
Hybrid cloud has become the dominant approach for enterprise cloud strategies, but it comes with complexity and concerns over integration, security and skills. To address these concerns the industry is embracing container runtime environments to abstract away infrastructure. Red Hat OpenShift Container Platform (RH OCP) has emerged as a leading solution for supporting the application development lifecycle, provisioning and managing container images and workloads into a platform for containerized applications and ecosystem. RH OCP provides a common deployment, control and management environment for workloads across a diverse set of infrastructures that underpin a hybrid cloud.
In brief, Red Hat OpenShift is the leading hybrid cloud application platform built on open-source innovation designed to build, deploy and run applications at massive scale, wherever you want.
Hybrid cloud is also forcing a significant rethinking of how to secure and protect data and assets. As such, the industry continues to move away from traditional moat-and-castle strategies towards zero trust-based architectures that micro-segment environments to minimize attack surfaces.
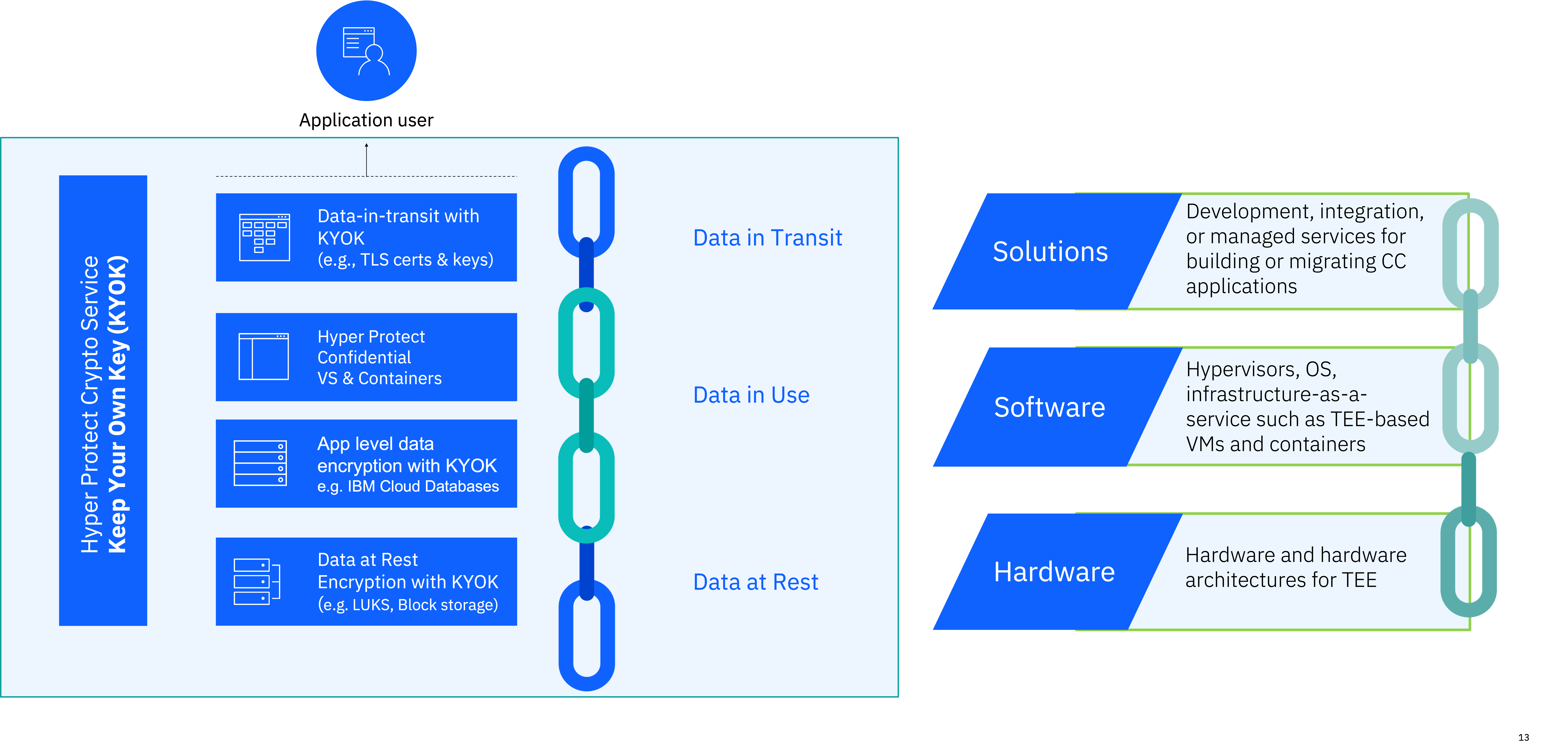
Confidential computing is an emerging foundational capability that enables the protection of data-in-use. The protection of data-at-rest and data-in-motion has been a standard practice in the industry for decades; however, with advent of hybrid and decentralized management of infrastructure it has now become imperative to equally protect data-in-use. More specifically, confidential computing uses hardware-based security-rich enclaves to allow a tenant to host workloads and data on untrusted infrastructure while ensuring that their workloads and data cannot be read or modified by anyone with privileged access to that infrastructure. This is typically referred to as technical assurance that can summarily be described as a provider or person cannot access your data. One can contrast technical assurance to the more commonly used operational assurance that provides the lesser guarantee that a provider or person only promises they will not access your data, even though they technically could. As compromised credential threats as well as insider threats have become a dominant cause of data-security incidents, technical assurance has become a priority for securing sensitive and regulated workloads whether the latter are running in traditional on-premises or in a public cloud data centers.
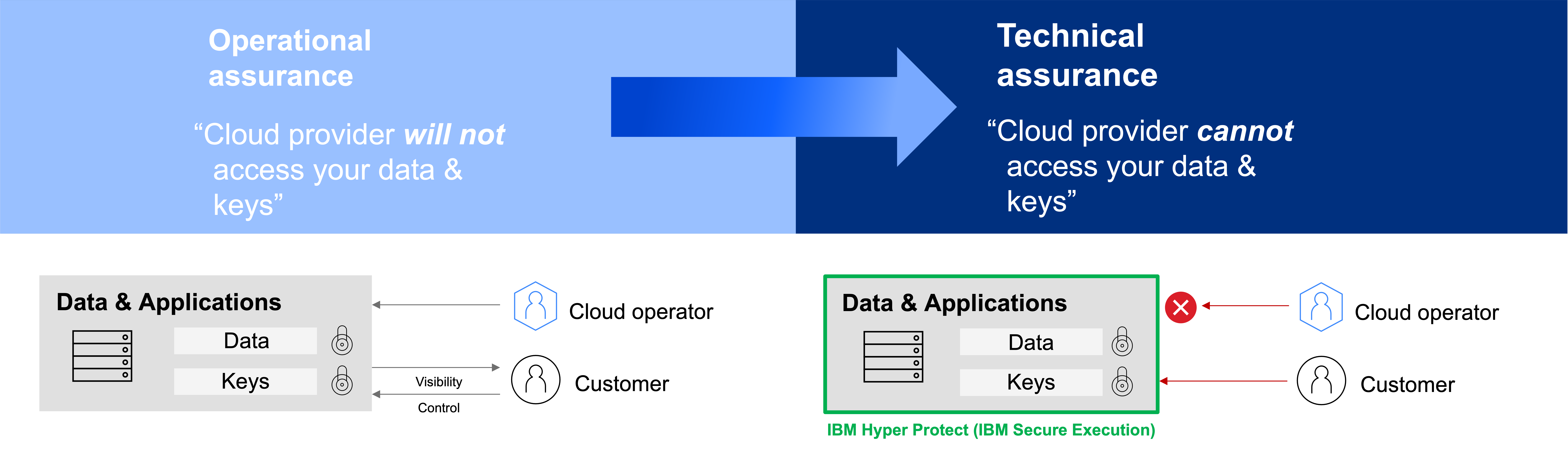
IBM and RedHat have recognized the requirement for technical assurance in a hybrid cloud platform. They have worked as part of the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) Confidential Containers open-source community to address this concern and are continuously working together to make confidential container technology available. The latter marries security-rich enclave technology such as IBM Secure Execution for Linux with Kubernetes-based OpenShift to allow for the deployment of containers into secured pods, providing all the advantages of a ubiquitous RH OCP operational experience while also designed to protect a tenant’s containers from privileged user access. Confidential containers go beyond prior efforts at solving this problem by isolating the container not only from infrastructure administrator but also from the Kubernetes administrator. This provides the tenant with the best of both worlds where they can fully leverage the abstraction of a managed OpenShift to develop-once-deploy-anywhere while being able to deploy data and workloads with technical assurance into a fully private and isolated enclave even if the latter is hosted and managed on third-party infrastructure.
IBM is further adding additional zero trust principles designed to increase security and ease of use with the IBM Hyper Protect Platform.

This unique capability is designed for workloads that have strong data sovereignty, regulatory or data privacy requirements.
As such, confidential containers play a key role across industries engineered to secure data and foster innovation. Some example use cases to highlight:
Confidential AI: leverage trustworthy AI and while ensuring the integrity of the models and confidentiality of data
Organizations leveraging AI models often encounter challenges related to the privacy and security of the data used for training and the integrity of the AI models themselves. Protecting the confidentiality of proprietary algorithms and sensitive training data is crucial. In many cases multiple party must collaborate and share sensitive data or models between each other to gain valuable AI-based insights. On the other hand, the valuable data needed to gain those insights has to stay confidential and is only allowed to be shared with certain parties or no third parties at all.
So, is there a way to gain insights of valuable data through AI without the need to expose the data set or the AI model (LLM, ML, DL) to another party?
Red Hat OpenShift, empowered by Confidential Containers based on IBM Secure Execution, provides a confidential AI platform. This safeguards both the AI model and the training data, allowing organizations to deploy machine learning models without compromising intellectual property or exposing sensitive information. By mitigating attack vectors through security-rich containers, Confidential Containers ensure the integrity of AI models, enhancing trust in AI applications.
Healthcare: enabling health tech while keeping patient data private
In the healthcare industry, the protection of sensitive patient data is paramount. With the increasing adoption of digital health records and collaborative research initiatives, there’s a growing concern about securing patient information from unauthorized access and potential breaches.
Red Hat OpenShift, leveraging Confidential Containers, establishes a security-rich enclave for healthcare applications. So that records and sensitive medical data are encrypted and processed securely, protecting against data leaks and unauthorized access. By safeguarding both the code and data, healthcare organizations are able to confidently embrace digital transformation while keeping their patients’ privacy by adopting data privacy-enhancing technologies, such as Confidential Compute.
This is designed to enable multiple use cases in the healthcare industry, one being secure multi-party collaboration between different institutions as shown in the following example.

Financial services: innovate customer experience while keeping sensitive information secure and stay compliant
Financial institutions face constant threats to their critical data and financial transactions. The industry demands a secure infrastructure that can protect sensitive financial information, prevent fraud and ensure regulatory compliance.
Red Hat OpenShift with confidential containers provides a fortified environment for financial services applications. This ensures that financial data and transactions are processed within security-rich enclaves, shielding them from external threats. By safeguarding code and data integrity, confidential containers on OpenShift helps financial institutions meet stringent regulatory requirements and enhances the overall security posture of their digital infrastructure.
Enhancing digital rights management and intellectual property protection through confidential compute-protected tokenization
In today’s digital landscape, the risk associated with stolen tokens or unauthorized signing of corresponding contracts, such as intellectual property and digital rights tokens, poses significant challenges. The potential financial losses and threats to the integrity of digital ecosystems demand a robust solution that goes beyond conventional security measures.
Confidential compute offers a practical solution to the risks associated with stolen tokens by incorporating confidential compute technology into the tokenization process, which is designed to establish end-to-end security. This approach ensures that sensitive operations occur in a secure and isolated environment, safeguarding the confidentiality and integrity of digital assets throughout their lifecycle. Confidential compute is engineered to prevent malicious actors from deciphering or manipulating sensitive information even if they gain access to the underlying infrastructure.
Implementing security-rich token platforms through confidential compute delivers tangible benefits. Digital rights holders can manage and monetize their intellectual property without the constant concern of piracy or unauthorized distribution. Stakeholders in various industries gain the ability to create, trade and enforce digital contracts with increased confidence in the security of their tokenized assets. Financial implications tied to token theft are significantly minimized, reducing the risk of revenue loss due to piracy or counterfeiting. This not only protects the economic interests of content creators and distributors but also promotes a more trustworthy digital ecosystem.
In conclusion, the adoption of confidential compute in the tokenization process addresses the crucial challenge of the expanding set of use cases from financial assets, real estate and to much larger scale tokens securing digital rights and intellectual property. The outcome is a shift towards more security-rich token platforms, providing content creators, distributors and consumers the confidence to engage in digital transactions while ensuring the sustained growth and integrity of the digital economy.
One example of growing use for tokens is online gaming. Confidential compute’s integration into tokenization safeguards in-game assets like virtual currencies and items. This is designed to promote heightened security, minimizing the financial risks and disruptions caused by stolen tokens in the dynamic landscape of online gaming.
Sovereign cloud: enhance data security to enable data privacy and sovereignty
National security and data sovereignty concerns drive the need for a secure hybrid cloud infrastructure that is designed to ensure that critical data and applications are not subject to unauthorized access or foreign jurisdiction.
Red Hat OpenShift, with confidential container capabilities, supports the implementation of sovereign clouds. By establishing secure containers, it enables nations to host critical applications and data within a protected environment, promoting data sovereignty and protecting against external threats. This solution provides a trusted platform for government agencies and critical infrastructure, fostering national security in the digital age.
Zero Trust SaaS: succeed at your SaaS transformation while keeping your client’s data private by applying built-in zero trust principles
As a SaaS provider aiming to offer scalable solutions to target customers with sensitive data or regulatory requirements, the challenge lies in providing cloud-based services without compromising the security and confidentiality of clients’ data. The need for a comprehensive Zero Trust framework becomes crucial to assure clients that their sensitive information remains inaccessible, not only by the SaaS provider but also by the underlying cloud infrastructure.
Red Hat OpenShift, fortified with confidential containers and integrated with Zero Trust as a service, revolutionizes the approach to Zero Trust SaaS from the provider’s standpoint. This solution helps that the SaaS provider, the cloud provider, IaaS Admin, and Kubernetes Admin have zero access to clients’ data.
The absence of isolation between different clusters within the cloud environment not only helps to optimize costs but also streamlines operational efficiency. Simultaneously, the isolation at the pod level within each cluster’s namespace enhances security, contributing to reduced certification audit efforts and reinforcing the SaaS provider’s commitment to data integrity.
Moreover, the implementation of multi-party Zero Trust allows clients and 4th party ISVs to run confidential workloads as containers without direct access to the underlying data. This innovative approach not only meets the stringent security requirements of clients but also positions the SaaS provider as a trusted partner capable of delivering scalable and security-rich solutions for clients with sensitive data or regulatory constraints.
Learn more about Confidential Compute with IBM Secure Execution on IBM LinuxONEIBM Newsletters
Get our newsletters and topic updates that deliver the latest thought leadership and insights on emerging trends.Subscribe now More newsletters
- SEO Powered Content & PR Distribution. Get Amplified Today.
- PlatoData.Network Vertical Generative Ai. Empower Yourself. Access Here.
- PlatoAiStream. Web3 Intelligence. Knowledge Amplified. Access Here.
- PlatoESG. Carbon, CleanTech, Energy, Environment, Solar, Waste Management. Access Here.
- PlatoHealth. Biotech and Clinical Trials Intelligence. Access Here.
- Source: https://www.ibm.com/blog/confidential-containers-with-red-hat-openshift-container-platform-and-ibm-secure-execution-for-linux/
- :has
- :is
- :not
- :where
- 1
- 10
- 12
- 15%
- 1800
- 2019
- 2023
- 2024
- 203
- 29
- 30
- 300
- 31
- 40
- 400
- 4th
- 9
- a
- ability
- Able
- About
- ABSTRACT
- abstraction
- abundance
- access
- across
- actors
- adding
- Additional
- address
- addresses
- admin
- Adopting
- Adoption
- advantages
- advent
- Advertising
- against
- age
- agencies
- aggregate
- AI
- AI models
- AI platform
- Aiming
- algorithms
- align
- All
- allow
- allowed
- Allowing
- allows
- also
- among
- amp
- an
- analytics
- and
- Another
- anyone
- APIs
- app
- Application
- Application Development
- applications
- Applying
- approach
- ARE
- AREA
- article
- AS
- assessment
- Assets
- associated
- assurance
- assure
- At
- attack
- audit
- author
- automating
- available
- away
- back
- based
- Battle
- BE
- become
- becomes
- been
- being
- benefits
- BEST
- between
- Beyond
- Blog
- blogs
- Blue
- both
- breaches
- Break
- build
- built
- built-in
- business
- businesses
- but
- button
- by
- CAN
- cannot
- capabilities
- capability
- capable
- carbon
- card
- Cards
- cases
- CAT
- Category
- Cause
- caused
- Centers
- certain
- Certification
- challenge
- challenges
- check
- Choose
- circles
- CIS
- class
- clear
- client
- clients
- Close
- Cloud
- cloud infrastructure
- cloud native
- Cloud Platform
- code
- collaborate
- collaboration
- collaborative
- colleagues
- color
- comes
- commitment
- Common
- commonly
- community
- Companies
- complex
- complexity
- compliance
- components
- comprehensive
- Compromised
- compromising
- Compute
- computer
- computing
- Concern
- Concerns
- conclusion
- confidence
- confidentiality
- confidently
- constant
- constraints
- Consumers
- Container
- Containers
- content
- content creators
- context
- continue
- continues
- continuous
- continuously
- contracts
- contrast
- contributing
- control
- conventional
- Corresponding
- Costs
- counterfeiting
- covered
- create
- Creating
- creators
- CREDENTIAL
- critical
- Critical Infrastructure
- crucial
- CSS
- currencies
- Current
- custom
- customer
- customer experience
- Customers
- cycle
- data
- data centers
- data management
- data privacy
- data security
- data set
- data warehouse
- Date
- decades
- December
- decentralized
- Default
- definitions
- deliver
- delivering
- delivers
- Demand
- demands
- Dependency
- deploy
- deployment
- described
- description
- designed
- Developer
- Development
- Devices
- DevOps
- diagnosing
- different
- digital
- digital age
- Digital Assets
- Digital economy
- digital ecosystem
- Digital Health
- digital rights
- digital transactions
- Digital Transformation
- direct
- Direct access
- disappointment
- disruptions
- Distinguished
- distribution
- distributors
- diverse
- dns
- drive
- due
- dynamic
- each
- ease
- ease of use
- easy
- Economic
- economy
- ecosystem
- Ecosystems
- effectively
- efficiency
- efforts
- embrace
- embracing
- emerged
- emergence
- emerging
- empowered
- enable
- enables
- enabling
- enclave
- encounter
- encrypted
- end
- end-to-end
- enforce
- engage
- engineered
- enhance
- Enhances
- enhancing
- ensure
- ensures
- ensuring
- Enter
- Enterprise
- Environment
- environments
- equally
- especially
- essential
- establish
- establishes
- establishing
- estate
- Ether (ETH)
- Even
- example
- execution
- Exit
- expanding
- expectations
- experience
- extends
- external
- Face
- false
- few
- financial
- financial data
- financial information
- Financial institutions
- financial services
- finding
- Flexibility
- focusing
- follow
- following
- fonts
- For
- forcing
- foreign
- Forrester
- fortified
- Foster
- fostering
- Foundation
- Foundational
- Framework
- fraud
- Freedom
- from
- fully
- further
- future
- Gain
- gaming
- Gartner
- generator
- get
- Go
- Goes
- Government
- government agencies
- Grid
- Growing
- Growth
- guarantee
- hand
- hat
- Have
- Heading
- Health
- Health Tech
- healthcare
- healthcare industry
- height
- heightened
- helps
- Highlight
- highly
- holders
- host
- hosted
- hosting
- How
- How To
- However
- HTTPS
- Hybrid
- hybrid cloud
- Hype
- IBM
- ICO
- ICON
- if
- image
- images
- imperative
- implementation
- implications
- in
- in-game
- inaccessible
- incorporating
- Increase
- increased
- increasing
- index
- industries
- industry
- information
- Infrastructure
- infrastructures
- Initiates
- initiatives
- innovate
- Innovation
- innovative
- Insider
- insights
- instances
- institutions
- integrated
- integration
- integrity
- intellectual
- intellectual property
- intellectual property protection
- interests
- into
- intricate
- intrinsic
- introduced
- isolated
- isolation
- issues
- IT
- items
- ITS
- January
- Java
- Job
- jpg
- jurisdiction
- keeping
- Key
- Kubernetes
- landscape
- large
- larger
- Last
- Last Year
- latest
- Leadership
- leading
- Leaks
- learning
- Led
- lesser
- Level
- Leverage
- leveraging
- Liberty
- lies
- lifecycle
- like
- linux
- local
- locale
- locations
- loss
- losses
- machine
- machine learning
- make
- malicious
- manage
- managed
- management
- manager
- managing
- manipulating
- many
- March
- massive
- max-width
- May..
- measures
- medical
- medical data
- Meet
- meeting
- Meets
- mesh
- microservices
- migrate
- migrating
- min
- minimize
- minimizing
- minutes
- mitigating
- ML
- Mobile
- model
- models
- Modern
- modified
- monetize
- monitoring
- more
- most
- move
- much
- multi-party
- multiple
- must
- National
- national security
- Nations
- native
- Navigation
- Need
- needed
- network
- networking
- New
- Newsletters
- no
- nothing
- now
- Nuance
- occur
- of
- off
- offer
- Offers
- often
- on
- ONE
- online
- online gaming
- only
- open
- open source
- operational
- Operations
- Optimize
- optimized
- or
- organizations
- Other
- our
- Outcome
- over
- overall
- page
- Paramount
- part
- parties
- partner
- party
- patient
- patient data
- Peak
- performance
- person
- PHP
- Piracy
- placed
- platform
- Platforms
- plato
- Plato Data Intelligence
- PlatoData
- Play
- plugin
- pods
- policy
- poses
- position
- positions
- Post
- potential
- Practical
- practice
- present
- prevent
- primary
- principles
- Prior
- priority
- privacy
- Privacy and Security
- private
- privileged
- Problem
- process
- processed
- promote
- promotes
- promoting
- property
- proprietary
- protect
- protected
- protecting
- protection
- protects
- provider
- provides
- providing
- public
- Public cloud
- Read
- Reading
- real
- real estate
- realm
- recent
- recognized
- records
- recovery
- Red
- Red Hat
- Reduced
- reducing
- referred
- reflect
- regulated
- regulatory
- Regulatory Compliance
- related
- remains
- requests
- requirement
- Requirements
- requires
- research
- responsive
- REST
- revenue
- revolutionizes
- right
- rights
- rising
- Risk
- risks
- robots
- robust
- Role
- Run
- running
- SaaS
- safeguarding
- safeguards
- scalable
- Scale
- Screen
- scripts
- secure
- Secured
- securely
- securing
- security
- Security Measures
- seems
- sensitive
- seo
- server
- service
- Services
- set
- Share
- shared
- shift
- Short
- shown
- significant
- significantly
- signing
- Simple
- simultaneously
- site
- skills
- small
- So
- Software
- solution
- Solutions
- Solving
- some
- sovereign
- sovereignty
- specific
- specifically
- Sponsored
- spring
- spring boot
- squares
- stakeholders
- standard
- standpoint
- start
- State
- stay
- steering
- Steps
- stolen
- strategies
- streamlines
- stringent
- strong
- subject
- subscribe
- succeed
- such
- support
- Supporting
- Supports
- sustained
- SVG
- tangible
- Target
- tech
- Technical
- technically
- Technologies
- Technology
- tenant
- tertiary
- that
- The
- The Future
- The State
- the world
- theft
- their
- Them
- theme
- themselves
- There.
- These
- they
- Third
- third parties
- third-party
- this
- those
- though?
- thought
- thought leadership
- threats
- Through
- throughout
- Tied
- time
- Title
- to
- today’s
- together
- token
- Tokenization
- tokenized
- tokenized assets
- Tokens
- tolerance
- top
- topic
- touches
- towards
- trade
- traditional
- traditionally
- traffic
- Training
- Transactions
- Transformation
- Trends
- truly
- Trust
- TRUST Framework
- trusted
- trusted partner
- trustworthy
- type
- types
- typically
- ubiquitous
- unauthorized
- underlying
- underneath
- underpin
- unique
- Updates
- URL
- use
- used
- User
- uses
- Valuable
- value
- various
- version
- Virtual
- virtual currencies
- W
- want
- Warehouse
- Warehousing
- Way..
- WELL
- whether
- which
- while
- why
- will
- with
- within
- without
- WordPress
- worked
- workflows
- working
- world
- world’s
- written
- year
- you
- Your
- zephyrnet
- zero
- zero trust
















