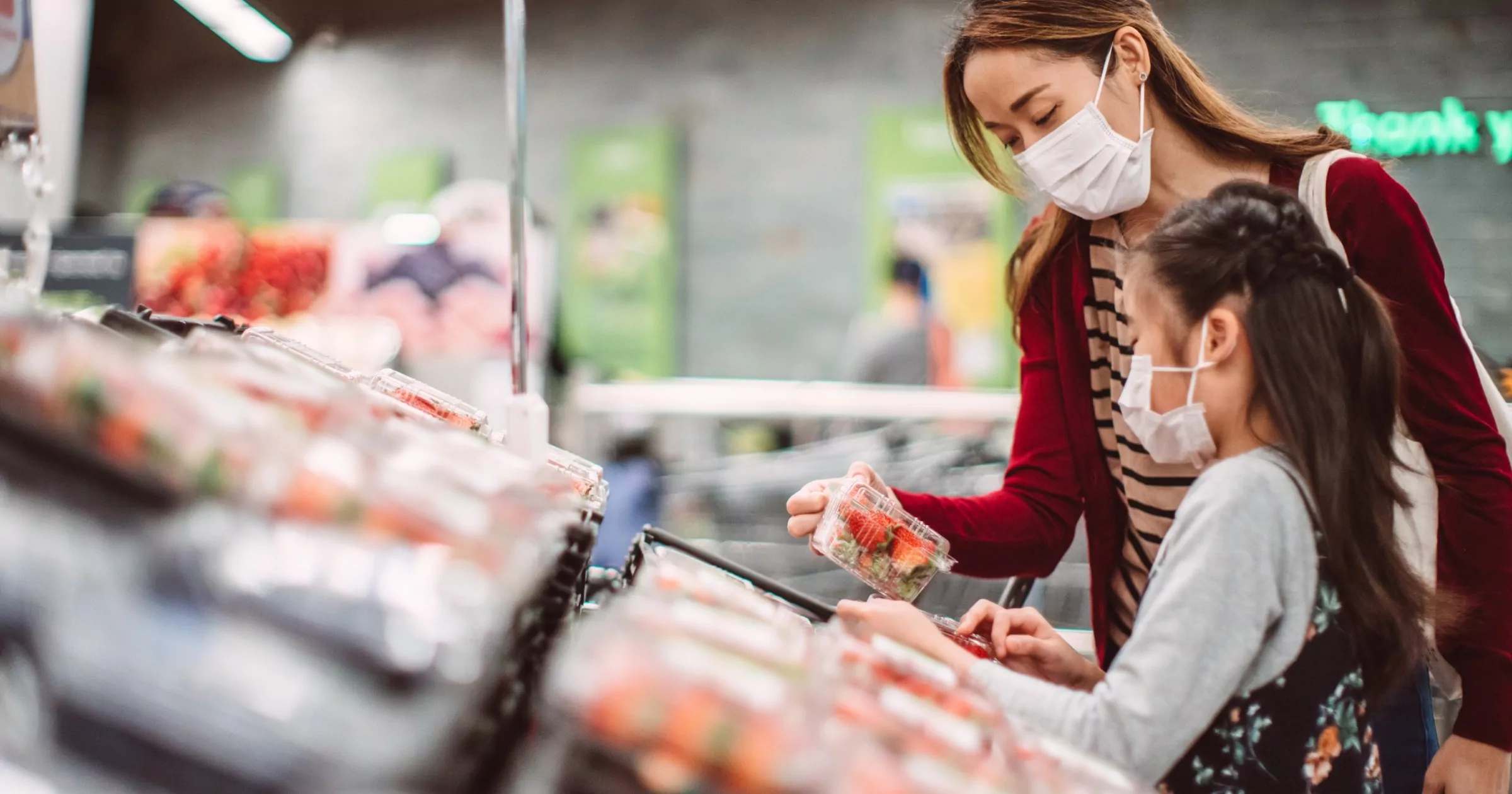
Picture this: You’re at your local supermarket, eagerly exploring the fresh produce section. You carefully select a carton of ripe, juicy fresh-cut strawberries, envisioning them as the star ingredient in your weekend’s mouthwatering desserts. You’re all set to enjoy a delightful culinary adventure. But as you savor your first bite of a luscious strawberry shortcake, you receive a notification on your smartphone. It’s breaking news: a food recall alert! Panic ensues as you wonder if those very strawberries are part of the recall, and you hastily check the label.
Now, while this might sound like a scene from a suspenseful thriller, it’s a real-life dilemma that food businesses face. In a world where food safety is paramount, compliance with the FDA Food Tracebility Rule FSMA 204 is non-negotiable.
Fortunately, in the ever-evolving world of food safety, a dynamic partnership between IBM and iFoodDS is rewriting the script, offering a solution that not only ensures compliance but also elevates food safety to new heights.
The FDA’s Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) Rule 204 is a game-changer for food traceability. This new regulation requires food companies that manufacture, process, pack, or hold foods on the Food Traceability List (FTL) implement traceability systems and new record keeping requirements. The goal of the regulation is to help prevent foodborne illness outbreaks by making it easier to track the movement of food from farm to fork. Today, outbreak investigations take an average of a month to complete, often with inconclusive results.1
The impact of the FSMA Rule 204(d) on traceability is significant. For the first time, the industry will be required to collect and maintain detailed information about the ingredients, processing, and distribution of their products. This information will be used to create a “traceability chain” that can be used to quickly identify and remove contaminated food from the market. The FDA estimates that the rule will help reduce outbreak investigations to less than one week.2
The FSMA Rule 204(d) is a complex regulation, and it will take time for the food industry to comply, however, IBM and iFoodDS are partnering to make it easier for companies to meet the upcoming compliance deadline.
The joint offering—called iFoodDS Trace Exchange with IBM Food Trust—will offer businesses in the food industry and their suppliers a comprehensive, scalable, and secure traceability solution that meets the requirements of FSMA Rule 204. Under the partnership, IBM will provide the backend data processing and storage capabilities on the IBM Food Trust network, while iFoodDS will provide a suite of applications and deep industry knowledge to assist companies with onboarding and organizational change needed to collect the required Key Data Elements (KDEs) and Critical Tracking Events (CTEs).
The joint solution will offer several benefits for food companies, including:
- The most comprehensive solution for FDA FSMA 204 compliance: The solution will cover all the requirements of FSMA Rule 204, including the ability to capture, store, share, monitor and report on traceability data for all foods on the Food Traceability List (FTL).
- Unmatched onboarding experience: iFoodDS has a deep understanding of the food industry and can provide food companies with a seamless onboarding experience. This includes helping companies to assess their current traceability capabilities, develop a compliance plan, and implement the solution.
- Purpose-built FSMA 204 data capture applications & methods: The solution includes a suite of purpose-built applications and methods for capturing the required KDEs and CTEs. This makes it easy for food companies to comply with the regulations without having to develop their own solutions.
- The most scalable and secure tech-enabled traceability solution in the industry: The solution is built on the IBM Food Trust network, which is a secure and scalable blockchain platform that can support the traceability needs of even the largest food companies.
- Trusted data sharing: The solution allows food companies to share traceability data with their trading partners in a secure and trusted manner. This allows companies to meet the requirements of the rule while providing visibility to help them run their supply chains more efficiently.
The partnership between IBM and iFoodDS is a significant step forward for food safety. The joint solution will help the industry achieve FSMA 204 compliance and improve food safety across the entire supply chain.
In addition to the benefits mentioned above, the partnership between IBM and iFoodDS also has the potential to:
- Recall food faster and more efficiently to reduce illness and waste: By making it easier for food companies to track the movement of food, the joint solution can help to reduce the number of foodborne illness outbreaks.
- Improve food waste reduction: By enabling a better understanding of the supply chain, the joint solution can help to reduce food waste.
- Increase food transparency: By making traceability data more accessible to consumers, the joint solution can increase food transparency and consumer confidence.
The partnership between IBM and iFoodDS has yielded a game-changing solution for the food industry, one that not only meets the stringent requirements of the FDA FSMA Rule 204(d) but also advances global food safety. iFoodDS Trace Exchange with IBM Food Trust is poised to make compliance effortless, data management secure, and traceability swift and accurate, ultimately ensuring safer food for consumers around the world. As the industry embarks on this transformative journey, it’s a clear signal we have truly entered a new era of smarter food safety.
Explore Food Traceability Software for the Whole Supply Chain
- CDC Update on Investigation of Multistate Outbreak of E. coli O157:H7 Infections Linked to Romaine Lettuce
- Final Regulatory Impact Analysis (Table 9)
More from Sustainability

September 15, 2023
The tsunami of sustainability disclosures facing American multinationals: Is your company prepared?
5 min read – Globally, there has been an uptick of landmark regulations forcing companies to address sustainability issues like climate change, and to disclose the work they are doing to address these issues. On July 31, 2023, the European Union (EU) adopted the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) and published them as “final rules” for the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), the most far-reaching set of disclosure requirements companies have to comply with, covering 12 environmental, social, and governance (ESG) standards. CSRD will…
<!—->

September 7, 2023
Harnessing AI and data analytics can make clean energy more viable
2 min read – The effects of climate change grow more tangible by the day. As a result, the electric power industry is hastening efforts to reduce environmental impact. To do so, they need help to get a clearer picture of where they fall on the emissions reduction roadmap, and to better understand their opportunities for improvement. This is where harnessing artificial intelligence (AI) and data analytics can help. To assist utility companies, IBM has created the Clean Electrification Maturity Model (CEMM) in conjunction…
<!—->

August 24, 2023
2018 Call for Code Winner Project OWL advances its natural disaster communication network
3 min read – For disaster-prone areas, fragile connectivity remains a major problem, often going offline in critical moments. Aerospace enterprises face a similar challenge when trying to run consistent high-altitude connectivity while operating in remote locations, which can also be very expensive. This is where Project OWL comes into play: developing new technologies to help address these challenges. Formed in 2018 to compete in the inaugural Call for Code Global Challenge — which it won — Project OWL is a global team of entrepreneurs…
<!—->

August 16, 2023
IBM’s dedication to responsible computing
2 min read – In response to concerns faced by corporations about the impact of technology on our environment, IBM founded the Responsible.Computing() movement, creating a membership consortium with Dell that is managed by the Object Management Group. Customers and partners expect responsible corporate policies and practices, and they also build loyalty with employees. Responsible computing establishes a cohesive, interconnected framework across six critical domains to provide every organization the ability to educate on their responsibilities, define goals and measure their progress against these aspirations:…
<!—->
- SEO Powered Content & PR Distribution. Get Amplified Today.
- PlatoData.Network Vertical Generative Ai. Empower Yourself. Access Here.
- PlatoAiStream. Web3 Intelligence. Knowledge Amplified. Access Here.
- PlatoESG. Carbon, CleanTech, Energy, Environment, Solar, Waste Management. Access Here.
- PlatoHealth. Biotech and Clinical Trials Intelligence. Access Here.
- BlockOffsets. Modernizing Environmental Offset Ownership. Access Here.
- Source: https://www.ibm.com/blog/ifoodds-and-ibm-forge-new-path-to-food-safety-with-ibm-food-trust/
- :has
- :is
- :not
- :where
- 1
- 12
- 13
- 15%
- 16
- 17
- 2018
- 2023
- 24
- 29
- 30
- 300
- 31
- 36
- 39
- 40
- 400
- 7
- 75
- 9
- a
- ability
- About
- above
- accessible
- accurate
- Achieve
- across
- Act
- addition
- address
- adopted
- advances
- Adventure
- Advertising
- Aerospace
- against
- AI
- All
- allows
- also
- American
- amp
- an
- analysis
- analytics
- and
- applications
- ARE
- areas
- around
- article
- artificial
- artificial intelligence
- Artificial intelligence (AI)
- AS
- assess
- assist
- At
- AUGUST
- author
- average
- back
- Backend
- BE
- been
- benefits
- Better
- between
- blockchain
- blockchain platform
- Blog
- Breaking
- breaking news
- build
- built
- businesses
- but
- by
- call
- CAN
- capabilities
- capture
- Capturing
- carbon
- card
- Cards
- carefully
- CAT
- CDC
- chain
- chains
- challenge
- challenges
- change
- check
- class
- clean energy
- clear
- clearer
- Climate
- Climate change
- code
- cohesive
- collect
- color
- comes
- Communication
- Companies
- company
- compete
- complete
- complex
- compliance
- comply
- comprehensive
- computing
- Concerns
- confidence
- Connectivity
- consistent
- consortium
- consumer
- Consumers
- Container
- continue
- Corporate
- Corporations
- cover
- covering
- create
- created
- Creating
- critical
- CSS
- Current
- custom
- Customers
- data
- Data Analytics
- data management
- data processing
- data sharing
- Date
- day
- dedication
- deep
- Default
- define
- definitions
- delightful
- Dell
- description
- detailed
- develop
- developing
- disaster
- Disclose
- disclosure
- Disclosures
- distribution
- do
- doing
- domains
- dynamic
- e
- E. coli
- eagerly
- easier
- easy
- educate
- effects
- efficiently
- effortless
- efforts
- Electric
- elements
- Emissions
- employees
- enabling
- energy
- enjoy
- ensures
- ensuring
- Enter
- entered
- enterprises
- Entire
- Environment
- environmental
- Era
- ESG
- establishes
- estimates
- Ether (ETH)
- EU
- European
- european union
- European Union (EU)
- Even
- events
- Every
- exchange
- Exit
- expect
- expensive
- experience
- Exploring
- Face
- faced
- facing
- Fall
- far-reaching
- farm
- faster
- fda
- First
- first time
- follow
- fonts
- food
- foods
- For
- For Consumers
- forge
- fork
- formed
- Forward
- Founded
- Framework
- fresh
- from
- fsma
- game-changer
- generator
- get
- Global
- goal
- Goals
- going
- governance
- Grid
- Group
- Grow
- Harnessing
- Have
- having
- height
- heights
- help
- helping
- hold
- However
- HTML
- HTTPS
- IBM
- ICO
- ICON
- identify
- if
- illness
- image
- Impact
- implement
- improve
- improvement
- in
- Inaugural
- includes
- Including
- Increase
- index
- industry
- Infections
- information
- ingredients
- Intelligence
- interconnected
- into
- investigation
- Investigations
- issues
- IT
- ITS
- joint
- journey
- jpg
- July
- keeping
- Key
- knowledge
- Label
- landmark
- large
- largest
- less
- like
- linked
- List
- local
- locale
- locations
- Loyalty
- made
- maintain
- major
- make
- MAKES
- Making
- managed
- management
- manner
- map
- Market
- maturity
- Maturity Model
- max-width
- measure
- Meet
- Meets
- membership
- mentioned
- methods
- might
- min
- minutes
- Mobile
- model
- modernization
- Moments
- Monitor
- Month
- more
- most
- movement
- Natural
- Navigation
- Need
- needed
- needs
- network
- New
- New technologies
- news
- nothing
- notification
- number
- object
- of
- offer
- offering
- offline
- often
- on
- Onboarding
- ONE
- only
- operating
- opportunities
- optimized
- or
- organization
- organizational
- our
- outbreak
- owl
- own
- Pack
- page
- Panic
- Paramount
- part
- partnering
- partners
- Partnership
- path
- PHP
- picture
- plan
- platform
- plato
- Plato Data Intelligence
- PlatoData
- Play
- plugin
- poised
- policies
- policy
- position
- Post
- potential
- power
- practices
- prepared
- prevent
- Problem
- process
- processing
- produce
- Products
- Progress
- project
- provide
- providing
- published
- quickly
- Reading
- receive
- record
- reduce
- reduction
- Regulation
- regulations
- regulatory
- remains
- remote
- remove
- report
- Reporting
- required
- Requirements
- requires
- response
- responsibilities
- responsible
- responsible computing
- responsive
- result
- Results
- rewriting
- roadmap
- robots
- Rule
- Run
- safer
- Safety
- scalable
- scene
- Screen
- script
- scripts
- seamless
- Section
- secure
- seo
- September
- set
- several
- Share
- sharing
- Signal
- significant
- similar
- site
- SIX
- small
- smarter
- smartphone
- So
- Social
- Software
- solution
- Solutions
- Sound
- Sponsored
- standards
- Star
- start
- Step
- storage
- store
- strawberry
- suite
- suppliers
- supply
- supply chain
- Supply chains
- support
- Sustainability
- SWIFT
- Systems
- table
- Take
- tangible
- team
- tech-enabled
- Technologies
- Technology
- than
- that
- The
- the joint
- the world
- their
- Them
- theme
- There.
- These
- they
- this
- those
- time
- Title
- to
- today
- top
- trace
- Traceability
- track
- Tracking
- Trading
- transformative
- Transparency
- truly
- Trust
- trusted
- trying
- Tsunami
- type
- Ultimately
- under
- understand
- understanding
- union
- upcoming
- Update
- URL
- used
- utility
- very
- viable
- visibility
- W
- Waste
- we
- week
- when
- which
- while
- whole
- will
- winner
- with
- without
- Won
- WordPress
- Work
- world
- written
- yielded
- you
- Your
- zephyrnet