ہوم پیج (-) > پریس > With new experimental method, researchers probe spin structure in 2D materials for first time: By observing spin structure in “magic-angle” graphene, a team of scientists led by Brown University researchers have found a workaround for a long-standing roadblock in the field of two
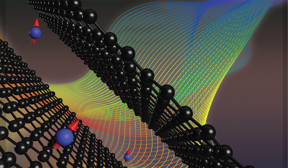 |
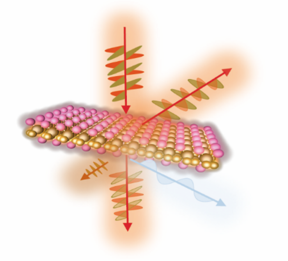
| By observing spin structure in “magic-angle” graphene, a team of scientists led by Brown University researchers have found a workaround for a long-standing roadblock in the field of two-dimensional electronics. CREDIT Jia Li/Brown University |
خلاصہ:
For two decades, physicists have tried to directly manipulate the spin of electrons in 2D materials like graphene. Doing so could spark key advances in the burgeoning world of 2D electronics, a field where super-fast, small and flexible electronic devices carry out computations based on quantum mechanics.
نئے تجرباتی طریقہ کار کے ساتھ، محققین نے پہلی بار 2D مواد میں اسپن ڈھانچے کی جانچ کی: "جادوئی زاویہ" گرافین میں اسپن کی ساخت کا مشاہدہ کرکے، براؤن یونیورسٹی کے محققین کی قیادت میں سائنسدانوں کی ایک ٹیم نے میدان میں ایک طویل عرصے سے روکے جانے والے روڈ بلاک کے لیے ایک حل تلاش کیا ہے۔ دو میں سے
Providence, RI | Posted on May 12th, 2023Standing in the way is that the typical way in which scientists measure the spin of electrons — an essential behavior that gives everything in the physical universe its structure — usually doesn’t work in 2D materials. This makes it incredibly difficult to fully understand the materials and propel forward technological advances based on them. But a team of scientists led by Brown University researchers believe they now have a way around this longstanding challenge. They describe their solution in a new study published in Nature Physics.
In the study, the team — which also include scientists from the Center for Integrated Nanotechnologies at Sandia National Laboratories, and the University of Innsbruck — describe what they believe to be the first measurement showing direct interaction between electrons spinning in a 2D material and photons coming from microwave radiation. Called a coupling, the absorption of microwave photons by electrons establishes a novel experimental technique for directly studying the properties of how electrons spin in these 2D quantum materials — one that could serve as a foundation for developing computational and communicational technologies based on those materials, according to the researchers.
“Spin structure is the most important part of a quantum phenomenon, but we’ve never really had a direct probe for it in these 2D materials,” said Jia Li, an assistant professor of physics at Brown and senior author of the research. “That challenge has prevented us from theoretically studying spin in these fascinating material for the last two decades. We can now use this method to study a lot of different systems that we could not study before.”
The researchers made the measurements on a relatively new 2D material called “magic-angle” twisted bilayer graphene. This graphene-based material is created when two sheets of ultrathin layers of carbon are stacked and twisted to just the right angle, converting the new double-layered structure into a superconductor that allows electricity to flow without resistance or energy waste. Just discovered in 2018, the researchers focused on the material because of the potential and mystery surrounding it.
براؤن میں لی کی لیب میں ایک گریجویٹ طالب علم ایرن موریسیٹ نے کہا کہ 2018 میں جو اہم سوالات اٹھائے گئے تھے ان میں سے بہت سے جوابات ابھی باقی ہیں۔
Physicists usually use nuclear magnetic resonance or NMR to measure the spin of electrons. They do this by exciting the nuclear magnetic properties in a sample material using microwave radiation and then reading the different signatures this radiation causes to measure spin.
The challenge with 2D materials is that the magnetic signature of electrons in response to the microwave excitation is too small to detect. The research team decided to improvise. Instead of directly detecting the magnetization of the electrons, they measured subtle changes in electronic resistance, which were caused by the changes in magnetization from the radiation using a device fabricated at the Institute for Molecular and Nanoscale Innovation at Brown. These small variations in the flow of the electronic currents allowed the researchers to use the device to detect that the electrons were absorbing the photos from the microwave radiation.
The researchers were able to observe novel information from the experiments. The team noticed, for instance, that interactions between the photons and electrons made electrons in certain sections of the system behave as they would in an anti-ferromagnetic system — meaning the magnetism of some atoms was canceled out by a set of magnetic atoms that are aligned in a reverse direction.
The new method for studying spin in 2D materials and the current findings won’t be applicable to technology today, but the research team sees potential applications the method could lead to in the future. They plan to continue to apply their method to twisted bilayer graphene but also expand it to other 2D material.
موریسیٹ نے کہا کہ "یہ واقعی ایک متنوع ٹول سیٹ ہے جسے ہم ان مضبوط مربوط نظاموں میں الیکٹرانک آرڈر کے ایک اہم حصے تک رسائی حاصل کرنے اور عام طور پر یہ سمجھنے کے لیے استعمال کر سکتے ہیں کہ الیکٹران 2D مواد میں کیسے برتاؤ کر سکتے ہیں،" موریسیٹ نے کہا۔
The experiment was carried out remotely in 2021 at the Center for Integrated Nanotechnologies in New Mexico. Mathias S. Scheurer from University of Innsbruck provided theoretical support for modeling and understanding the result. The work included funding from the National Science Foundation, the U.S. Department of Defense and the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science.
####
مزید معلومات کے لئے، براہ مہربانی کلک کریں یہاں
رابطے:
Juan Siliezar
براؤن یونیورسٹی
آفس: 401-863-3766
Copyright © Brown University
اگر آپ کے پاس کوئی تبصرہ ہے، تو براہ مہربانی رابطہ کریں ہم سے.خبروں کی ریلیز جاری کرنے والے، نہ کہ 7th Wave, Inc. یا Nanotechnology Now، مواد کی درستگی کے لیے مکمل طور پر ذمہ دار ہیں۔
| متعلقہ لنکس |
| متعلقہ خبریں پریس |
2 جہتی مواد
![]() MXenes کی نظری خصوصیات میں پیش رفت - دو جہتی heterostructures نئے خیالات فراہم کرتے ہیں مئی 12th، 2023
MXenes کی نظری خصوصیات میں پیش رفت - دو جہتی heterostructures نئے خیالات فراہم کرتے ہیں مئی 12th، 2023
![]() گرافین بڑھتا ہے - اور ہم اسے دیکھ سکتے ہیں۔ مارچ 24th، 2023
گرافین بڑھتا ہے - اور ہم اسے دیکھ سکتے ہیں۔ مارچ 24th، 2023
![]() HKUMed نے ہڈیوں کے بافتوں کے انفیکشن کو مؤثر طریقے سے حل کرنے کے لیے ایک ناول دو جہتی (2D) الٹراساؤنڈ کے جوابی اینٹی بیکٹیریل نینو شیٹس ایجاد کی مارچ 24th، 2023
HKUMed نے ہڈیوں کے بافتوں کے انفیکشن کو مؤثر طریقے سے حل کرنے کے لیے ایک ناول دو جہتی (2D) الٹراساؤنڈ کے جوابی اینٹی بیکٹیریل نینو شیٹس ایجاد کی مارچ 24th، 2023
خبریں اور معلومات۔
![]() Ga2O3/مائع دھات پر مبنی لچکدار نمی کے سینسر کی لیزر ڈائریکٹ رائٹنگ مئی 12th، 2023
Ga2O3/مائع دھات پر مبنی لچکدار نمی کے سینسر کی لیزر ڈائریکٹ رائٹنگ مئی 12th، 2023
![]() MXenes کی نظری خصوصیات میں پیش رفت - دو جہتی heterostructures نئے خیالات فراہم کرتے ہیں مئی 12th، 2023
MXenes کی نظری خصوصیات میں پیش رفت - دو جہتی heterostructures نئے خیالات فراہم کرتے ہیں مئی 12th، 2023
گرافین / گریفائٹ
![]() گرافین بڑھتا ہے - اور ہم اسے دیکھ سکتے ہیں۔ مارچ 24th، 2023
گرافین بڑھتا ہے - اور ہم اسے دیکھ سکتے ہیں۔ مارچ 24th، 2023
حکومت- قانون سازی/ ضابطہ/ فنڈنگ/ پالیسی
![]() پرڈیو کے محققین نے دریافت کیا کہ سپر کنڈکٹیو تصاویر دراصل 3D اور خرابی سے چلنے والے فریکٹلز ہیں۔ مئی 12th، 2023
پرڈیو کے محققین نے دریافت کیا کہ سپر کنڈکٹیو تصاویر دراصل 3D اور خرابی سے چلنے والے فریکٹلز ہیں۔ مئی 12th، 2023
![]() ریکارڈ کی رفتار پر آپٹیکل سوئچنگ انتہائی تیز، روشنی پر مبنی الیکٹرانکس اور کمپیوٹرز کے لیے دروازے کھولتی ہے: مارچ 24th، 2023
ریکارڈ کی رفتار پر آپٹیکل سوئچنگ انتہائی تیز، روشنی پر مبنی الیکٹرانکس اور کمپیوٹرز کے لیے دروازے کھولتی ہے: مارچ 24th، 2023
![]() روبوٹ کیٹرپلر نرم روبوٹکس کے لیے لوکوموشن کے لیے نئے انداز کا مظاہرہ کرتا ہے۔ مارچ 24th، 2023
روبوٹ کیٹرپلر نرم روبوٹکس کے لیے لوکوموشن کے لیے نئے انداز کا مظاہرہ کرتا ہے۔ مارچ 24th، 2023
![]() سیمی کنڈکٹر جالی الیکٹران اور مقناطیسی لمحات سے شادی کرتی ہے۔ مارچ 24th، 2023
سیمی کنڈکٹر جالی الیکٹران اور مقناطیسی لمحات سے شادی کرتی ہے۔ مارچ 24th، 2023
ممکنہ مستقبل
![]() پرڈیو کے محققین نے دریافت کیا کہ سپر کنڈکٹیو تصاویر دراصل 3D اور خرابی سے چلنے والے فریکٹلز ہیں۔ مئی 12th، 2023
پرڈیو کے محققین نے دریافت کیا کہ سپر کنڈکٹیو تصاویر دراصل 3D اور خرابی سے چلنے والے فریکٹلز ہیں۔ مئی 12th، 2023
![]() Ga2O3/مائع دھات پر مبنی لچکدار نمی کے سینسر کی لیزر ڈائریکٹ رائٹنگ مئی 12th، 2023
Ga2O3/مائع دھات پر مبنی لچکدار نمی کے سینسر کی لیزر ڈائریکٹ رائٹنگ مئی 12th، 2023
![]() MXenes کی نظری خصوصیات میں پیش رفت - دو جہتی heterostructures نئے خیالات فراہم کرتے ہیں مئی 12th، 2023
MXenes کی نظری خصوصیات میں پیش رفت - دو جہتی heterostructures نئے خیالات فراہم کرتے ہیں مئی 12th، 2023
![]() روشنی کے اخراج اور روشنی کا پتہ لگانے کے لیے ناول ڈیزائن پیرووسکائٹ الیکٹرو کیمیکل سیل مئی 12th، 2023
روشنی کے اخراج اور روشنی کا پتہ لگانے کے لیے ناول ڈیزائن پیرووسکائٹ الیکٹرو کیمیکل سیل مئی 12th، 2023
چپ ٹیکنالوجی۔
![]() Ga2O3/مائع دھات پر مبنی لچکدار نمی کے سینسر کی لیزر ڈائریکٹ رائٹنگ مئی 12th، 2023
Ga2O3/مائع دھات پر مبنی لچکدار نمی کے سینسر کی لیزر ڈائریکٹ رائٹنگ مئی 12th، 2023
![]() MXenes کی نظری خصوصیات میں پیش رفت - دو جہتی heterostructures نئے خیالات فراہم کرتے ہیں مئی 12th، 2023
MXenes کی نظری خصوصیات میں پیش رفت - دو جہتی heterostructures نئے خیالات فراہم کرتے ہیں مئی 12th، 2023
دریافتیں
![]() Ga2O3/مائع دھات پر مبنی لچکدار نمی کے سینسر کی لیزر ڈائریکٹ رائٹنگ مئی 12th، 2023
Ga2O3/مائع دھات پر مبنی لچکدار نمی کے سینسر کی لیزر ڈائریکٹ رائٹنگ مئی 12th، 2023
![]() MXenes کی نظری خصوصیات میں پیش رفت - دو جہتی heterostructures نئے خیالات فراہم کرتے ہیں مئی 12th، 2023
MXenes کی نظری خصوصیات میں پیش رفت - دو جہتی heterostructures نئے خیالات فراہم کرتے ہیں مئی 12th، 2023
![]() روشنی کے اخراج اور روشنی کا پتہ لگانے کے لیے ناول ڈیزائن پیرووسکائٹ الیکٹرو کیمیکل سیل مئی 12th، 2023
روشنی کے اخراج اور روشنی کا پتہ لگانے کے لیے ناول ڈیزائن پیرووسکائٹ الیکٹرو کیمیکل سیل مئی 12th، 2023
اعلانات
![]() Ga2O3/مائع دھات پر مبنی لچکدار نمی کے سینسر کی لیزر ڈائریکٹ رائٹنگ مئی 12th، 2023
Ga2O3/مائع دھات پر مبنی لچکدار نمی کے سینسر کی لیزر ڈائریکٹ رائٹنگ مئی 12th، 2023
![]() MXenes کی نظری خصوصیات میں پیش رفت - دو جہتی heterostructures نئے خیالات فراہم کرتے ہیں مئی 12th، 2023
MXenes کی نظری خصوصیات میں پیش رفت - دو جہتی heterostructures نئے خیالات فراہم کرتے ہیں مئی 12th، 2023
![]() روشنی کے اخراج اور روشنی کا پتہ لگانے کے لیے ناول ڈیزائن پیرووسکائٹ الیکٹرو کیمیکل سیل مئی 12th، 2023
روشنی کے اخراج اور روشنی کا پتہ لگانے کے لیے ناول ڈیزائن پیرووسکائٹ الیکٹرو کیمیکل سیل مئی 12th، 2023
انٹرویوز/کتابوں کے جائزے/مضمون/رپورٹس/پوڈکاسٹ/جرائد/سفید کاغذات/پوسٹر
![]() پرڈیو کے محققین نے دریافت کیا کہ سپر کنڈکٹیو تصاویر دراصل 3D اور خرابی سے چلنے والے فریکٹلز ہیں۔ مئی 12th، 2023
پرڈیو کے محققین نے دریافت کیا کہ سپر کنڈکٹیو تصاویر دراصل 3D اور خرابی سے چلنے والے فریکٹلز ہیں۔ مئی 12th، 2023
![]() Ga2O3/مائع دھات پر مبنی لچکدار نمی کے سینسر کی لیزر ڈائریکٹ رائٹنگ مئی 12th، 2023
Ga2O3/مائع دھات پر مبنی لچکدار نمی کے سینسر کی لیزر ڈائریکٹ رائٹنگ مئی 12th، 2023
![]() MXenes کی نظری خصوصیات میں پیش رفت - دو جہتی heterostructures نئے خیالات فراہم کرتے ہیں مئی 12th، 2023
MXenes کی نظری خصوصیات میں پیش رفت - دو جہتی heterostructures نئے خیالات فراہم کرتے ہیں مئی 12th، 2023
![]() روشنی کے اخراج اور روشنی کا پتہ لگانے کے لیے ناول ڈیزائن پیرووسکائٹ الیکٹرو کیمیکل سیل مئی 12th، 2023
روشنی کے اخراج اور روشنی کا پتہ لگانے کے لیے ناول ڈیزائن پیرووسکائٹ الیکٹرو کیمیکل سیل مئی 12th، 2023
فوجی
![]() نیا تجربہ کوانٹم انٹرنیٹ کے لیے ایک اہم قدم میں ٹیکنالوجیز کے درمیان کوانٹم معلومات کا ترجمہ کرتا ہے۔ مارچ 24th، 2023
نیا تجربہ کوانٹم انٹرنیٹ کے لیے ایک اہم قدم میں ٹیکنالوجیز کے درمیان کوانٹم معلومات کا ترجمہ کرتا ہے۔ مارچ 24th، 2023
![]() ریکارڈ کی رفتار پر آپٹیکل سوئچنگ انتہائی تیز، روشنی پر مبنی الیکٹرانکس اور کمپیوٹرز کے لیے دروازے کھولتی ہے: مارچ 24th، 2023
ریکارڈ کی رفتار پر آپٹیکل سوئچنگ انتہائی تیز، روشنی پر مبنی الیکٹرانکس اور کمپیوٹرز کے لیے دروازے کھولتی ہے: مارچ 24th، 2023
![]() سیمی کنڈکٹر جالی الیکٹران اور مقناطیسی لمحات سے شادی کرتی ہے۔ مارچ 24th، 2023
سیمی کنڈکٹر جالی الیکٹران اور مقناطیسی لمحات سے شادی کرتی ہے۔ مارچ 24th، 2023
![]() انہیں کافی پتلا بنائیں، اور اینٹی فیرو الیکٹرک مواد فیرو الیکٹرک بن جاتا ہے۔ فروری 10th، 2023
انہیں کافی پتلا بنائیں، اور اینٹی فیرو الیکٹرک مواد فیرو الیکٹرک بن جاتا ہے۔ فروری 10th، 2023
- SEO سے چلنے والا مواد اور PR کی تقسیم۔ آج ہی بڑھا دیں۔
- پلیٹوآئ اسٹریم۔ ویب 3 ڈیٹا انٹیلی جنس۔ علم میں اضافہ۔ یہاں تک رسائی حاصل کریں۔
- ایڈریین ایشلے کے ساتھ مستقبل کا نقشہ بنانا۔ یہاں تک رسائی حاصل کریں۔
- PREIPO® کے ساتھ PRE-IPO کمپنیوں میں حصص خریدیں اور بیچیں۔ یہاں تک رسائی حاصل کریں۔
- ماخذ: http://www.nanotech-now.com/news.cgi?story_id=57341
- : ہے
- : ہے
- : نہیں
- :کہاں
- 10
- 10th
- 2018
- 2021
- 27
- 2D
- 2D مواد
- 3d
- a
- قابلیت
- تک رسائی حاصل
- کے مطابق
- درستگی
- اصل میں
- پتہ
- اعلی درجے کی
- ترقی
- AI
- منسلک
- کی اجازت دیتا ہے
- بھی
- an
- اور
- قابل اطلاق
- ایپلی کیشنز
- کا اطلاق کریں
- نقطہ نظر
- اپریل
- کیا
- ارد گرد
- مصنوعی
- مصنوعی ذہانت
- AS
- اسسٹنٹ
- At
- مصنف
- کی بنیاد پر
- BE
- کیونکہ
- بن
- اس سے پہلے
- یقین ہے کہ
- کے درمیان
- ہڈی
- توڑ
- براؤن یونیورسٹی
- لیکن
- by
- کہا جاتا ہے
- کر سکتے ہیں
- منسوخ
- کاربن
- لے جانے کے
- وجہ
- وجوہات
- سینٹر
- کچھ
- CGI
- چیلنج
- چیلنجوں
- تبدیلیاں
- کلک کریں
- COM
- آنے والے
- تبصرہ
- تجارتی
- گنتی
- کمپیوٹر
- کمپیوٹنگ
- مواد
- جاری
- تبدیل کرنا
- سکتا ہے
- بنائی
- کریڈٹ
- موجودہ
- نمٹنے کے
- بحث
- دہائیوں
- فیصلہ کیا
- دفاع
- ثبوت
- شعبہ
- محکمہ دفاع
- بیان
- ڈیزائن
- ترقی
- آلہ
- کے الات
- مختلف
- مشکل
- براہ راست
- سمت
- براہ راست
- دریافت
- دریافت
- متنوع
- do
- نہیں کرتا
- کر
- دروازے
- مؤثر طریقے
- بجلی
- الیکٹرانک
- الیکٹرونکس
- برقی
- آخر
- توانائی
- توانائی کا فضلہ
- کافی
- ضروری
- قائم ہے
- Ether (ETH)
- سب کچھ
- دلچسپ
- توسیع
- تجربہ
- تجربات
- فیس بک
- دلچسپ
- فروری
- میدان
- نتائج
- پہلا
- پہلی بار
- لچکدار
- بہاؤ
- توجہ مرکوز
- کے لئے
- آگے
- ملا
- فاؤنڈیشن
- سے
- مکمل طور پر
- فنڈنگ
- مستقبل
- جنرل
- GIF
- فراہم کرتا ہے
- گلوبل
- گوگل
- چلے
- گرافین
- بڑھتا ہے
- تھا
- ہے
- مدد
- کس طرح
- HTTP
- HTTPS
- شناخت
- if
- تصاویر
- اہم
- in
- انکارپوریٹڈ
- شامل
- شامل
- ناقابل یقین حد تک
- معلومات
- جدت طرازی
- مثال کے طور پر
- کے بجائے
- انسٹی ٹیوٹ
- ضم
- انٹیلی جنس
- بات چیت
- بات چیت
- بین الاقوامی سطح پر
- میں
- IT
- میں
- صرف
- کلیدی
- لیب
- تاریخی
- آخری
- تہوں
- قیادت
- قیادت
- کی طرح
- لنکس
- دیرینہ
- بہت
- بنا
- مقناطیسیت
- اہم
- بناتا ہے
- مارچ
- مواد
- مواد
- مئی..
- مطلب
- پیمائش
- پیمائش
- پیمائش
- میکینکس
- طریقہ
- میکسیکو
- ماڈلنگ
- آناخت
- زیادہ
- سب سے زیادہ
- اسرار
- نےنو
- قومی
- قومی سائنس
- فطرت، قدرت
- خالص
- کبھی نہیں
- نئی
- خبر
- ناول
- اب
- جوہری
- مشاہدہ
- of
- دفتر
- on
- ایک
- کھولتا ہے
- or
- حکم
- نکالنے
- دیگر
- باہر
- حصہ
- رجحان
- فوٹون
- تصویر
- پی ایچ پی
- جسمانی
- طبعیات
- منصوبہ
- پلاٹا
- افلاطون ڈیٹا انٹیلی جنس
- پلیٹو ڈیٹا
- مہربانی کرکے
- پوسٹ
- پوسٹ کیا گیا
- ممکنہ
- پریس
- ریلیز دبائیں
- تحقیقات
- ٹیچر
- پروپل
- خصوصیات
- فراہم
- فراہم
- شائع
- کوانٹم
- کوانٹم معلومات
- کوانٹم مواد
- کوانٹم میکینکس
- سوالات
- تابکاری
- پڑھنا
- واقعی
- ریکارڈ
- اٹ
- نسبتا
- جاری
- ریلیز
- تحقیق
- محقق
- محققین
- مزاحمت
- گونج
- جواب
- ذمہ دار
- نتیجہ
- واپسی
- ریورس
- ٹھیک ہے
- s
- کہا
- محفوظ کریں
- سائنس
- سائنسدانوں
- تلاش کریں
- سیکشنز
- دیکھنا
- دیکھتا
- سینئر
- خدمت
- مقرر
- آباد
- سیکنڈ اور
- دستخط
- نشانیاں
- چھوٹے
- So
- سافٹ
- حل
- کچھ
- چنگاری
- رفتار
- سپن
- سجا دیئے
- شروع کریں
- مرحلہ
- ابھی تک
- سختی
- ساخت
- طالب علم
- مطالعہ
- مطالعہ
- جمع
- حمایت
- ارد گرد
- پائیداری
- کے نظام
- سسٹمز
- ٹیکل
- ٹیم
- تکنیکی
- ٹیکنالوجی
- ٹیکنالوجی
- کہ
- ۔
- مستقبل
- ان
- ان
- تو
- نظریاتی
- یہ
- وہ
- اس
- ان
- وقت
- کرنے کے لئے
- آج
- بھی
- ٹریور
- کوشش کی
- دو
- ٹھیٹھ
- ہمیں
- امریکی محکمہ دفاع
- سمجھ
- افہام و تفہیم
- کائنات
- یونیورسٹی
- us
- استعمال کی شرائط
- کا استعمال کرتے ہوئے
- عام طور پر
- تھا
- فضلے کے
- لہر
- راستہ..
- we
- تھے
- کیا
- جب
- جس
- ڈبلیو
- ساتھ
- بغیر
- کام
- دنیا
- گا
- تحریری طور پر
- یاہو
- ابھی
- آپ
- زیفیرنیٹ