For many years the primary method of consumption for marijuana in modern society has been smoking the flowers which contain most of the THC and other cannabinoids found in the plant.
For many years the primary method of consumption for marijuana in modern society has been smoking the flowers which contain most of the THC and other cannabinoids found in the plant.
Sure, some people like to bake infused brownies and others use vaporizers, but the vast majority prefer to pack a bowl or light a joint. That is rapidly changing as medical marijuana is becoming increasingly legal in the U.S. and other countries.
Hashish, or hash, has been around since ancient times and is a concentrated form of cannabis that is popular as an alternative to smoking cannabis flowers. In this blog, we will explore the many different types of cannabis concentrates, the various methods of making them, and how they can be consumed or used to make infused products.
Whether you call it BHO, hash, honey oil, Tears of Phoenix, an extraction, or cannabis concentrates, there are a thriving culture and a significant amount of science behind this wonderful goo. For as long as human beings have known about the cannabis plant, we have been experimenting with methods to obtain higher doses of the main psychoactive ingredient, THC.
Simple methods employ mechanical and physical separation of the resin-rich glands that contain most of the active ingredients to produce a rather crude cannabis concentrate that has a lower potency and a high amount of plant material.
20th Century Cannabis Concentrates
 In the 20th century, chemical extraction became increasingly popular with books like Cannabis Alchemy by D. Gold explaining how solvents such as alcohol or petroleum-based hydrocarbons can be used to produce very potent and pure cannabis concentrates.
In the 20th century, chemical extraction became increasingly popular with books like Cannabis Alchemy by D. Gold explaining how solvents such as alcohol or petroleum-based hydrocarbons can be used to produce very potent and pure cannabis concentrates.
Not long thereafter, butane honey oil, or BHO as it is often called became popular because it can be produced easily and quickly with cheap and readily available materials.
In the new millennium, cannabis concentrates got a high-tech boost as super-critical carbon dioxide extraction, the same process used to make decaf coffee, began being used to make hash. Now there are a handful of companies that produce extractors that are designed specifically for making hash, although many are marketed as generic herbal essential oil extractors for legal reasons.
The earliest hashish was not surprisingly the simplest form of cannabis concentrate. The buds of the cannabis plant are covered in tiny glands called trichomes, which can be thought of as cannabinoid factories where the plant makes most of its THC and other similar compounds.
When the flowers are rubbed or otherwise mechanically agitated, the trichomes separate from the plant material and bring along a lot of cannabinoids with them. 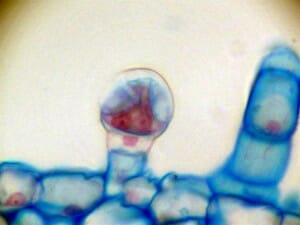
 For example, when cannabis flowers are being harvested and manicured a significant amount of resin becomes stuck to the scissors being used to trim the plants.
For example, when cannabis flowers are being harvested and manicured a significant amount of resin becomes stuck to the scissors being used to trim the plants.
This sticky, dark solid is often referred to as “scissor hash” and is usually a cultivator’s first opportunity to sample some of their new harvests. Ancient people in Western Asia prepared crude hashish using similar methods to remove trichomes from the plant material to make some of the first cannabis concentrates in the world.
A simple modification to this basic procedure produces a higher quality hash that has been termed “bubble hash”. By using water to aid in the separation of the resin glands from the rest of the plant material, a much lighter-colored and higher potency hash can be obtained.
The water helps to remove chlorophyll and other impurities from the hash, thus resulting in lighter-colored oil with a higher THC potency. While bubble hash made with water is a concentrated form of cannabis, it is a physical separation and not a true extract.
Solvent Extraction To Make Cannabis Concentrates
Extraction is a process that involves the use of a solvent to dissolve the essential oils in the plant and chemically separate them from the plant material, not all that different from making tea or coffee. There are many advantages to extracting cannabis with a solvent, the greatest being the ability to filter the extract and remove all of the plant material.
This will afford a more potent cannabis concentrate, burns/vaporizes cleaner, and is easier to infuse into products such as edibles or vaporizer pens. Using a liquid solvent also allows the extract to be refined and purified to remove color, waxes, and other impurities.
Using extraction methods, it is possible to obtain cannabis extracts that are upwards of 90% THC. There are, however, some drawbacks to using certain extraction solvents that can have major health and safety implications which will be discussed in more detail later.
Simple Fat-Based Cannabis Concentrates
 The simplest cannabis extracts are fat-based cannabis concentrates such as infused butter or cooking oils like canola, coconut, or olive oil. The fat-based concentrates are prepared by steeping cannabis plant material in the fat while heating to extract cannabinoids and other phytochemicals.
The simplest cannabis extracts are fat-based cannabis concentrates such as infused butter or cooking oils like canola, coconut, or olive oil. The fat-based concentrates are prepared by steeping cannabis plant material in the fat while heating to extract cannabinoids and other phytochemicals.
The plant material is then strained and the fat-based cannabis concentrate is ready for oral consumption. Often these cannabis concentrates are used to make infused edible products like candies and baked goods.
Whenever a fat-based cannabis concentrate is to be eaten, it is important to activate the plant material before extraction. Activation is the process that converts the non-psychoactive, natural product THCA to its psychoactive form, THC.
This decarboxylation reaction can be achieved by heating the plant material above 210 degrees Fahrenheit for at least an hour. Although glycerin is not technically fat, it can be used to prepare a tincture similar as with cooking oils.
Because fat-based and glycerin cannabis concentrates are prepared by direct infusion of plant material into the fat, the THC potency of the oil is unknown. The infused fat must be tested for potency before it can be used to make precision-dosed products.
Alternatively, hash that is made from solvent extraction and tested for potency can be diluted with a known amount of fat to prepare an infusion of known potency. The vast majority of commercial marijuana-infused product manufacturers use this method, while the direct infusion is generally used by individuals at home.
One major drawback of fat-based cannabis concentrates is that it is very difficult, if not impossible, to isolate the THC and other cannabinoids from the cooking oil to make hash. Cooking oils are not volatile, meaning they have a high boiling point and cannot be removed by distillation.
Cannabis Concentrates Using Volatile Solvents
 When a volatile solvent is used in place of the cooking oil, it can be distilled off resulting in a high-potency hash. When using volatile solvents to extract cannabis, it is important to fully remove or purge all of the solvents from the hash for health and safety reasons.
When a volatile solvent is used in place of the cooking oil, it can be distilled off resulting in a high-potency hash. When using volatile solvents to extract cannabis, it is important to fully remove or purge all of the solvents from the hash for health and safety reasons.
This is usually done with a vacuum chamber and/or heat to boil off the residual solvent. Several volatile organic solvents are used to extract cannabis, but butane is by far the most popular.
Butane is cheap and readily available and also has a very low boiling point of 30 degrees Fahrenheit, so it is simple to purge the solvent from the concentrate. Butane is used by home and commercial producers alike to make very high-quality hash but has some serious safety risks.
Butane is a highly flammable compressed gas, so extractions using butane should be done outside or in a well-ventilated room with a spark-free exhaust fan to prevent explosions. The use of butane to extract cannabis is illegal in many areas, so it is important to know the law before blasting your hash.
The toxicity of butane is low, but it is still important to purge all of the butane from the hash and this must also be done safely and responsibly. Most people make BHO by “open-blasting” where they force compressed butane through a tube or column containing the plant material and collect the hash in a pan and the end of the tube.
This process is dangerous, wastes butane and also sends butane into the atmosphere where it can have a negative environmental impact. Some states have banned open blasting for commercial hash production and require the use of expensive recapture machines that recycle almost all of the butane.
Other Volatile Organic Solvents
 An alternative to butane blasting is the use of other volatile organic solvents with higher boiling points to extract the hash. Grain alcohol such as Everclear (95% ethanol) or hexane is a common liquid extraction solvent with respective boiling points of 173 and 154 degrees Fahrenheit.
An alternative to butane blasting is the use of other volatile organic solvents with higher boiling points to extract the hash. Grain alcohol such as Everclear (95% ethanol) or hexane is a common liquid extraction solvent with respective boiling points of 173 and 154 degrees Fahrenheit.
Other common solvents include petroleum ether, isopropyl alcohol, acetone, or liquid hydrocarbons such as pentane or heptane. The choice of solvent will greatly impact the quality of the cannabis concentrate and we will go into more detail on this in a subsequent blog focused on the solvent extraction of cannabis.
Non-polar solvents such as hexane are quite selective for cannabinoids and other essential oils in the plant and give a high purity and potency hash. More polar solvents like alcohols or acetone are less selective and will extract chlorophyll and other phytochemicals resulting in a darker, less pure, and less potent hash.
Because the boiling points of these solvents are higher, they are liquids at room temperature which allows for simple and direct chemical manipulation of the cannabis concentrates. While the hash is still dissolved in the solvent, it can be purified to remove colors or waxes to give a more potent or cleaner hash and this is not possible with butane.
Many of the liquid solvents used to extract cannabis such as hexane or isopropyl alcohol are toxic, so it is critical to purge all of the solvents from the hash and test for residual solvents using gas chromatography. The only liquid solvent that is considered safe and acceptable to have residual solvent in the hash is ethanol because it has very low toxicity.
Super-Critical Carbon Dioxide Extraction
 Another extraction method that is becoming increasingly popular to prepare hash is super-critical carbon dioxide extraction. This process is used industrially to produce decaffeinated coffee and to extract essential oils for flavorings and fragrances.
Another extraction method that is becoming increasingly popular to prepare hash is super-critical carbon dioxide extraction. This process is used industrially to produce decaffeinated coffee and to extract essential oils for flavorings and fragrances.
The carbon dioxide is compressed in a chamber until it reaches the super-critical phase which is a hybrid liquid gas. Under these conditions, CO2 can act as a solvent and will dissolve organic material such as cannabinoids.
Because there are no organic solvents used in the process, it is usually thought of as the cleanest extraction method for making hash. If that’s the case, then you may wonder why people are still using butane and liquid organic solvents.
That is because super-critical CO2 extractors are expensive and range from about $20,000 up to $250,000. Additionally, the operation of these machines is complex and requires a highly skilled operator.
To obtain high yields and good quality hash with this process is not trivial, the maintenance and repairs of this type of extractor can also be costly. A handful of extraction artists can make great quality hash with carbon dioxide extraction, but much of the time the hash oil that is obtained is a thin, runny consistency and will be used in edibles or vaporizer pen formulas.
Cannabis Concentrates Final Points
 There is a wide range of textures of cannabis concentrates that can be made. The properties of the final product are highly dependent upon the starting plant material, the extraction process, and post-extraction processing and refinement.
There is a wide range of textures of cannabis concentrates that can be made. The properties of the final product are highly dependent upon the starting plant material, the extraction process, and post-extraction processing and refinement.
Bubble hash made by water extraction is typically solid with a dark amber to brown to green color. Hash oil made by extraction with butane or liquid solvents can have a wide range of textures from very thin and runny honey oil to thicker sap-like consistency to the much-coveted shatter.
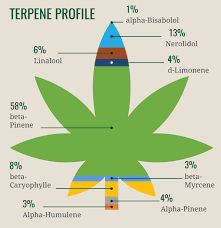
The viscosity of the hash oil is highly dependent upon the terpene content of the oil. Terpenes are low molecular weight, volatile oils that are responsible for the flavor and aroma of cannabis.
By purging the hash oil in a vacuum oven at elevated temperatures, many of the terpenes are evaporated off leaving very high potency oil that has a crystalline structure that is known as shatter.
The wax content of the hash will also impact its texture so strains that are very rich in paraffin waxes tend to yield hash oil that is more opaque and softer, earning names such as butter or earwax.
Waxes can be removed through a process called winterization which we will cover in detail later in this series of blogs. Cannabis concentrates can be used in many ways for recreational and medicinal purposes, they can be added to the cooking oil in a recipe and used to make infused edible products of all sorts.
It is also possible to make gel capsules with precise doses of THC, CBD, or other cannabinoids. Cannabis concentrates can be smoked on their own, or people often combine them with cannabis flowers when smoking.
In recent years, dabbing has become very popular for cannabis concentrates. To do a dab, a piece of metal or glass is heated with a torch, and the concentrate is applied and immediately vaporizes and is inhaled.
There are also tabletop and portable electronic vaporizers that work similarly by heating an electric coil. Electronic cigarette vaporizers that are the size of an ink pen are becoming hugely popular, some of the vape pens work with pure concentrate, while others require it to be thinned with some sort of carrier such as glycerin.
Let us know what you think.
- SEO Powered Content & PR Distribution. Get Amplified Today.
- Platoblockchain. Web3 Metaverse Intelligence. Knowledge Amplified. Access Here.
- Source: https://greencultured.co/cannabis-concentrates-infused-products/
- 000
- 95%
- a
- ability
- About
- above
- acceptable
- Act
- Activation
- active
- added
- Additionally
- advantages
- Alchemy
- Alcohol
- All
- allows
- alternative
- Although
- amber
- amount
- Ancient
- and
- applied
- areas
- around
- Artists
- asia
- auto
- available
- banned
- basic
- because
- become
- becomes
- becoming
- before
- began
- behind
- being
- Blog
- blogs
- Books
- boost
- bring
- bubble
- call
- called
- cannabis
- cannabis flowers
- cannot
- capsules
- carbon
- carbon dioxide
- case
- cbd
- Century
- certain
- Chamber
- changing
- cheap
- chemical
- choice
- co2
- Coffee
- coil
- collect
- color
- Column
- combine
- commercial
- Common
- Companies
- complex
- concentrate
- Concentrated
- Concentrates
- conditions
- considered
- consumed
- consumption
- content
- cooking
- countries
- cover
- covered
- critical
- crude
- Culture
- Dark
- dependent
- designed
- detail
- different
- difficult
- direct
- discussed
- drawbacks
- Dust
- easier
- easily
- edible
- Electric
- Electronic
- elevated
- environmental
- essential
- Ether
- example
- expensive
- explaining
- explore
- explosions
- extract
- extraction
- Extracts
- factories
- fan
- Fat
- filter
- final
- First
- focused
- Force
- form
- found
- from
- fully
- GAS
- generally
- Give
- glass
- Go
- Gold
- GOO
- good
- goods
- great
- greatest
- greatly
- Green
- handful
- hash
- Health
- helps
- herb
- High
- high-quality
- higher
- highly
- Home
- Honey
- How
- However
- HTTPS
- Hugely
- human
- Hybrid
- Illegal
- immediately
- Impact
- implications
- important
- impossible
- in
- include
- increasingly
- individuals
- infused
- infusion
- IT
- Know
- known
- Law
- leaving
- Legal
- light
- Liquid
- Long
- Lot
- Low
- Machines
- made
- Main
- maintenance
- major
- Majority
- make
- MAKES
- Making
- Manipulation
- Manufacturer
- many
- marijuana
- material
- max-width
- meaning
- mechanical
- medical
- Medical Marijuana
- medicinal
- metal
- method
- methods
- Millennium
- molecular
- more
- most
- Most Popular
- names
- Natural
- negative
- New
- non-psychoactive
- obtain
- obtained
- Oil
- oils
- open
- operation
- operator
- Opportunity
- organic
- Other
- Others
- otherwise
- outside
- Pack
- PAN
- People
- phase
- physical
- piece
- Place
- plants
- plato
- Plato Data Intelligence
- PlatoData
- Point
- points
- polar
- Popular
- possible
- pot
- potency
- precise
- prefer
- Prepare
- prepared
- prevent
- primary
- process
- processing
- produce
- Produced
- Producers
- Product
- Products
- properties
- purposes
- quality
- quickly
- range
- rapidly
- Reaches
- reaction
- reasons
- recent
- recipe
- Recreational
- referred
- refined
- remove
- Removed
- require
- requires
- Resin
- respective
- responsible
- REST
- resulting
- Rich
- Risk
- Room
- safe
- safely
- Safety
- same
- selective
- separate
- Series
- serious
- several
- significant
- similar
- Similarly
- Simple
- since
- Size
- skilled
- Smoking
- So
- Society
- solid
- some
- specifically
- Starting
- States
- Still
- Strains
- structure
- subsequent
- such
- Tea
- THC
- The
- the Law
- the world
- their
- thought
- thriving
- Through
- time
- to
- torch
- true
- types
- typically
- u.s.
- under
- upwards
- us
- use
- usually
- Vacuum
- various
- Vast
- volatile
- Water
- WAX
- ways
- What
- which
- while
- wide
- Wide range
- will
- wonderful
- Work
- world
- years
- Yield
- yields
- Your
- zephyrnet


![[NEW] HIPAA and Medical Cannabis Patients “Freshly Released” | Green CulturED](https://platoaistream.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/new-hipaa-and-medical-cannabis-patients-freshly-released-green-cultured-300x300.png)
![[NEW] Cannabis Safety and Health Concerns Training Released | Green CulturED](https://platoaistream.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/new-cannabis-safety-and-health-concerns-training-released-green-cultured.png)