In today's business landscape, organizations face a myriad of challenges related to financial integrity, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency. Among the critical areas that require careful attention is the control of purchasing activities. Effective purchases controls ensure compliance with regulations, mitigate risks and promote operational efficiency.
To ensure the effectiveness of purchases controls, organizations must document and assess their control mechanisms through a comprehensive test of control. This blog explores the significance of documenting the test of control for purchases controls and how automation tools can streamline this process, enhancing accuracy, efficiency, and decision-making.
Join us as we delve into the importance of documenting a test of control for purchases controls and discover how leveraging advanced technologies can optimize control environments and drive organizational success.
Understanding Purchases Controls
Purchases controls are a vital component of an organization's internal control system. They are designed to ensure that purchases made by the organization are authorized, appropriate, and comply with relevant policies and regulations. Purchasing controls help prevent fraudulent activities, minimize errors, and ensure that the organization obtains goods and services at reasonable prices.
When it comes to understanding purchase controls, it is essential to have a clear understanding of their purpose and objectives. The main objectives of purchases controls include:
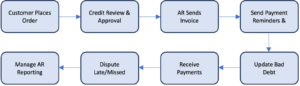
- Authorization and Approval: Purchases controls ensure that all purchases are properly authorized by authorized personnel within the organization. This helps prevent unauthorized purchases and ensures that purchases are in line with the organization's budget and objectives.
- Vendor Selection and Evaluation: Purchases controls involve processes for selecting and evaluating vendors to ensure that goods and services are procured from reputable and reliable sources. This helps minimize the risk of purchasing from fraudulent or unqualified suppliers.
- Purchase Order Processing: Purchases controls cover the processing of purchase orders, including their accuracy, completeness, and timely execution. This ensures that purchase orders are generated correctly, approved, and processed efficiently.
- Receipt and Inspection of Goods: Purchases controls include procedures for receiving and inspecting goods to ensure that they meet the organization's specifications and quality standards. This helps prevent the acceptance of defective or substandard goods, protecting the organization from financial losses.
- Invoice Verification and Payment: Purchases controls involve verifying and approving vendor invoices to ensure that they are accurate and appropriate. This helps prevent overpayment or payment for goods or services that were not received.
By implementing effective purchase controls, organizations can mitigate risks such as fraud, error, and non-compliance. Purchases controls provide a structure and framework to ensure that the purchasing process is transparent, accountable, and efficient.
Understanding purchase controls requires a comprehensive understanding of the specific controls in place within an organization, as these can vary based on industry, organisation size, and regulatory requirements. Evaluating the effectiveness of purchase controls requires thorough documentation and testing to ensure that they are designed appropriately and operating effectively.
Overall, understanding purchase controls is crucial for organizations to maintain financial integrity, minimize risks, and ensure compliance with applicable laws and regulations. By having a strong understanding of purchase controls, organizations can strengthen their internal controls and promote transparency and accountability in the purchasing process.

What are Test of Control Procedures?
A test of control procedures is an audit procedure performed by auditors to evaluate the effectiveness of internal controls within a company. It is conducted after the initial planning and understanding phase of an audit assignment to obtain audit evidence about the controls' effectiveness.
The main purpose of a test of control procedure is to assess whether the controls designed by a client entity are operating effectively in preventing or detecting material misstatements]. By conducting these tests, auditors can determine whether they can rely on the client's system of controls as part of their auditing activities.
The test of control procedures aims to find evidence of how well the controls operate to prevent or detect risks of material misstatements. It primarily supports the assessment of control risk, which is the risk of material misstatement remaining undetected by internal controls.
The specific procedures used in a test of control can vary depending on the nature of the controls being evaluated. They may include inquiry, observation, inspection of documents, and reperformance of control procedures. The selection of the testing methods depends on the control objectives, risks, and the auditor's judgment.
During the test of control procedures, auditors document their test plan and objectives, perform the tests, and accurately record the results. The documentation includes details of the procedures performed, the sample tested, and any exceptions or deviations identified.
By conducting these tests, auditors obtain assurance about the effectiveness of the controls in place and provide insights into the reliability and accuracy of the organization's financial statements.
How can a Test of Control Procedure Evaluate Purchase Controls?
A test of control procedure is crucial for evaluating the effectiveness of purchases controls within an organization. Purchases controls are designed to ensure that all purchases made by the organization are authorized, appropriate, and comply with relevant policies and regulations. Conducting a test of control procedures helps auditors evaluate whether these controls are effectively designed and operating as intended.
By conducting the test, auditors gather evidence to evaluate whether purchases controls are effective in preventing or detecting the risks of material misstatements that can arise from purchasing activities. The testing procedures selected are based on the specific control objectives and the identified risks associated with the purchase controls. By evaluating whether the control objectives are met, auditors can obtain reasonable assurance about the effectiveness of the purchasing controls.
For example, if an organization has a control in place to require authorization of all purchases of more than $5,000, the auditor would test a sample of purchase orders to confirm that they had received appropriate authorization. If the auditor finds that a significant number of purchase orders exceeding $5,000 were not authorized, the auditor might conclude that the control has not been operating effectively. This would indicate that there is a risk of material misstatement associated with purchases within the organization.
The auditor would then recommend that the organization reassesses the design or application of the control to mitigate the identified risks.
Designing a Test of Control for Purchases Controls
Documenting a test of control procedure for purchases controls is an important step in the auditing process. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to document a test of control for purchases controls:
- Understand the Purchases Controls: Begin by reviewing the organization's policies, procedures, and control documentation related to purchases controls. Gain a thorough understanding of the control objectives, key controls, and inherent risks associated with purchases.
- Define the Testing Objectives: Clearly define the objectives of the test of control procedure for purchases controls. Determine the specific control procedures that will be tested and the criteria against which the controls will be evaluated.
- Develop a Test Plan: Create a test plan that outlines the scope, approach, and methodology of the test of control procedure. This plan should detail the sample size, sampling method, and the specific control procedures that will be performed.
- Document the Testing Procedures: Clearly document the testing procedures that will be executed during the test of control. This includes the steps to be followed, the information to be gathered, and any evidence to be obtained. Specify the control activities to be observed, the documents to be reviewed, and any inquiries that will be made.
- Identify the Sample: Determine the sample size and selection criteria for the test. Select a representative sample of purchase transactions or control activities to be tested. Consider factors such as risk, materiality, and statistical sampling techniques, if applicable.
- Perform the Control Testing: Execute the testing procedures as documented in the test plan. Follow the step-by-step instructions for each control activity or transaction selected in the sample. Record the results accurately, documenting any exceptions or deviations encountered.
- Record and Analyze the Findings: Document the test results and analyze the findings. Clearly record any observed control weaknesses, deviations from controls, or instances of non-compliance with policies and procedures. Analyze the impact and significance of these findings on the effectiveness of the purchases controls.
- Assess Control Effectiveness: Evaluate the effectiveness of the purchases controls based on the test findings. Determine whether the control objectives are being met, and the level of reliance that can be placed on the controls. Consider the potential impact on the risk of material misstatement and the need for additional substantive testing.
- Document the Test Conclusion: Summarize the findings and conclusions of the test of control procedure for purchases controls. Clearly communicate any control deficiencies, recommendations, or areas for improvement. Ensure that the documentation is comprehensive and provides a clear audit trail of the work performed.
- Review and Finalize the Documentation: Review the documented test of control procedure, ensuring completeness and accuracy. Make any necessary revisions or additions to improve clarity or address feedback from stakeholders. Finalize the documentation for inclusion in the audit workpapers or report.
Review and Validation
In today's rapidly evolving business landscape, maintaining effective internal controls is crucial for organizations to mitigate risks and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements. As such, documenting tests of control becomes paramount in assessing the effectiveness of these controls.
However, it is equally important to review and validate this documentation periodically to ensure accuracy and reliability.
Reviewing the test of control documentation allows auditors or management teams to identify any gaps or inconsistencies that could potentially undermine the overall effectiveness of internal controls. It enables stakeholders to verify if the documented procedures align with industry standards and regulatory guidelines. Validating this documentation helps in ensuring that tests are conducted accurately without any bias or manipulation. By scrutinizing each step outlined in the document, auditors can assess whether appropriate evidence has been gathered to support assertions made about control activities effectively.
Tips on how to ensure the accuracy and reliability of test of control documentation:
1. Standardize Documentation: Establish a standardized template for documenting tests across different processes within an organization. This ensures consistency and ease when reviewing various control activities.
2. Conduct Periodic Reviews: Set up regular intervals (quarterly or annually) for thoroughly reviewing all test documents against actual practice followed by detailed feedback sessions with relevant personnel involved.
3. Implement Peer Review Mechanism: Encourage cross-functional collaboration where peers review each other's work as a quality assurance measure before final submission.
How can Nanonets Help?
- Data Extraction: Nanonets can extract information from different documents such as purchase orders, invoices, receipts, and supplier contracts. It can identify key data points such as purchase order numbers, invoice numbers, supplier names, purchase quantities, prices, and other relevant details.
- Data Organization: Once the data is extracted, Nanonets can help organize it in a structured format. It can categorize the data based on different attributes, such as supplier information, purchase order details, or invoice details. This makes it easier to analyze and review the data for control testing purposes.
- Error Detection: Nanonets can help identify potential errors or inconsistencies in the data. For example, it can flag instances where the purchase order amount differs from the invoiced amount or where the supplier information does not match the approved vendor list. These error detection capabilities assist in identifying control weaknesses and anomalies.
- Data Validation: Nanonets can compare the extracted data against predefined control criteria. For instance, it can verify if purchase orders are properly authorized, if invoice approvals match the appropriate levels, or if discounts and rebates are correctly applied. By automating the validation process, Nanonets helps ensure that the controls are functioning as intended.
- Reporting and Analytics: Nanonets can generate comprehensive reports and analytics based on the extracted data. It can provide insights into the effectiveness of the control environment, identify trends or patterns in purchasing activities, and highlight potential areas for improvement or further investigation.
By leveraging Nanonets' capabilities, the process of documenting a test of control for purchases controls becomes more efficient and accurate. It reduces manual effort, increases consistency, and provides a structured approach to analyzing and validating data, ultimately improving the overall effectiveness of the control testing process.
Looking to automate your test of controls for Purchase Orders? Book a 30-min live demo to see how Nanonets can help your team implement end-to-end AP automation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, documenting a test of control for purchases controls is an essential process for organizations. It serves multiple purposes, including compliance, risk mitigation, operational efficiency, assurance, and continuous improvement. By documenting the test of control, organizations can demonstrate their adherence to regulatory requirements and internal policies, identify control weaknesses, mitigate risks, and optimize their purchasing activities.
Through the use of automation tools like Nanonets, the process of documenting a test of control becomes more efficient and accurate. Nanonets can extract relevant data from various sources, organize it in a structured format, detect errors and inconsistencies, validate the data against control criteria, and generate comprehensive reports and analytics. This technology reduces manual effort, increases consistency, and provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of control environments.
By documenting the test of control for purchases controls, organizations not only ensure compliance but also enhance operational efficiency, gain internal and external assurance, and drive continuous improvement. It becomes a foundation for effective governance, transparent reporting, and building trust among stakeholders.
In an era where businesses face increasing scrutiny and the need for efficient processes, documenting the test of control for purchases controls becomes a strategic imperative. It empowers organizations to maintain robust control environments, effectively manage risks, and optimize their purchasing practices. Ultimately, it enables organizations to safeguard their financial integrity, foster trust, and drive sustainable growth.
- SEO Powered Content & PR Distribution. Get Amplified Today.
- PlatoData.Network Vertical Generative Ai. Empower Yourself. Access Here.
- PlatoAiStream. Web3 Intelligence. Knowledge Amplified. Access Here.
- PlatoESG. Automotive / EVs, Carbon, CleanTech, Energy, Environment, Solar, Waste Management. Access Here.
- BlockOffsets. Modernizing Environmental Offset Ownership. Access Here.
- Source: https://nanonets.com/blog/test-of-control-purchases-controls/
- :has
- :is
- :not
- :where
- $UP
- 000
- a
- About
- acceptance
- accountability
- accountable
- accuracy
- accurate
- accurately
- across
- activities
- activity
- actual
- Additional
- additions
- address
- advanced
- After
- against
- aims
- align
- All
- allows
- also
- among
- amount
- an
- analytics
- analyze
- analyzing
- and
- Annually
- any
- applicable
- Application
- applied
- approach
- appropriate
- appropriately
- approval
- approvals
- approved
- ARE
- areas
- arise
- AS
- assess
- Assessing
- assessment
- assist
- associated
- assurance
- At
- attention
- attributes
- audit
- auditing
- auditors
- authorization
- authorized
- automate
- automating
- Automation
- based
- BE
- becomes
- been
- before
- being
- bias
- Blog
- book
- budget
- Building
- business
- businesses
- but
- by
- CAN
- capabilities
- careful
- challenges
- clarity
- clear
- clearly
- client
- collaboration
- COM
- comes
- communicate
- company
- compare
- compliance
- comply
- component
- comprehensive
- conclude
- conclusion
- Conduct
- conducted
- conducting
- Confirm
- Consider
- continuous
- contracts
- control
- controls
- could
- cover
- create
- criteria
- critical
- crucial
- data
- data points
- Decision Making
- Demo
- demonstrate
- Depending
- depends
- Design
- designed
- detail
- detailed
- details
- Detection
- Determine
- different
- discounts
- discover
- document
- documentation
- documented
- documenting
- documents
- does
- drive
- during
- each
- ease
- easier
- Effective
- effectively
- effectiveness
- efficiency
- efficient
- efficiently
- effort
- empowers
- enables
- encourage
- enhance
- enhancing
- ensure
- ensures
- ensuring
- entity
- Environment
- environments
- equally
- Era
- error
- Errors
- essential
- establish
- evaluate
- evaluated
- evaluating
- evaluation
- evidence
- evolving
- example
- executed
- execution
- explores
- external
- extract
- extraction
- Face
- factors
- feedback
- final
- finalize
- financial
- Find
- findings
- finds
- follow
- followed
- For
- format
- Foster
- Foundation
- Framework
- fraud
- fraudulent
- from
- functioning
- further
- Gain
- gaps
- gather
- gathered
- generate
- generated
- goods
- governance
- Growth
- guide
- guidelines
- had
- Have
- having
- help
- helps
- here
- Highlight
- How
- How To
- HTTPS
- identified
- identify
- identifying
- if
- Impact
- imperative
- implement
- implementing
- importance
- important
- improve
- improvement
- improving
- in
- include
- includes
- Including
- inclusion
- Increases
- increasing
- indicate
- industry
- industry standards
- information
- inherent
- initial
- Inquiries
- inquiry
- insights
- instance
- instructions
- integrity
- intended
- internal
- into
- investigation
- involve
- involved
- IT
- Key
- landscape
- Laws
- Laws and regulations
- Level
- levels
- leveraging
- like
- Line
- List
- live
- losses
- made
- Main
- maintain
- maintaining
- make
- MAKES
- manage
- management
- Manipulation
- manual
- Match
- material
- May..
- measure
- mechanism
- mechanisms
- Meet
- met
- method
- Methodology
- methods
- might
- Mitigate
- mitigation
- more
- more efficient
- multiple
- must
- names
- Nature
- necessary
- Need
- number
- numbers
- objectives
- observed
- obtain
- obtained
- obtains
- of
- on
- only
- operate
- operating
- operational
- Optimize
- or
- order
- orders
- organisation
- organization
- organizational
- organizations
- Other
- outlined
- outlines
- overall
- Paramount
- part
- patterns
- payment
- peer
- perform
- performed
- periodic
- Personnel
- phase
- Place
- plan
- planning
- plato
- Plato Data Intelligence
- PlatoData
- points
- policies
- potential
- potentially
- practice
- practices
- prevent
- preventing
- Prices
- primarily
- procedure
- procedures
- process
- processed
- processes
- processing
- promote
- properly
- protecting
- provide
- provides
- purchase
- purchase order
- purchases
- purchasing
- purpose
- purposes
- quality
- rapidly
- reasonable
- receipts
- received
- receiving
- recommend
- recommendations
- record
- reduces
- regular
- regulations
- regulatory
- Regulatory Compliance
- related
- relevant
- reliability
- reliable
- reliable sources
- reliance
- rely
- remaining
- report
- Reporting
- Reports
- representative
- reputable
- require
- Requirements
- requires
- Results
- review
- reviewed
- reviewing
- Reviews
- revisions
- Risk
- Risk Mitigation
- risks
- robust
- s
- scope
- scrutiny
- see
- selected
- selecting
- selection
- serves
- Services
- sessions
- should
- significance
- significant
- Size
- Sources
- specific
- specifications
- stakeholders
- standards
- statements
- statistical
- Step
- Steps
- Strategic
- streamline
- Strengthen
- strong
- structure
- structured
- submission
- success
- such
- suppliers
- support
- Supports
- sustainable
- Sustainable Growth
- system
- team
- teams
- techniques
- Technologies
- Technology
- template
- test
- tested
- Testing
- tests
- than
- that
- The
- the information
- their
- then
- There.
- These
- they
- this
- thoroughly
- Through
- to
- today
- tools
- transaction
- Transactions
- Transparency
- transparent
- Trends
- Trust
- Ultimately
- Undermine
- understanding
- unqualified
- Unsplash
- us
- use
- used
- VALIDATE
- validating
- validation
- Valuable
- various
- vendor
- vendors
- Verification
- verify
- verifying
- vital
- we
- WELL
- were
- when
- whether
- which
- will
- with
- within
- without
- Work
- would
- Your
- zephyrnet