| Mar 14, 2023 |
| (Nanowerk News) Each year, an estimated two trillion dollars is lost globally due to counterfeit products ranging from jewelry to medicine. As current security labels and product authentication methods are rapidly becoming obsolete or easy to hack, there is a rising urgency for more secure anti- counterfeiting labels.
|
|
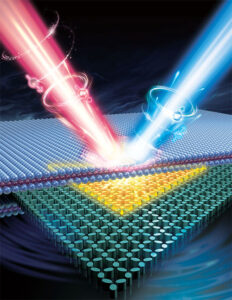
A research team fabricated a 3D printed nano optical security label that provides 33100 possible combinations for heightened security in optical anti-counterfeiting. Associate Professor Joel Yang and team from the Singapore University of Technology and Design (SUTD) collaborated with Professor Min Gu from University of Shanghai for Science and Technology (USST) and Associate Professor Cheng-Wei Qiu from National University of Singapore (NUS), along with their respective teams and published their research paper in Nature Nanotechnology (“Coloured vortex beams with incoherent white light illumination”).
|
|
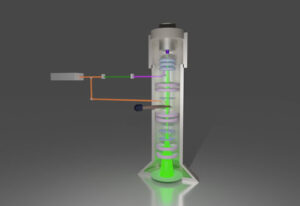
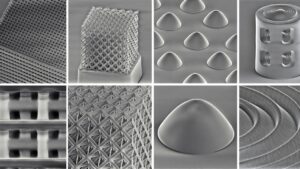
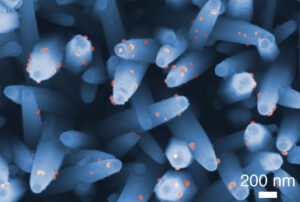
The research team achieved such a feat by exploiting higher dimensional structured light, i.e., coloured Orbital Angular Momentum (OAM) beams, through the fabrication of 3D printed spiral phase plates. Importantly, these plates were miniaturised down to a diameter smaller than that of a strand of human hair and further integrated with structural colour filters – spiky looking structures that allow specific colours of light through (refer to image).
|
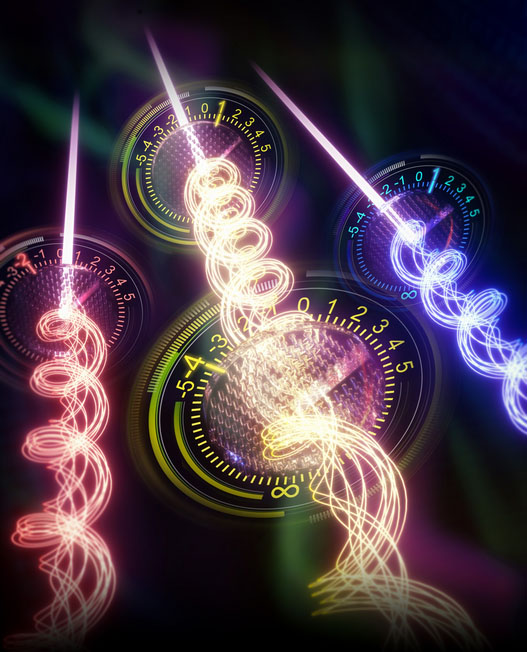 |
| 3D printed nano-optical security label that provides 33(100) possible combinations for heightened security in optical anti-counterfeiting. (Image: Singapore University of Technology and Design)
|
|
“Orbital Angular Momentum or OAM light beam is increasingly being used in exciting research spaces such as optical communications, super-resolution imaging and quantum computing and we wanted to explore its capabilities in the anti-counterfeiting field as well. But OAM requires coherent light sources like lasers. We wanted to see if we could use incoherent light from the sun or a light bulb to generate OAM beams instead,” explained Hongtao Wang, first author of the paper and SUTD-NUS joint PhD student.
|
|
In their study, they included colour, spatial position, and OAM of light (one degree of freedom of light) onto a small coloured vortex beam (CVB) generator (25 µm). With only 10-by-10 CVB unit array to demonstrate, the optical security label they designed could open pathways for the next generation of optical anti-counterfeiting.
|
|
“We see things clearly when we hold them up to the light. What our team has done is to learn how to use the natural light that surrounds us and extract tiny beams from it that carry information encoded in not just colour, but also by how much we ‘twist’ its wavefront. This optical version of the combination lock that utilises high-dimensional structured light provides us with a powerful platform for advanced anti-counterfeiting and information security,” explained principal investigator Associate Professor Yang.
|
- SEO Powered Content & PR Distribution. Get Amplified Today.
- Platoblockchain. Web3 Metaverse Intelligence. Knowledge Amplified. Access Here.
- Source: https://www.nanowerk.com/nanotechnology-news2/newsid=62576.php