A new technical paper titled “A Novel LBIST Signature Computation Method for Automotive Microcontrollers using a Digital Twin” was written by researchers at Infineon Technologies, University of Bremen, and DFKI GmbH.
Abstract
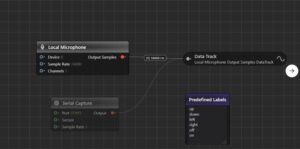
“LBIST has been proven to be an effective measure for reaching functional safety goals for automotive microcontrollers. Due to a large variety of recent innovative features, every customer can adjust LBIST settings in a way that fits their use case. The downside of these user-defined configurations is the handling of their golden signatures: Traditionally, they can be computed only with access to the gate-level netlist. This is typically not possible for MCU customers because a netlist contains protected IP, which cannot be disclosed to third parties.
This paper proposes a digital twin of the LBIST functionality that can overcome this drawback. It is an executable model that can be delivered together with the product. As a result, for the first time, a customer can compute a golden signature without knowledge of the netlist or other support of the supplier. We prove the efficacy of the digital twin in an industrial environment on an automotive microcontroller.”
Find the technical link here. 2023.
Tille, Daniel, Leon Klimasch, and Sebastian Huhn. “A Novel LBIST Signature Computation Method for Automotive Microcontrollers using a Digital Twin.”
- SEO Powered Content & PR Distribution. Get Amplified Today.
- Platoblockchain. Web3 Metaverse Intelligence. Knowledge Amplified. Access Here.
- Source: https://semiengineering.com/automotive-mcus-digital-twin-of-the-lbist-functionality/
- 2023
- a
- access
- and
- automotive
- because
- cannot
- case
- computation
- Compute
- contains
- customer
- Customers
- Daniel
- delivered
- digital
- digital twin
- downside
- Effective
- Environment
- Every
- Features
- First
- first time
- functional
- functionality
- GmBH
- Goals
- Golden
- Handling
- HTTPS
- in
- industrial
- Infineon
- innovative
- IP
- IT
- knowledge
- large
- LINK
- MCU
- measure
- method
- model
- New
- novel
- Other
- Overcome
- Paper
- parties
- plato
- Plato Data Intelligence
- PlatoData
- possible
- Product
- proposes
- protected
- Prove
- proven
- reaching
- recent
- researchers
- result
- Safety
- settings
- Signatures
- support
- Technical
- Technologies
- The
- their
- Third
- third parties
- time
- titled
- to
- together
- traditionally
- typically
- university
- use
- use case
- variety
- which
- without
- written
- zephyrnet