עמוד הבית > חדשות ועדכונים > With new experimental method, researchers probe spin structure in 2D materials for first time: By observing spin structure in “magic-angle” graphene, a team of scientists led by Brown University researchers have found a workaround for a long-standing roadblock in the field of two
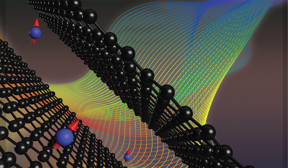 |
| By observing spin structure in “magic-angle” graphene, a team of scientists led by Brown University researchers have found a workaround for a long-standing roadblock in the field of two-dimensional electronics. CREDIT Jia Li/Brown University |
תקציר:
For two decades, physicists have tried to directly manipulate the spin of electrons in 2D materials like graphene. Doing so could spark key advances in the burgeoning world of 2D electronics, a field where super-fast, small and flexible electronic devices carry out computations based on quantum mechanics.
עם שיטה ניסויית חדשה, חוקרים בודקים לראשונה את מבנה הספין בחומרים דו-ממדיים: על ידי התבוננות במבנה הספין בגרפן "זווית קסם", צוות מדענים בראשות חוקרי אוניברסיטת בראון מצא פתרון לחסימה ארוכת שנים בתחום של שניים
Providence, RI | Posted on May 12th, 2023Standing in the way is that the typical way in which scientists measure the spin of electrons — an essential behavior that gives everything in the physical universe its structure — usually doesn’t work in 2D materials. This makes it incredibly difficult to fully understand the materials and propel forward technological advances based on them. But a team of scientists led by Brown University researchers believe they now have a way around this longstanding challenge. They describe their solution in a new study published in Nature Physics.
In the study, the team — which also include scientists from the Center for Integrated Nanotechnologies at Sandia National Laboratories, and the University of Innsbruck — describe what they believe to be the first measurement showing direct interaction between electrons spinning in a 2D material and photons coming from microwave radiation. Called a coupling, the absorption of microwave photons by electrons establishes a novel experimental technique for directly studying the properties of how electrons spin in these 2D quantum materials — one that could serve as a foundation for developing computational and communicational technologies based on those materials, according to the researchers.
“Spin structure is the most important part of a quantum phenomenon, but we’ve never really had a direct probe for it in these 2D materials,” said Jia Li, an assistant professor of physics at Brown and senior author of the research. “That challenge has prevented us from theoretically studying spin in these fascinating material for the last two decades. We can now use this method to study a lot of different systems that we could not study before.”
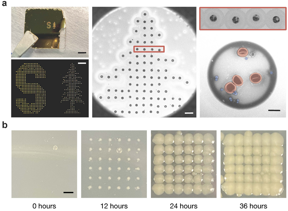
The researchers made the measurements on a relatively new 2D material called “magic-angle” twisted bilayer graphene. This graphene-based material is created when two sheets of ultrathin layers of carbon are stacked and twisted to just the right angle, converting the new double-layered structure into a superconductor that allows electricity to flow without resistance or energy waste. Just discovered in 2018, the researchers focused on the material because of the potential and mystery surrounding it.
"הרבה מהשאלות העיקריות שהוצגו ב-2018 עדיין לא זכו לתשובה", אמרה ארין מוריסט, סטודנטית לתואר שני במעבדה של לי בבראון שהובילה את העבודה.
Physicists usually use nuclear magnetic resonance or NMR to measure the spin of electrons. They do this by exciting the nuclear magnetic properties in a sample material using microwave radiation and then reading the different signatures this radiation causes to measure spin.
The challenge with 2D materials is that the magnetic signature of electrons in response to the microwave excitation is too small to detect. The research team decided to improvise. Instead of directly detecting the magnetization of the electrons, they measured subtle changes in electronic resistance, which were caused by the changes in magnetization from the radiation using a device fabricated at the Institute for Molecular and Nanoscale Innovation at Brown. These small variations in the flow of the electronic currents allowed the researchers to use the device to detect that the electrons were absorbing the photos from the microwave radiation.
The researchers were able to observe novel information from the experiments. The team noticed, for instance, that interactions between the photons and electrons made electrons in certain sections of the system behave as they would in an anti-ferromagnetic system — meaning the magnetism of some atoms was canceled out by a set of magnetic atoms that are aligned in a reverse direction.
The new method for studying spin in 2D materials and the current findings won’t be applicable to technology today, but the research team sees potential applications the method could lead to in the future. They plan to continue to apply their method to twisted bilayer graphene but also expand it to other 2D material.
"זהו ערכת כלים מאוד מגוונת שאנו יכולים להשתמש בה כדי לגשת לחלק חשוב מהסדר האלקטרוני במערכות המתואמות הללו ובאופן כללי כדי להבין כיצד אלקטרונים יכולים להתנהג בחומרים דו-ממדיים," אמרה מוריסט.
The experiment was carried out remotely in 2021 at the Center for Integrated Nanotechnologies in New Mexico. Mathias S. Scheurer from University of Innsbruck provided theoretical support for modeling and understanding the result. The work included funding from the National Science Foundation, the U.S. Department of Defense and the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science.
####
לקבלת מידע נוסף, לחץ על כאן
ליצירת קשר:
חואן סילייזאר
אוניברסיטת בראון
Office: 401-863-3766
Copyright © Brown University
אם יש לך תגובה בבקשה צרו קשר שלנו.מנפיקי מהדורות חדשות, לא 7th Wave, Inc. או Nanotechnology Now, אחראים בלעדית לדיוק התוכן.
| קישורים קשורים |
| עיתונות חדשות קשורה |
2 חומרים ממדיים
![]() חוקר רנסלר משתמש בבינה מלאכותית כדי לגלות חומרים חדשים למחשוב מתקדם טרבור רון משתמש בבינה מלאכותית כדי לזהות מגנטים דו מימדיים של ואן דר ואלס ה- 12 במאי, 2023
חוקר רנסלר משתמש בבינה מלאכותית כדי לגלות חומרים חדשים למחשוב מתקדם טרבור רון משתמש בבינה מלאכותית כדי לזהות מגנטים דו מימדיים של ואן דר ואלס ה- 12 במאי, 2023
![]() פריצת דרך במאפיינים האופטיים של MXenes - מבנים הטרו-ממדיים דו מימדיים מספקים רעיונות חדשים ה- 12 במאי, 2023
פריצת דרך במאפיינים האופטיים של MXenes - מבנים הטרו-ממדיים דו מימדיים מספקים רעיונות חדשים ה- 12 במאי, 2023
![]() הגרפן גדל - ואנחנו יכולים לראות את זה במרץ 24th, 2023
הגרפן גדל - ואנחנו יכולים לראות את זה במרץ 24th, 2023
![]() HKUMed ממציאה יריעות ננו אנטיבקטריאליות דו-ממדיות (2D) חדשניות המגיבות לאולטרסאונד כדי לטפל ביעילות בזיהום ברקמת העצם במרץ 24th, 2023
HKUMed ממציאה יריעות ננו אנטיבקטריאליות דו-ממדיות (2D) חדשניות המגיבות לאולטרסאונד כדי לטפל ביעילות בזיהום ברקמת העצם במרץ 24th, 2023
חדשות ומידע
![]() מחקר מוכיח ש-Ta2NiSe5 אינו מבודד אקציטוני צוות מחקר בינלאומי מיישב את הוויכוח בן העשור סביב המקור המיקרוסקופי של שבירת סימטריה בגבישים בתפזורת ה- 12 במאי, 2023
מחקר מוכיח ש-Ta2NiSe5 אינו מבודד אקציטוני צוות מחקר בינלאומי מיישב את הוויכוח בן העשור סביב המקור המיקרוסקופי של שבירת סימטריה בגבישים בתפזורת ה- 12 במאי, 2023
![]() כתיבה ישירה בלייזר של חיישני לחות גמישים המבוססים על מתכת נוזלית Ga2O3 ה- 12 במאי, 2023
כתיבה ישירה בלייזר של חיישני לחות גמישים המבוססים על מתכת נוזלית Ga2O3 ה- 12 במאי, 2023
![]() פריצת דרך במאפיינים האופטיים של MXenes - מבנים הטרו-ממדיים דו מימדיים מספקים רעיונות חדשים ה- 12 במאי, 2023
פריצת דרך במאפיינים האופטיים של MXenes - מבנים הטרו-ממדיים דו מימדיים מספקים רעיונות חדשים ה- 12 במאי, 2023
גרפין / גרפיט
![]() ספין-אאוט של גרפן מנצ'סטר חותמת על עסקה שמשנה את המשחק של מיליארד דולר כדי לעזור להתמודד עם אתגרי הקיימות העולמיים: עסקה מובילה למסחור של גרפן ה-14 באפריל, 2023
ספין-אאוט של גרפן מנצ'סטר חותמת על עסקה שמשנה את המשחק של מיליארד דולר כדי לעזור להתמודד עם אתגרי הקיימות העולמיים: עסקה מובילה למסחור של גרפן ה-14 באפריל, 2023
![]() הגרפן גדל - ואנחנו יכולים לראות את זה במרץ 24th, 2023
הגרפן גדל - ואנחנו יכולים לראות את זה במרץ 24th, 2023
הממשלה - חקיקה / תקנה / מימון / מדיניות
![]() חוקרים ב-Purdue מגלים שתמונות מוליכות-על הן למעשה פרקטלים תלת-ממדיים ומונעי הפרעות ה- 12 במאי, 2023
חוקרים ב-Purdue מגלים שתמונות מוליכות-על הן למעשה פרקטלים תלת-ממדיים ומונעי הפרעות ה- 12 במאי, 2023
![]() מיתוג אופטי במהירויות שיא פותח דלת לאלקטרוניקה ומחשבים מהירים במיוחד, מבוססי אור: במרץ 24th, 2023
מיתוג אופטי במהירויות שיא פותח דלת לאלקטרוניקה ומחשבים מהירים במיוחד, מבוססי אור: במרץ 24th, 2023
![]() זחל רובוט מדגים גישה חדשה לתנועה לרובוטיקה רכה במרץ 24th, 2023
זחל רובוט מדגים גישה חדשה לתנועה לרובוטיקה רכה במרץ 24th, 2023
![]() סריג מוליכים למחצה מתחתן עם אלקטרונים ומומנטים מגנטיים במרץ 24th, 2023
סריג מוליכים למחצה מתחתן עם אלקטרונים ומומנטים מגנטיים במרץ 24th, 2023
עתידיים אפשריים
![]() חוקרים ב-Purdue מגלים שתמונות מוליכות-על הן למעשה פרקטלים תלת-ממדיים ומונעי הפרעות ה- 12 במאי, 2023
חוקרים ב-Purdue מגלים שתמונות מוליכות-על הן למעשה פרקטלים תלת-ממדיים ומונעי הפרעות ה- 12 במאי, 2023
![]() כתיבה ישירה בלייזר של חיישני לחות גמישים המבוססים על מתכת נוזלית Ga2O3 ה- 12 במאי, 2023
כתיבה ישירה בלייזר של חיישני לחות גמישים המבוססים על מתכת נוזלית Ga2O3 ה- 12 במאי, 2023
![]() פריצת דרך במאפיינים האופטיים של MXenes - מבנים הטרו-ממדיים דו מימדיים מספקים רעיונות חדשים ה- 12 במאי, 2023
פריצת דרך במאפיינים האופטיים של MXenes - מבנים הטרו-ממדיים דו מימדיים מספקים רעיונות חדשים ה- 12 במאי, 2023
![]() תא אלקטרוכימי פרוסקיט בעיצוב חדשני לפליטת אור וזיהוי אור ה- 12 במאי, 2023
תא אלקטרוכימי פרוסקיט בעיצוב חדשני לפליטת אור וזיהוי אור ה- 12 במאי, 2023
טכנולוגיית שבבים
![]() חוקר רנסלר משתמש בבינה מלאכותית כדי לגלות חומרים חדשים למחשוב מתקדם טרבור רון משתמש בבינה מלאכותית כדי לזהות מגנטים דו מימדיים של ואן דר ואלס ה- 12 במאי, 2023
חוקר רנסלר משתמש בבינה מלאכותית כדי לגלות חומרים חדשים למחשוב מתקדם טרבור רון משתמש בבינה מלאכותית כדי לזהות מגנטים דו מימדיים של ואן דר ואלס ה- 12 במאי, 2023
![]() מחקר מוכיח ש-Ta2NiSe5 אינו מבודד אקציטוני צוות מחקר בינלאומי מיישב את הוויכוח בן העשור סביב המקור המיקרוסקופי של שבירת סימטריה בגבישים בתפזורת ה- 12 במאי, 2023
מחקר מוכיח ש-Ta2NiSe5 אינו מבודד אקציטוני צוות מחקר בינלאומי מיישב את הוויכוח בן העשור סביב המקור המיקרוסקופי של שבירת סימטריה בגבישים בתפזורת ה- 12 במאי, 2023
![]() כתיבה ישירה בלייזר של חיישני לחות גמישים המבוססים על מתכת נוזלית Ga2O3 ה- 12 במאי, 2023
כתיבה ישירה בלייזר של חיישני לחות גמישים המבוססים על מתכת נוזלית Ga2O3 ה- 12 במאי, 2023
![]() פריצת דרך במאפיינים האופטיים של MXenes - מבנים הטרו-ממדיים דו מימדיים מספקים רעיונות חדשים ה- 12 במאי, 2023
פריצת דרך במאפיינים האופטיים של MXenes - מבנים הטרו-ממדיים דו מימדיים מספקים רעיונות חדשים ה- 12 במאי, 2023
תגליות
![]() מחקר מוכיח ש-Ta2NiSe5 אינו מבודד אקציטוני צוות מחקר בינלאומי מיישב את הוויכוח בן העשור סביב המקור המיקרוסקופי של שבירת סימטריה בגבישים בתפזורת ה- 12 במאי, 2023
מחקר מוכיח ש-Ta2NiSe5 אינו מבודד אקציטוני צוות מחקר בינלאומי מיישב את הוויכוח בן העשור סביב המקור המיקרוסקופי של שבירת סימטריה בגבישים בתפזורת ה- 12 במאי, 2023
![]() כתיבה ישירה בלייזר של חיישני לחות גמישים המבוססים על מתכת נוזלית Ga2O3 ה- 12 במאי, 2023
כתיבה ישירה בלייזר של חיישני לחות גמישים המבוססים על מתכת נוזלית Ga2O3 ה- 12 במאי, 2023
![]() פריצת דרך במאפיינים האופטיים של MXenes - מבנים הטרו-ממדיים דו מימדיים מספקים רעיונות חדשים ה- 12 במאי, 2023
פריצת דרך במאפיינים האופטיים של MXenes - מבנים הטרו-ממדיים דו מימדיים מספקים רעיונות חדשים ה- 12 במאי, 2023
![]() תא אלקטרוכימי פרוסקיט בעיצוב חדשני לפליטת אור וזיהוי אור ה- 12 במאי, 2023
תא אלקטרוכימי פרוסקיט בעיצוב חדשני לפליטת אור וזיהוי אור ה- 12 במאי, 2023
הודעות
![]() מחקר מוכיח ש-Ta2NiSe5 אינו מבודד אקציטוני צוות מחקר בינלאומי מיישב את הוויכוח בן העשור סביב המקור המיקרוסקופי של שבירת סימטריה בגבישים בתפזורת ה- 12 במאי, 2023
מחקר מוכיח ש-Ta2NiSe5 אינו מבודד אקציטוני צוות מחקר בינלאומי מיישב את הוויכוח בן העשור סביב המקור המיקרוסקופי של שבירת סימטריה בגבישים בתפזורת ה- 12 במאי, 2023
![]() כתיבה ישירה בלייזר של חיישני לחות גמישים המבוססים על מתכת נוזלית Ga2O3 ה- 12 במאי, 2023
כתיבה ישירה בלייזר של חיישני לחות גמישים המבוססים על מתכת נוזלית Ga2O3 ה- 12 במאי, 2023
![]() פריצת דרך במאפיינים האופטיים של MXenes - מבנים הטרו-ממדיים דו מימדיים מספקים רעיונות חדשים ה- 12 במאי, 2023
פריצת דרך במאפיינים האופטיים של MXenes - מבנים הטרו-ממדיים דו מימדיים מספקים רעיונות חדשים ה- 12 במאי, 2023
![]() תא אלקטרוכימי פרוסקיט בעיצוב חדשני לפליטת אור וזיהוי אור ה- 12 במאי, 2023
תא אלקטרוכימי פרוסקיט בעיצוב חדשני לפליטת אור וזיהוי אור ה- 12 במאי, 2023
ראיונות / ביקורות ספרים / מאמרים / דוחות / פודקאסטים / כתבי עת / מאמרים לבנים / פוסטרים
![]() חוקרים ב-Purdue מגלים שתמונות מוליכות-על הן למעשה פרקטלים תלת-ממדיים ומונעי הפרעות ה- 12 במאי, 2023
חוקרים ב-Purdue מגלים שתמונות מוליכות-על הן למעשה פרקטלים תלת-ממדיים ומונעי הפרעות ה- 12 במאי, 2023
![]() כתיבה ישירה בלייזר של חיישני לחות גמישים המבוססים על מתכת נוזלית Ga2O3 ה- 12 במאי, 2023
כתיבה ישירה בלייזר של חיישני לחות גמישים המבוססים על מתכת נוזלית Ga2O3 ה- 12 במאי, 2023
![]() פריצת דרך במאפיינים האופטיים של MXenes - מבנים הטרו-ממדיים דו מימדיים מספקים רעיונות חדשים ה- 12 במאי, 2023
פריצת דרך במאפיינים האופטיים של MXenes - מבנים הטרו-ממדיים דו מימדיים מספקים רעיונות חדשים ה- 12 במאי, 2023
![]() תא אלקטרוכימי פרוסקיט בעיצוב חדשני לפליטת אור וזיהוי אור ה- 12 במאי, 2023
תא אלקטרוכימי פרוסקיט בעיצוב חדשני לפליטת אור וזיהוי אור ה- 12 במאי, 2023
צבאי
![]() ניסוי חדש מתרגם מידע קוונטי בין טכנולוגיות בצעד חשוב עבור האינטרנט הקוונטי במרץ 24th, 2023
ניסוי חדש מתרגם מידע קוונטי בין טכנולוגיות בצעד חשוב עבור האינטרנט הקוונטי במרץ 24th, 2023
![]() מיתוג אופטי במהירויות שיא פותח דלת לאלקטרוניקה ומחשבים מהירים במיוחד, מבוססי אור: במרץ 24th, 2023
מיתוג אופטי במהירויות שיא פותח דלת לאלקטרוניקה ומחשבים מהירים במיוחד, מבוססי אור: במרץ 24th, 2023
![]() סריג מוליכים למחצה מתחתן עם אלקטרונים ומומנטים מגנטיים במרץ 24th, 2023
סריג מוליכים למחצה מתחתן עם אלקטרונים ומומנטים מגנטיים במרץ 24th, 2023
![]() הפוך אותם לדקים מספיק, וחומרים אנטי-פרואלקטריים הופכים לפרו-אלקטריים ה-10 בפברואר, 2023
הפוך אותם לדקים מספיק, וחומרים אנטי-פרואלקטריים הופכים לפרו-אלקטריים ה-10 בפברואר, 2023
- הפצת תוכן ויחסי ציבור מופעל על ידי SEO. קבל הגברה היום.
- PlatoAiStream. Web3 Data Intelligence. הידע מוגבר. גישה כאן.
- הטבעת העתיד עם אדריאן אשלי. גישה כאן.
- קנה ומכירה של מניות בחברות PRE-IPO עם PREIPO®. גישה כאן.
- מקור: http://www.nanotech-now.com/news.cgi?story_id=57341
- :יש ל
- :הוא
- :לֹא
- :איפה
- 10
- 10th
- 2018
- 2021
- 27
- 2D
- חומרים דו מימדיים
- 3d
- a
- יכול
- גישה
- פי
- דיוק
- למעשה
- כתובת
- מתקדם
- התקדמות
- AI
- מיושר
- מאפשר
- גם
- an
- ו
- ישים
- יישומים
- החל
- גישה
- אַפּרִיל
- ARE
- סביב
- מלאכותי
- בינה מלאכותית
- AS
- עוזר
- At
- מחבר
- מבוסס
- BE
- כי
- להיות
- לפני
- תאמינו
- בֵּין
- עֶצֶם
- שבירה
- אוניברסיטת בראון
- אבל
- by
- נקרא
- CAN
- מבוטל
- פַּחמָן
- לשאת
- גרם
- גורמים
- מרכז
- מסוים
- CGI
- לאתגר
- האתגרים
- שינויים
- קליק
- COM
- מגיע
- הערה
- שיווק
- חישובים
- מחשבים
- מחשוב
- תוכן
- להמשיך
- המרת
- יכול
- נוצר
- אשראי
- נוֹכְחִי
- עסקה
- דיון
- עשרות שנים
- החליט
- גופי בטחון
- מדגים
- מַחלָקָה
- משרד ההגנה
- לתאר
- עיצוב
- מתפתח
- מכשיר
- התקנים
- אחר
- קשה
- ישיר
- כיוון
- ישירות
- לגלות
- גילה
- שונה
- do
- לא
- עושה
- דֶלֶת
- יעילות
- חשמל
- אֶלֶקטרוֹנִי
- מכשירי חשמל
- אלקטרונים
- סוף
- אנרגיה
- ביזבוז אנרגיה
- מספיק
- חיוני
- מקימה
- Ether (ETH)
- הכל
- מרגש
- לְהַרְחִיב
- לְנַסוֹת
- ניסויים
- פייסבוק
- מקסים
- פבואר
- שדה
- ממצאים
- ראשון
- firsttime
- גמיש
- תזרים
- מרוכז
- בעד
- קדימה
- מצא
- קרן
- החל מ-
- לגמרי
- מימון
- עתיד
- כללי
- gif
- נותן
- גלוֹבָּלִי
- בוגר
- גרפן
- גדל
- היה
- יש
- לעזור
- איך
- http
- HTTPS
- לזהות
- if
- תמונות
- חשוב
- in
- בע"מ
- לכלול
- כלול
- בצורה מדהימה
- מידע
- חדשנות
- למשל
- במקום
- מכון
- משולב
- מוֹדִיעִין
- אינטראקציה
- יחסי גומלין
- ברמה בינלאומית
- אל תוך
- IT
- שֶׁלָה
- רק
- מפתח
- מעבדה
- ציון דרך
- אחרון
- שכבות
- עוֹפֶרֶת
- הוביל
- כמו
- קישורים
- ותיק
- מגרש
- עשוי
- מגנטיות
- גדול
- עושה
- צעדה
- חוֹמֶר
- חומרים
- מאי..
- משמעות
- למדוד
- מדידה
- מידות
- מכניקה
- שיטה
- MEXICO
- דוגמנות
- מולקולרי
- יותר
- רוב
- תעלומה
- ננוטכנולוגיה
- לאומי
- מדע לאומי
- טבע
- נטו
- לעולם לא
- חדש
- חדשות
- רומן
- עַכשָׁיו
- גַרעִינִי
- להתבונן
- of
- Office
- on
- ONE
- נפתח
- or
- להזמין
- מָקוֹר
- אחר
- הַחוּצָה
- חלק
- תופעה
- פוטונים
- תמונות
- PHP
- גופני
- פיסיקה
- תכנית
- אפלטון
- מודיעין אפלטון
- אפלטון נתונים
- אנא
- הודעה
- פורסם
- פוטנציאל
- ללחוץ
- עיתונות ופרסומים
- בדיקה
- פרופסור
- להניע
- נכסים
- לספק
- ובלבד
- לאור
- קוונטית
- מידע קוונטי
- חומרים קוונטיים
- מכניקה קוואנטית
- שאלות
- קרינה
- קריאה
- בֶּאֱמֶת
- שיא
- יחסית
- לשחרר
- עיתונות
- מחקר
- חוקר
- חוקרים
- התנגדות
- תהודה
- תגובה
- אחראי
- תוצאה
- לַחֲזוֹר
- להפוך
- תקין
- s
- אמר
- שמור
- מדע
- מדענים
- חיפוש
- סעיפים
- לִרְאוֹת
- רואה
- לחצני מצוקה לפנסיונרים
- לשרת
- סט
- מתיישב
- שיתוף
- חתימות
- שלטים
- קטן
- So
- רך
- פִּתָרוֹן
- כמה
- לעורר
- מהירויות
- לְסוֹבֵב
- מְגוּבָּב
- התחלה
- שלב
- עוד
- בְּתוֹקֶף
- מִבְנֶה
- סטודנט
- לימוד
- לומד
- להגיש
- תמיכה
- הסובב
- קיימות
- מערכת
- מערכות
- לְהִתְמוֹדֵד
- נבחרת
- טכנולוגי
- טכנולוגיות
- טכנולוגיה
- זֶה
- אל האני
- העתיד
- שֶׁלָהֶם
- אותם
- אז
- תיאורטי
- אלה
- הֵם
- זֶה
- אלה
- זמן
- ל
- היום
- גַם
- טרבור
- ניסיתי
- שתיים
- טיפוסי
- לָנוּ
- משרד ההגנה האמריקני
- להבין
- הבנה
- עולם
- אוניברסיטה
- us
- להשתמש
- באמצעות
- בְּדֶרֶך כְּלַל
- היה
- לבזבז
- גל
- דֶרֶך..
- we
- היו
- מה
- מתי
- אשר
- מי
- עם
- לְלֹא
- תיק עבודות
- עוֹלָם
- היה
- כתיבה
- יאהו
- עוד
- אתה
- זפירנט