As the tech-driven economic landscape continues to evolve at a remarkable pace, Singapore remains at the forefront of this transformation, particularly in the realm of fintech. In 2024, some of the most prevalent fintech trends in Singapore showcase how the city-state continues to cement its position as a hub for innovation and technological advancements in the financial sector.
This booming scene is driven by supportive government policies, a robust tech-savvy population, and an increasing number of fintech startups. With the Singapore fintech market size in terms of transaction value expected to grow from US$38.80 billion in 2024 to US$63.18 billion by 2029, today we examine five of the top fintech trends set to shape the Singaporean financial industry this year.
From breakthroughs in digital banking to advancements in blockchain technology, we explore the cutting-edge developments that are not only revolutionising the way financial services are delivered in Singapore but also setting benchmarks for the global fintech landscape.
So what are the top fintech trends in Singapore for 2024, and how are these innovations paving the way for a more efficient, inclusive, and forward-thinking financial ecosystem? The top fintech trends in Singapore shaping this growth include instant cross-border transactions, generative AI across financial services, emerging digital currency uses, embedded finance “as-a-Service”, and increased ESG reporting and data convergence.
Embracing these emerging fintech trends will be crucial for Singapore to stay ahead in this rapidly-developing sector.
Proliferation of Real-time, Cross-border Transactions

Banks’ biggest competition in cross-border payments in the next five years, Source: Future of Cross-Border Payments: Who Will Be Moving $250 Trillion in the Next Five Years?, Citi GPS, Sep 2023
The year 2023 marked a notable transition towards cross-border payment partnerships across Southeast Asia, fueled by economic expansion, advancements in digital infrastructure, and a burgeoning tourism industry. As a regional frontrunner, Singapore has been instrumental in shaping the development of cross-border payment systems. Traditional challenges associated with these transactions, such as exorbitant costs, protracted processing times, opacity and security concerns are being systematically addressed through collaborative efforts among regulators, financial institutions, and industry players.
The year 2024 is poised to witness a significant enhancement in cross-border payment connectivity across Southeast Asia, underscored by the adoption of real-time payments. A local QR-code-based real-time payments ecosystem is established in Singapore, and now includes cross-border QR payment collaborations with Indonesia and the integration of Singapore’s PayNow with Malaysia’s DuitNow. These initiatives build upon existing linkages with Thailand’s PromptPay and India’s Unified Payments Interface, as well as QR payment connections with China and Thailand.
In an effort to fortify its payment infrastructure, the Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) is developing an interoperable SGQR+ scheme to boost QR code payment interoperability. A proof-of-concept for this scheme, conducted in November 2023, explored the feasibility of enabling Singaporean merchants to accept QR payments from diverse payment schemes through a singular financial institution.
GenAI: Enhancing Customer Service and Tackling Identity Fraud
The acceleration of real-time payments brings with it an escalated risk of fraud, necessitating the integration of sophisticated fraud services capable of screening and, if needed, blocking transactions almost instantaneously. Generative AI (GenAI) is expected to play a pivotal role in advancing the battle against identity fraud, particularly in the context of the rising threat posed by deep fakes. Financial services’ Chief Information Security Officers (CISOs) are, therefore, integrating this technology into their cybersecurity arsenals.
Large Language Models (LLMs) are anticipated to bolster investigation processes, enhancing the consistency of decisions across data volumes previously unmanageable by humans. These models will be instrumental in transaction reviews, adept at extracting pertinent information, recognising transaction patterns, and flagging anomalous activities.
Local banks have begun to integrate GenAI across their operations, with OCBC recognising GenAI’s potential to handle tasks such as writing job descriptions, doing investment research reports, drafting responses to customer complaints, doing translation of documents, onboard OCBC internal staff, and to personalise customer experiences.
OCBC’s Head of Group Data Office, Donald MacDonald, told Fintech News Singapore that AI makes over four million daily decisions for the bank across risk management, customer service, and sales, with OCBC projecting this number to reach 10 million by 2025. AI delivers personalised recommendations and insights through the mobile banking app, sending 250 million recommendations per year towards assisting customers
The Emergence of Stablecoins and CBDCs
Project Guardian, spearheaded by MAS in conjunction with industry stakeholders, is at the vanguard of tokenising various asset classes such as foreign exchange, bonds, and funds. This initiative aims to unlock liquidity, streamline operational efficiency, and extend investor access. MAS is collaborating with global regulators, including the International Monetary Fund (IMF), to establish international standards and frameworks for asset tokenisation, thereby fostering global trust and cooperation.
In 2024, MAS is set to initiate a pilot program for the issuance of wholesale Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs), surpassing previous simulations to actual applications in collaboration with local banks. This initiative underscores the potential of digital currencies in facilitating domestic payments. Concurrently, the provisional approval of stablecoins, aligning with MAS’ regulatory framework, highlights the potential of well-regulated stablecoins in broadening the applications of digital money.
MAS is collaborating with policymakers and financial institutions to explore the design of an open digital infrastructure that would host tokenized financial assets and applications, called Global Layer One (GL1). This system will facilitates tokenised assets to be traded across global liquidity pools, while meeting relevant regulatory requirements and guidelines.
Embedded Financial Services: A Game Changer
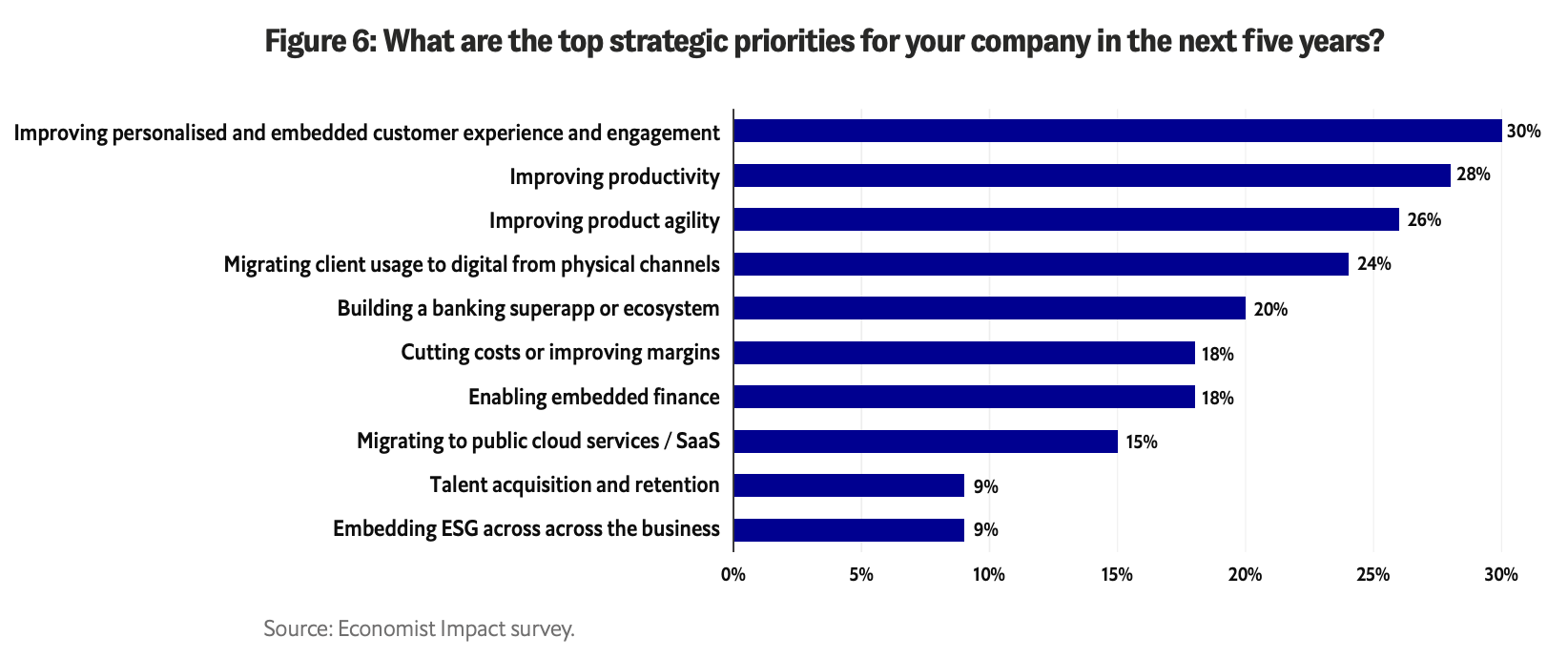
What are the top strategic priorities for your company in the next five years?, Source: Byte-sized banking: Can banks create a true ecosystem with embedded finance?, Economist Impact/Temenos, Sep 2023
Embedded finance (EmFi) is revolutionising the way non-financial service companies incorporate financial services into their core offerings. This year, we are likely to witness a significant surge in cross-sector convergence, as financial components are seamlessly integrated into customer purchasing experiences. Traditional retail banks may soon offer brokerage services as an added value for customers with savings accounts. Similarly, financial health platforms are expected to expand their services to include investment options.
EmFi presents traditional financial institutions with opportunities to explore new markets and reinvent their core businesses by partnering with third-party platforms to offer interoperable financial services. For instance, Standard Chartered spinoff audax offers Banking-as-a-Service solutions to power embedded finance solutions for non-banks.
Insurance and lending are expected to dominate the EmFi product spectrum, often being bundled together. Singapore and regional super-app Grab offers a plethora of embedded options, from GrabFinance micro loans to a variety of insurance products including for travel, medical and personal accident coverage — all from within its single, unified app.
For insurance companies, adopting bold embedded insurance strategies could be key to avoiding disintermediation. Insurance-as-a-Service is likely to be integrated into mobile apps and websites, enabling the purchase of insurance with a single click at the point of sale. In contrast, wealth and asset managers might face challenges due to their slower adoption of AI and technology. To remain competitive, they will need to rapidly embrace technological advancements by partnering with fintechs.
In Southeast Asia, particularly in emerging markets where access to traditional credit can be challenging, the most prevalent form of embedded lending is expected to be buy now, pay later (BNPL) schemes. These schemes, integrated into retail platforms, are set to provide a financial lifeline to a significant portion of the population.
Taking ESG Data Reporting to the Next Level

Source: MAS
At the Singapore Fintech Festival 2023, Ravi Menon, the Managing Director of MAS, introduced the next phase of Project Greenprint, which includes the launch of a new integrated platform named “Gprnt” (also pronounced “Greenprint”). This initiative, backed by industry giants such as HSBC, KPMG, MUFG, and Microsoft, is designed to revolutionise the financial ecosystem with advanced capabilities for national-level sustainability reporting and data requirements.
A key aspect of Gprnt.ai is its user-friendly ESG reporting tool, specifically tailored for SMEs. This tool is expected to simplify the reporting process, making it more accessible and cost-effective. It will consolidate data from various digital systems, including utility meters and business accounting software. In cases where source data is unavailable, AI tools will enable users to upload documents and extract critical data. A Microsoft GPT-4 powered chatbot will assist in bridging data gaps and crafting sustainability narratives.
Project Greenprint is set to extend its impact beyond Singapore, engaging in international collaborations to gather data essential for climate risk management and supporting the transition to a net-zero future.
These five fintech trends in Singapore for 2024 underscore the nation’s commitment to establishing a more efficient, inclusive, and forward-thinking financial ecosystem. The advancements in real-time payments, the adoption of GenAI in combating fraud, the development of digital currencies, the integration of financial services into non-financial sectors, and the progression in ESG reporting highlight Singapore’s role as a leader in financial innovation, setting benchmarks not only locally but also on a global scale.
- SEO Powered Content & PR Distribution. Get Amplified Today.
- PlatoData.Network Vertical Generative Ai. Empower Yourself. Access Here.
- PlatoAiStream. Web3 Intelligence. Knowledge Amplified. Access Here.
- PlatoESG. Carbon, CleanTech, Energy, Environment, Solar, Waste Management. Access Here.
- PlatoHealth. Biotech and Clinical Trials Intelligence. Access Here.
- Source: https://fintechnews.sg/83255/fintech/5-top-fintech-trends-set-to-define-singapore-in-2024/
- :has
- :is
- :not
- :where
- $10 million
- 1
- 10
- 11
- 2023
- 2024
- 2025
- 250
- 32
- 36
- 500
- 600
- 7
- 80
- a
- acceleration
- Accept
- access
- accessible
- accident
- Accounting
- accounting software
- Accounts
- across
- activities
- actual
- added
- addressed
- adept
- Adopting
- Adoption
- advanced
- advancements
- advancing
- against
- ahead
- AI
- aims
- aligning
- All
- almost
- also
- among
- an
- and
- Anticipated
- app
- applications
- approval
- apps
- ARE
- AS
- asia
- aspect
- asset
- asset-managers
- Assets
- assist
- assisting
- associated
- At
- author
- authority
- avoiding
- backed
- Bank
- Banking
- Banks
- Battle
- BE
- been
- begin
- begun
- being
- benchmarks
- Beyond
- Biggest
- Billion
- blockchain
- blockchain technology
- blocking
- BNPL
- bold
- bolster
- Bonds
- boost
- breakthroughs
- bridging
- Brings
- brokerage
- build
- bundled
- burgeoning
- business
- businesses
- but
- by
- CAN
- capabilities
- capable
- caps
- cases
- CBDCs
- cement
- central
- Central Bank
- central bank digital currencies
- CENTRAL BANK DIGITAL CURRENCIES (CBDCS)
- challenges
- challenging
- Chartered
- chatbot
- chief
- China
- Citi
- classes
- click
- Climate
- code
- collaborating
- collaboration
- collaborations
- collaborative
- combating
- commitment
- Companies
- company
- competition
- competitive
- complaints
- components
- Concerns
- conducted
- conjunction
- Connections
- Connectivity
- consolidate
- content
- context
- continues
- contrast
- Convergence
- cooperation
- Core
- cost-effective
- Costs
- could
- coverage
- create
- credit
- critical
- cross-border
- cross-border payments
- crucial
- currencies
- Currency
- customer
- Customer Service
- Customers
- cutting-edge
- Cybersecurity
- daily
- data
- decisions
- deep
- Deep Fakes
- define
- delivered
- delivers
- Design
- designed
- developing
- Development
- developments
- digital
- Digital Asset
- digital banking
- digital currencies
- digital currency
- Digital Money
- Director
- diverse
- documents
- doing
- Domestic
- dominate
- donald
- driven
- due
- Economic
- Economist
- ecosystem
- efficiency
- efficient
- effort
- efforts
- embedded
- Embedded Finance
- embrace
- emergence
- emerging
- emerging markets
- Employee
- enable
- enabling
- end
- engaging
- enhancement
- enhancing
- ESG
- essential
- establish
- established
- establishing
- evolve
- examine
- exchange
- existing
- Expand
- expands
- expansion
- expected
- Experiences
- explore
- Explored
- extend
- extract
- Face
- facilitates
- facilitating
- feasibility
- FESTIVAL
- finance
- financial
- financial health
- financial innovation
- financial institution
- Financial institutions
- Financial sector
- financial services
- fintech
- Fintech News
- fintech startups
- FinTech Trends
- fintechs
- five
- For
- forefront
- foreign
- foreign exchange
- form
- fortify
- forward-thinking
- fostering
- four
- Framework
- frameworks
- fraud
- from
- fueled
- fund
- funds
- future
- game
- gaps
- gather
- generative
- Generative AI
- giants
- Global
- global scale
- Government
- gps
- grab
- Group
- Grow
- Growth
- guardian
- guidelines
- handle
- Have
- head
- Health
- High
- Highlight
- highlights
- host
- hottest
- How
- HSBC
- HTTPS
- Hub
- Humans
- Identity
- if
- IMF
- Impact
- in
- include
- includes
- Including
- Inclusive
- incorporate
- increased
- increasing
- industry
- information
- information security
- Infrastructure
- initiate
- Initiative
- initiatives
- Innovation
- innovations
- insights
- instance
- instant
- instantaneously
- Institution
- institutions
- instrumental
- insurance
- integrate
- integrated
- Integrating
- integration
- Interface
- internal
- International
- international monetary fund
- International Monetary Fund (IMF)
- Interoperability
- interoperable
- into
- investigation
- investment
- investor
- issuance
- IT
- ITS
- Job
- jpg
- Key
- KPMG
- landscape
- language
- later
- launch
- layer
- layer one
- leader
- Leap
- lending
- likely
- Liquidity
- liquidity pools
- local
- LOCAL BANKS
- locally
- macdonald
- mailchimp
- MAKES
- Making
- management
- Managers
- managing
- Managing Director
- marked
- Market
- Markets
- MAS
- max-width
- May..
- medical
- meeting
- Merchants
- micro
- Microsoft
- might
- million
- Mobile
- Mobile banking
- mobile-apps
- models
- Monetary
- monetary authority
- Monetary Authority of Singapore
- Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS)
- money
- Month
- more
- more efficient
- most
- moving
- MUFG
- Named
- narratives
- Nations
- Need
- needed
- net-zero
- New
- news
- next
- notable
- November
- now
- number
- ocbc
- OCBC Bank
- of
- offer
- Offerings
- Offers
- Office
- officers
- often
- on
- once
- ONE
- only
- open
- operational
- Operations
- Options
- over
- Pace
- particularly
- partnering
- partnerships
- patterns
- Paving
- Pay
- payment
- Payment Systems
- payments
- PayNow
- per
- personal
- Personalised
- phase
- pilot
- pivotal
- platform
- Platforms
- plato
- Plato Data Intelligence
- PlatoData
- Play
- players
- plethora
- Point
- point of sale
- poised
- policies
- policymakers
- Pools
- population
- portion
- posed
- position
- Posts
- potential
- power
- powered
- prevalent
- previous
- previously
- process
- processes
- processing
- Product
- Products
- progression
- project
- Promptpay
- pronounced
- proposes
- provide
- purchase
- purchasing
- purchasing experiences
- QR code
- qr payments
- rapidly
- RAVI MENON
- reach
- real-time
- real-time payments
- realm
- recognising
- recommendations
- regional
- Regulators
- regulatory
- reinvent
- relevant
- remain
- remains
- remarkable
- Reporting
- Reports
- Requirements
- research
- responses
- retail
- Reviews
- revolutionising
- rising
- Risk
- risk management
- robust
- Role
- sale
- sales
- Savings
- Scale
- scene
- scheme
- schemes
- scope
- screening
- seamlessly
- sector
- Sectors
- security
- sending
- service
- Services
- set
- setting
- Shape
- shaping
- showcase
- significant
- Similarly
- simplify
- Singapore
- Singapore Fintech Festival
- Singapore’s
- Singaporean
- single
- singular
- Size
- SMEs
- Software
- Solutions
- some
- Soon
- sophisticated
- Source
- southeast
- Southeast Asia
- spearheaded
- specifically
- Spectrum
- Stablecoins
- stakeholders
- standard
- Standard Chartered
- standards
- Startups
- stay
- Strategic
- strategies
- streamline
- such
- Super-app
- Supporting
- supportive
- surge
- surpassing
- Sustainability
- system
- Systems
- tackling
- tailored
- tasks
- technological
- Technology
- terms
- Thailand
- Thailand’s
- that
- The
- their
- thereby
- therefore
- These
- they
- third-party
- this
- this year
- threat
- Through
- times
- to
- today
- together
- tokenisation
- tokenised
- tokenising
- tokenized
- tool
- tools
- top
- Tourism
- towards
- traded
- traditional
- transaction
- Transactions
- Transformation
- transition
- Translation
- travel
- Trends
- Trillion
- true
- Trust
- underscore
- underscores
- unified
- unlock
- upon
- user-friendly
- users
- uses
- using
- utility
- value
- Vanguard
- variety
- various
- volumes
- Way..
- we
- Wealth
- websites
- WELL
- well-regulated
- What
- which
- while
- WHO
- wholesale
- will
- with
- within
- witness
- would
- writing
- year
- years
- Your
- zephyrnet