- The Euro appreciates further as the Dollar falls ahead of the ECB decision.
- The Dollar remains on the defensive after the Fed’s dovish pivot.
- Investors will be looking for dovish hints by the ECB, which would hurt the pair.
The Euro (EUR) keeps a positive tone on Thursday, extending gains beyond the 1.0900 mark, boosted by US Dollar’s (USD) weakness after the Federal Reserve (Fed) signaled the end of rate hikes on Wednesday.
The Fed surprised investors with an unexpectedly dovish tone. The bank kept interest rates unchanged, as expected, but Fed Chair Jerome Powell suggested that interest rates have peaked with 17 of the 19 policymakers projecting rate cuts in 2024.
Risk appetite surged after the decision and the US Dollar was sold across the board. The Euro rallied more than 100 pips higher to fresh two-week highs right above 1.0900, where the pair has steadied ahead of the European Central Bank’s (ECB) decision due later on Thursday.
The ECB is expected to leave its main refinancing operations rate on hold at 4.5% and keep a hawkish stance, leaving the door open for further rate hikes if inflation pressures remain high. Investors, however, will be looking for dovish hints as the weaker economic outlook and declining inflation are posing a challenge for ECB hawks.
Daily digest market movers: The ECB might limit Euro rally
- The Euro maintains its bullish tone, with the US Dollar weighed by a dovish Fed.
- US Treasury yields plunged. The benchmark 10-year yield has dropped below 4.0% for the first time since July, adding negative pressure on the US Dollar.
- The Federal Reserve flagged the end of rate hikes, and interest rate projections foresee 75 basis points in cuts next year.
- Futures markets are now pricing a 75% chance of a rate cut in March from about 40% before the Fed decision.
- The ECB is expected to leave its key rate unchanged at 4.5%, leaving options open for further hikes.
- The market will be looking for signals of a pivot that might send the Euro lower.
Technical Analysis: Euro consolidates around 1.0900 ahead of ECB
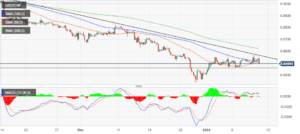
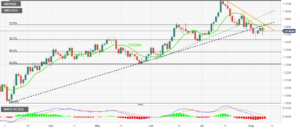
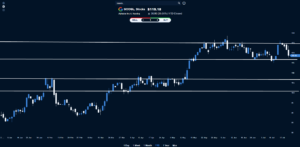
EUR/USD maintains a near-term bullish tone after Wednesday’s sharp rally as the US Dollar licks its wounds. The US Dollar Index (DXY) seems unable to put a significant distance from the 102.50 support area.
A look at the 4-hour charts shows the pair standing comfortably above the main SMAs, with oscillators at overbought levels, and a resistance area at 1.0915 holding bulls ahead of the outcome of the ECB’s meeting.
If the bank manages to convince investors that rate cuts are off the table, we might see a further rally towards 1.0960, which closes the path to November’s peak at 1.1010.
Euro price today
The table below shows the percentage change of Euro (EUR) against listed major currencies today. Euro was the strongest against the US Dollar.
| USD | EUR | GBP | CAD | AUD | JPY | NZD | CHF | |
| USD | -0.43% | -0.36% | -0.46% | -0.76% | -1.02% | -0.41% | -0.30% | |
| EUR | 0.44% | 0.07% | -0.02% | -0.34% | -0.59% | 0.01% | 0.13% | |
| GBP | 0.36% | -0.08% | -0.09% | -0.38% | -0.66% | -0.04% | 0.04% | |
| CAD | 0.45% | 0.01% | 0.08% | -0.33% | -0.60% | 0.01% | 0.14% | |
| AUD | 0.74% | 0.31% | 0.36% | 0.29% | -0.29% | 0.30% | 0.43% | |
| JPY | 1.02% | 0.57% | 0.66% | 0.55% | 0.25% | 0.64% | 0.68% | |
| NZD | 0.40% | -0.06% | 0.01% | -0.08% | -0.39% | -0.65% | 0.07% | |
| CHF | 0.30% | -0.12% | -0.04% | -0.12% | -0.43% | -0.68% | -0.08% |
The heat map shows percentage changes of major currencies against each other. The base currency is picked from the left column, while the quote currency is picked from the top row. For example, if you pick the Euro from the left column and move along the horizontal line to the Japanese Yen, the percentage change displayed in the box will represent EUR (base)/JPY (quote).
ECB FAQs
The European Central Bank (ECB) in Frankfurt, Germany, is the reserve bank for the Eurozone. The ECB sets interest rates and manages monetary policy for the region.
The ECB primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which means keeping inflation at around 2%. Its primary tool for achieving this is by raising or lowering interest rates. Relatively high interest rates will usually result in a stronger Euro and vice versa.
The ECB Governing Council makes monetary policy decisions at meetings held eight times a year. Decisions are made by heads of the Eurozone national banks and six permanent members, including the President of the ECB, Christine Lagarde.
In extreme situations, the European Central Bank can enact a policy tool called Quantitative Easing. QE is the process by which the ECB prints Euros and uses them to buy assets – usually government or corporate bonds – from banks and other financial institutions. QE usually results in a weaker Euro.
QE is a last resort when simply lowering interest rates is unlikely to achieve the objective of price stability. The ECB used it during the Great Financial Crisis in 2009-11, in 2015 when inflation remained stubbornly low, as well as during the covid pandemic.
Quantitative tightening (QT) is the reverse of QE. It is undertaken after QE when an economic recovery is underway and inflation starts rising. Whilst in QE the European Central Bank (ECB) purchases government and corporate bonds from financial institutions to provide them with liquidity, in QT the ECB stops buying more bonds, and stops reinvesting the principal maturing on the bonds it already holds. It is usually positive (or bullish) for the Euro.
- SEO Powered Content & PR Distribution. Get Amplified Today.
- PlatoData.Network Vertical Generative Ai. Empower Yourself. Access Here.
- PlatoAiStream. Web3 Intelligence. Knowledge Amplified. Access Here.
- PlatoESG. Carbon, CleanTech, Energy, Environment, Solar, Waste Management. Access Here.
- PlatoHealth. Biotech and Clinical Trials Intelligence. Access Here.
- Source: https://www.fxstreet.com/news/euro-remains-strong-favoured-by-us-dollar-weakness-with-ecb-decision-on-tap-202312141046
- :has
- :is
- :where
- 1
- 100
- 102
- 17
- 19
- 2%
- 2015
- 2024
- 32
- 33
- 35%
- 41
- 50
- 75
- 75 basis points
- a
- About
- above
- Achieve
- achieving
- across
- adding
- After
- against
- ahead
- along
- already
- an
- analysis
- and
- Animate
- ARE
- AREA
- around
- AS
- Assets
- At
- Bank
- Banks
- base
- basis
- BE
- before
- below
- Benchmark
- board
- Bonds
- Boosted
- Box
- Bullish
- Bulls
- but
- buy
- Buying
- by
- called
- CAN
- central
- Central Bank
- Chair
- challenge
- Chance
- change
- Changes
- Charts
- Christine
- CHRISTINE LAGARDE
- Closes
- Column
- Consolidates
- content
- convince
- Corporate
- Council
- Covid
- crisis
- currencies
- Currency
- Cut
- cuts
- decision
- decisions
- Declining
- defensive
- Digest
- displayed
- distance
- Dollar
- Door
- Dovish
- dropped
- due
- during
- Dxy
- each
- easing
- ECB
- Economic
- economic recovery
- end
- ends
- EUR
- Euro
- European
- European Central Bank
- Euros
- Eurozone
- example
- expanded
- expected
- extreme
- FAQ
- Fed
- Fed Chair
- Federal
- federal reserve
- financial
- financial crisis
- Financial institutions
- First
- first time
- flagged
- For
- foresee
- frankfurt
- fresh
- from
- further
- Gains
- Germany
- governing
- Government
- great
- Have
- Hawkish
- heads
- Held
- High
- higher
- Highs
- Hikes
- hints
- hold
- holding
- holds
- Horizontal
- However
- HTTPS
- Hurt
- if
- in
- Including
- inflation
- institutions
- interest
- INTEREST RATE
- Interest Rates
- Investors
- IT
- ITS
- Japanese
- Japanese Yen
- jpg
- July
- Keep
- keeping
- kept
- Key
- Lagarde
- Last
- later
- Leave
- leaving
- left
- levels
- LIMIT
- Line
- Liquidity
- Listed
- Look
- looking
- Low
- lower
- lowering
- made
- Main
- maintain
- maintains
- major
- MAKES
- manages
- mandate
- map
- March
- mark
- Market
- Markets
- means
- meeting
- meetings
- Members
- might
- module
- Monetary
- Monetary Policy
- more
- move
- Movers
- National
- National Banks
- negative
- next
- now
- objective
- of
- off
- on
- open
- Operations
- Options
- or
- Other
- Outcome
- pair
- pandemic
- path
- Peak
- percentage
- permanent
- pick
- picked
- Pivot
- plato
- Plato Data Intelligence
- PlatoData
- points
- policy
- policymakers
- positive
- president
- pressure
- price
- pricing
- primary
- Principal
- prints
- process
- projections
- provide
- purchases
- put
- QE
- QT
- quantitative
- Quantitative Easing
- quote
- raising
- rally
- Rate
- rate hikes
- Rates
- recovery
- region
- relatively
- remain
- remained
- remains
- represent
- Reserve
- reserve bank
- Resistance
- Resort
- result
- Results
- reverse
- right
- rising
- ROW
- see
- seems
- send
- Sets
- sharp
- Shows
- signals
- significant
- simply
- since
- situations
- SIX
- SMAs
- sold
- Stability
- stance
- standing
- starts
- Stops
- stronger
- strongest
- support
- Surged
- surprised
- table
- than
- that
- The
- the Fed
- Them
- this
- thursday
- tightening
- time
- times
- to
- today
- TONE
- tool
- top
- towards
- treasury
- Treasury yields
- unable
- Underway
- unlikely
- us
- US Dollar
- USD
- used
- uses
- usually
- vice
- was
- we
- weaker
- weakness
- Wednesday
- WELL
- when
- which
- while
- Whilst
- will
- with
- would
- wounds
- year
- Yen
- Yield
- yields
- you
- zephyrnet