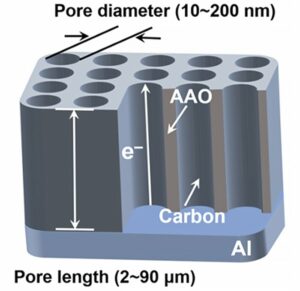
17 באוקטובר 2023 (חדשות Nanowerk) אנו חיים בעידן של מבול נתונים. מרכזי הנתונים המופעלים על מנת לאחסן ולעבד את המבול הזה של נתונים צורכים הרבה חשמל, מה שנקרא תורם מרכזי לזיהום הסביבה. כדי להתגבר על המצב הזה, נחקרות מערכות מחשוב פוליגונליות בעלות צריכת חשמל נמוכה יותר ומהירות חישוב גבוהה יותר, אך הן אינן מסוגלות להתמודד עם הביקוש העצום לעיבוד נתונים מכיוון שהן פועלות עם אותות חשמליים, בדיוק כמו מערכות מחשוב בינאריות רגילות.
חוקרים פיתחו חומר מוליכים למחצה 2D-0D חדש שיכול לתפקד כזיכרון אופטי המופעל על ידי פולסי אור.
החומר מאפשר מצבי התנגדות מרובים, המאפשרים יותר ממצבי 0 ו-1 בלבד כמו זיכרון רגיל.
זה יכול לאפשר העברת נתונים אופטית במהירות גבוהה בין חלקי מחשוב ואחסון של מערכת.
בבדיקות, הזיכרון האופטי השיג דיוק של 91% במודל AI, מה שמראה הבטחה למחשוב הדור הבא.
החוקרים אומרים שזה יכול לעזור להתגבר על מגבלות של מוליכים למחצה סיליקון עבור AI ומערכות מתקדמות אחרות.
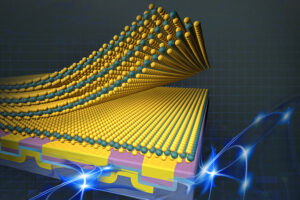
 התקני זיכרון אופטי היברידי 2D-0D. (תמונה: KIST)
התקני זיכרון אופטי היברידי 2D-0D. (תמונה: KIST)
המנות העיקריות
 התקני זיכרון אופטי היברידי 2D-0D. (תמונה: KIST)
התקני זיכרון אופטי היברידי 2D-0D. (תמונה: KIST)
המחקר
המכון למדע וטכנולוגיה של קוריאה (KIST) הודיע כי ד"ר דו קיונג הוואנג מהמרכז לחומרים אופטו-אלקטרוניים והתקנים ופרופסור ג'ונג-סו לי מהמחלקה למדע והנדסת אנרגיה במכון למדע וטכנולוגיה ב-Daegu Gyeongbuk ( DGIST) פיתחה במשותף חומר צומת מוליכים למחצה מלאכותי אפסי ודו מימדי (2D-0D) וצפה בהשפעה של זיכרון מהדור הבא המופעל על ידי אור. העברת נתונים בין חלקי המחשוב והאחסון של מחשב רב-שכבתי באמצעות אור ולא אותות חשמליים יכולה להגביר באופן דרמטי את מהירות העיבוד. המחקר פורסם ב חומרים מתקדמים (“Probing optical multi-level memory effects in single core-shell quantum dots and application through 2D-0D hybrid inverters”). צוות המחקר ייצר חומר חדש לצומת מוליכים למחצה 2D-0D על ידי הצטרפות נקודות קוונטיות במבנה ליבה-קליפה עם אבץ גופרתי (ZnS) על פני השטח של קדמיום סלניד (CdSe) וסולפיד מוליבדן (MoS)2) semiconductor. The new material enables the storage and manipulation of electronic states within quantum dots measuring 10 nm or less. When light is applied to the cadmium selenide core, a certain number of electrons flow out of the molybdenum sulfide semiconductor, trapping holes in the core and making it conductive. The electron state inside cadmium selenide is also quantized. Intermittent light pulses trap electrons in the electron band one after the other, inducing a change in the resistance of the molybdenum sulfide through the field effect, and the resistance changes in a cascading manner depending on the number of light pulses. This process makes it possible to divide and maintain more than 0 and 10 states, unlike conventional memory, which has only 0 and 1 states. The zinc sulfide shell also prevents charge leakage between neighboring quantum dots, allowing each single quantum dot to function as a memory. While quantum dots in conventional 2D-0D semiconductor artificial junction structures simply amplify signals from light sensors, the team’s quantum dot structure perfectly mimics the floating gate memory structure, confirming its potential for use as a next-generation optical memory. The researchers verified the effectiveness of the polynomial memory phenomenon with neural network modeling using the CIFAR-10 dataset and achieved a 91% recognition rate. Dr. Hwang of KIST said, “The new multi-level optical memory device will contribute to accelerating the industrialization of next-generation system technologies such as artificial intelligence systems, which have been difficult to commercialize due to technical limitations arising from the miniaturization and integration of existing silicon semiconductor devices.”- הפצת תוכן ויחסי ציבור מופעל על ידי SEO. קבל הגברה היום.
- PlatoData.Network Vertical Generative Ai. העצים את עצמך. גישה כאן.
- PlatoAiStream. Web3 Intelligence. הידע מוגבר. גישה כאן.
- PlatoESG. פחמן, קלינטק, אנרגיה, סביבה, שמש, ניהול פסולת. גישה כאן.
- PlatoHealth. מודיעין ביוטכנולוגיה וניסויים קליניים. גישה כאן.
- מקור: https://www.nanowerk.com/nanotechnology-news2/newsid=63861.php
- :יש ל
- :הוא
- :לֹא
- 1
- 10
- 17
- 7
- 8
- 9
- a
- יכול
- מאיצה
- דיוק
- הושג
- מתקדם
- לאחר
- AI
- מאפשר
- מאפשר
- גם
- להגביר
- an
- ו
- הודיע
- בקשה
- יישומית
- ARE
- מלאכותי
- בינה מלאכותית
- AS
- At
- להקה
- כי
- היה
- להיות
- בֵּין
- אבל
- by
- נקרא
- CAN
- מרכז
- מרכזים
- מסוים
- שינוי
- שינויים
- תשלום
- לְמַסְחֵר
- חישוב
- המחשב
- מחשוב
- צְרִיכָה
- לתרום
- תורם
- מקובל
- ליבה
- יכול
- נתונים
- מרכז נתונים
- עיבוד נתונים
- תַאֲרִיך
- דרישה
- מַחלָקָה
- משרד האנרגיה
- תלוי
- מפותח
- מכשיר
- התקנים
- קשה
- לחלק
- do
- נקודה
- dr
- באופן דרמטי
- ראוי
- כל אחד
- השפעה
- יְעִילוּת
- תופעות
- חשמל
- אֶלֶקטרוֹנִי
- אלקטרונים
- לאפשר
- מאפשר
- מה שמאפשר
- אנרגיה
- הנדסה
- סביבתי
- תקופה
- Ether (ETH)
- קיימים
- שדה
- צף
- מבול
- תזרים
- בעד
- החל מ-
- פונקציה
- לטפל
- יש
- לעזור
- גבוה יותר
- חורים
- HTTPS
- עצום
- היברידי
- תמונה
- in
- להגדיל
- בתוך
- מכון
- השתלבות
- מוֹדִיעִין
- IT
- שֶׁלָה
- הצטרפות
- jpg
- רק
- קוריאה
- מחסה
- פחות
- אוֹר
- כמו
- מגבלות
- לחיות
- מגרש
- להוריד
- לתחזק
- גדול
- עושה
- עשייה
- מניפולציה
- דרך
- חוֹמֶר
- חומרים
- מדידת
- זכרונות
- זכרון
- אמצע
- מודל
- דוגמנות
- יותר
- מספר
- שָׁכֵן
- רשת
- עצביים
- רשת עצבית
- חדש
- הדור הבא
- מספר
- שנצפה
- of
- on
- ONE
- רק
- להפעיל
- מופעל
- or
- אחר
- הַחוּצָה
- להתגבר על
- חלקים
- בצורה מושלמת
- תופעה
- PHP
- אפלטון
- מודיעין אפלטון
- אפלטון נתונים
- זהום
- אפשרי
- פוטנציאל
- כּוֹחַ
- מופעל
- מונע
- תהליך
- תהליך
- פרופסור
- הבטחה
- לאור
- קוונטית
- נקודה קוונטית
- נקודות קוונטיות
- ציון
- במקום
- הכרה
- מחקר
- חוקרים
- התנגדות
- s
- אמר
- לומר
- מדע
- מדע וטכנולוגיה
- סמיקונדקטור
- סמיקונדקטורס
- חיישנים
- פָּגָז
- הצגה
- אותות
- סיליקון
- בפשטות
- יחיד
- מצב
- מְהִירוּת
- מדינה
- הברית
- אחסון
- חנות
- מִבְנֶה
- מבנים
- כזה
- משטח
- מערכת
- מערכות
- נבחרת
- טכני
- טכנולוגיות
- טכנולוגיה
- בדיקות
- מֵאֲשֶׁר
- זֶה
- השמיים
- הֵם
- זֶה
- דרך
- ל
- לְכִידָה
- בניגוד
- להשתמש
- סַדרָנוּת
- באמצעות
- מְאוּמָת
- we
- מתי
- אשר
- בזמן
- יצטרך
- עם
- בתוך
- זפירנט